Water quality characteristics of irrigation and drainage ditches in western Erhai Lake Basin and the effect of land uses
-
摘要:
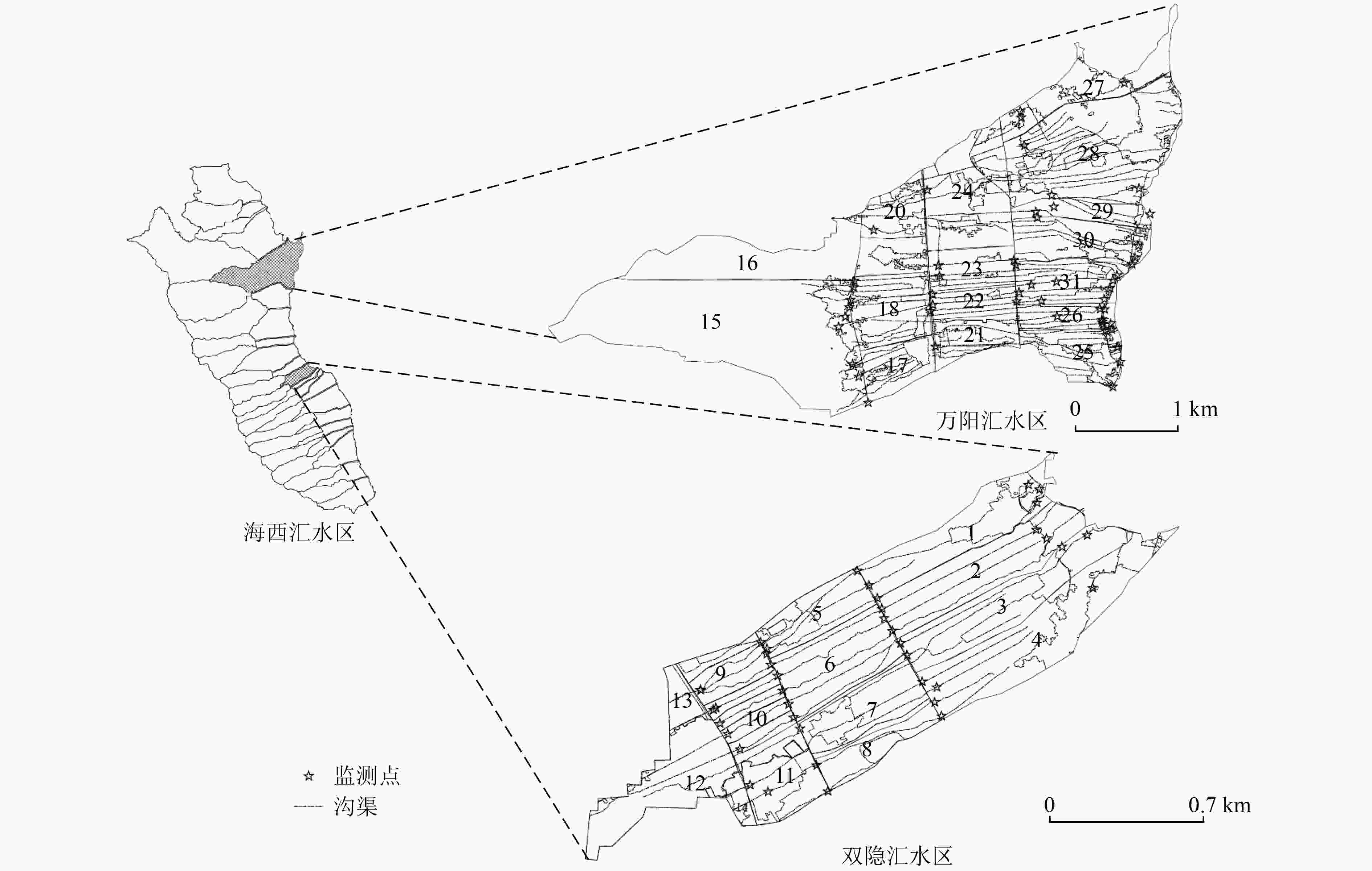
灌排沟渠径流是洱海氮、磷营养盐输入的主要来源。2020年秋季,研究选取洱海西部2个汇水区,分析了降雨条件下汇水区和沟渠子汇水区2个空间尺度下沟渠水质的变化特征,以及土地利用对沟渠水质的影响。结果表明:沟渠水质表现出显著的空间差异性,其中双隐汇水区东南部沟渠化学需氧量(COD)较高,为5.68~20.49 mg/L,北部沟渠总氮(TN)浓度较高,为1.04~1.44 mg/L,总磷(TP)浓度自东向西递减,氨氮(NH3-N)浓度整体较低;万阳汇水区南部沟渠COD较高,为5.02~14.22 mg/L,TN浓度整体较低,环洱海和中部靠北沟渠TP和NH3-N浓度整体偏高。冗余分析结果表明,村镇、农田是沟渠TP和NH3-N的主要来源,秋季库塘未被利用的蓄水也可能对沟渠水质造成影响,林草地面积占比与沟渠水质呈负相关,但由于占比小和空间分布原因,对入海污染负荷的削减效用较小。洱海西部应加强灌溉用水循环利用,完善环湖截污工程,以减少灌排沟渠退水和农村生活污水对洱海水质的影响。
Abstract:The runoffs from irrigation and drainage ditches are the major sources of nitrogen and phosphorus of Erhai Lake. In the Autumn of 2020, two catchments in the western Erhai Lake Basin were selected to analyze the change characteristics of ditch water quality in catchment scale and sub catchment scale under the rain condition, as well as the impact of land use on ditch water quality. The results indicated that the water quality of the ditches presented obvious spatial variation. In Shuangying catchment, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) of the ditch runoff was relatively high in the southeast, which ranged from 5.68-20.49 mg/L, and that of total nitrogen (TN) of the ditches in the north was relatively high, which ranged from 1.04-1.44 mg/L. The total phosphorus (TP) concentration decreased from east to west, and ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) concentration was generally low in the catchment. In Wanyang catchment, the COD concentration of the ditch runoff was relatively high in the south, which ranged from 5.02-14.22 mg/L, and the TN concentration was generally low, and the TP and NH3-N concentrations were generally high in the ditches around Erhai Lake and north of the central part. The redundancy analysis indicated that the farmland and village were the major source of TP and NH3-N in the ditch runoff. The unutilized water storage in ponds and wetlands may cause the ditch water quality pollution in the Autumn. The grass and forest land area presented negative relationship with the ditch water quality, but due to the low proportion and spatial location, it had little effect on reducing the pollution load into the sea. To reduce the impact of irrigation and drainage ditch backwater and rural domestic sewage on Erhai Lake, measures should be taken to strengthen the recycling of irrigation water, and improve the sewage interception project around the lake.
-
表 1 2个汇水区沟渠水质统计分析结果
Table 1. Results of statistical analysis of ditch water quality in two catchment areas
汇水
区水质
指标样本
数/个最小值/
(mg/L)最大值/
(mg/L)平均值/
(mg/L)标准差/
(mg/L)双隐汇水区 COD 41 <3 29.30 5.02 5.13 TP 41 0.04 1.45 0.19 0.18 TN 41 0.40 3.19 1.14 0.40 NH3-N 41 <0.025 3.56 0.22 0.12 万阳汇水区 COD 52 <3 24.09 9.23 5.14 TP 52 <0.01 1.27 0.17 0.22 TN 52 <0.05 7.74 1.04 1.12 NH3-N 52 <0.025 2.40 0.54 0.49 表 2 子汇水区不同土地利用类型面积占比
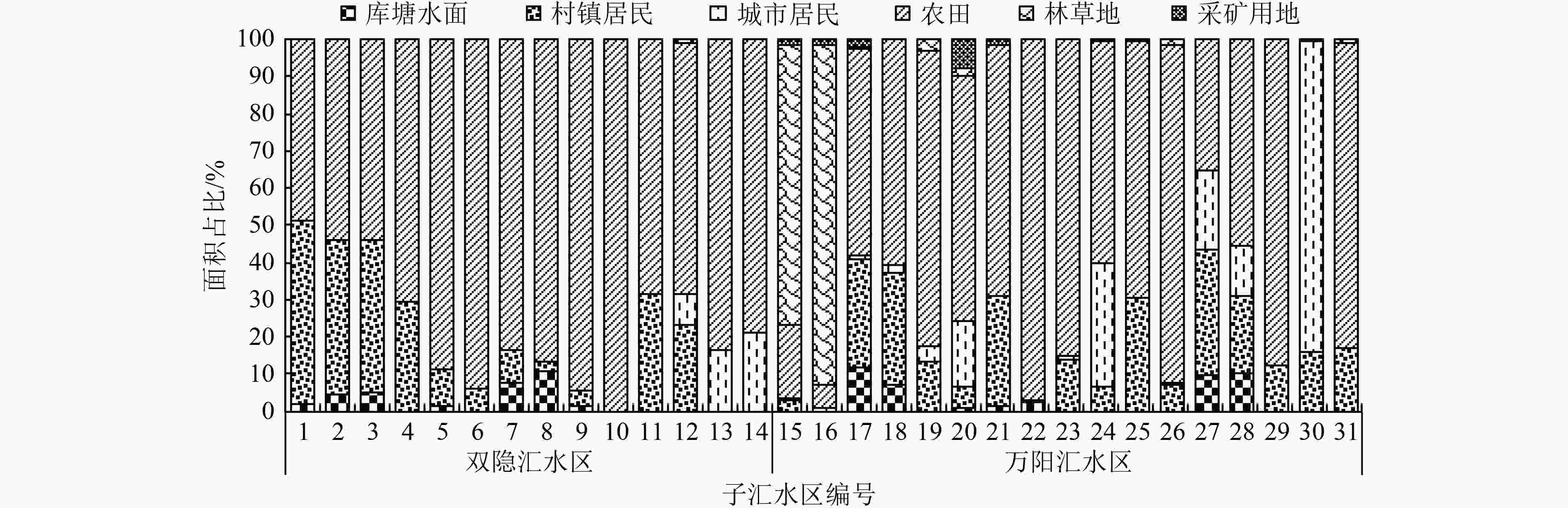
Table 2. Area proportions of different land use types in sub-catchment areas
% 土地利用类型 面积占比 库塘
水面村镇
居民城市
居民农田 林草地 采矿
用地村镇—农田型 0.97 30.73 1.37 66.43 0.27 0.21 村镇—农田—库塘型 9.38 20.71 6.40 63.06 0.09 0.36 林地—草地型 0.02 1.42 0.38 13.09 83.82 1.27 城镇—农田型 0.40 10.69 50.50 33.48 1.17 3.76 农田型 0.41 6.80 5.81 86.50 0.46 0.01 -
[1] 陈小华, 钱晓雍, 李小平, 等.洱海富营养化时间演变特征(1988—2013年)及社会经济驱动分析[J]. 湖泊科学,2018,30(1):70-78. doi: 10.18307/2018.0107CHEN X H, QIAN X Y, LI X P, et al. Long-term trend of eutrophication state of Lake Erhai in 1988-2013 and analyses of its socio-economic drivers[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2018,30(1):70-78. doi: 10.18307/2018.0107 [2] 颜昌宙, 金相灿, 赵景柱, 等.云南洱海的生态保护及可持续利用对策[J]. 环境科学,2005,26(5):38-42. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2005.05.008YAN C Z, JIN X C, ZHAO J Z, et al. Ecological protection and sustainable utilization of Erhai Lake, Yunnan[J]. Environmental Science,2005,26(5):38-42. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2005.05.008 [3] 赵顺娟, 李正祥.洱海流域农业面源污染的控制[J]. 云南农业,2020(4):54-57. [4] 张发祥.洱海流域农业面源污染基层防治经验探析: 以大理市银桥镇为例[J]. 南方农机,2018,49(3):89-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3872.2018.03.055 [5] 项颂, 吴越, 吕兴菊, 等.洱海流域农业面源污染空间分布特征及分类控制策略[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(11):2474-2483.XIANG S, WU Y, LÜ X J, et al. Characteristics and spatial distribution of agricultural non-point source pollution in Erhai Lake Basin and its classified control strategy[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(11):2474-2483. [6] 窦嘉顺, 杨四坤, 黄明雨, 等.洱海流域蔬菜种植业污染特征浅析[J]. 环境科学导刊,2019,38(5):35-38.DOU J S, YANG S K, HUANG M Y, et al. Pollution characteristics of vegetable planting in the Erhai Lake Basin[J]. Environmental Science Survey,2019,38(5):35-38. [7] 晏维金, 尹澄清, 孙濮, 等.磷氮在水田湿地中的迁移转化及径流流失过程[J]. 应用生态学报,1999,10(3):312. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.1999.03.015YAN W J, YIN C Q, SUN P, et al. Phosphorus and nitrogen transfers and runoff losses from rice field wetlands of Chaohu Lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,1999,10(3):312. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.1999.03.015 [8] 金春玲, 高思佳, 叶碧碧, 等.洱海西部雨季地表径流氮磷污染特征及受土地利用类型的影响[J]. 环境科学研究,2018,31(11):1891-1899.JIN C L, GAO S J, YE B B, et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus pollution characteristics of surface runoff and the impacts of land use on runoff water quality in rainy season in the western Erhai Lake Basin[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2018,31(11):1891-1899. [9] 项颂, 庞燕, 储昭升, 等.入湖河流水质对土地利用时空格局的响应研究: 以洱海北部流域为例[J]. 环境科学,2016,37(8):2947-2956.XIANG S, PANG Y, CHU Z S, et al. Response of inflow water quality to land use pattern in northern watershed of Lake Erhai[J]. Environmental Science,2016,37(8):2947-2956. [10] WANG X L, LI J S, LI S M, et al. A study on removing nitrogen from paddy field rainfall runoff by an ecological ditch-zeolite barrier system[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2017,24(35):27090-27103. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0269-7 [11] LI W C, LIU H B, ZHAI L M, et al. Evaluation of concentration-discharge dynamics and nitrogen export on anthropogenic inputs and stormflow across alternative time-scales[J]. Ecological Indicators,2019,98:879-887. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.11.057 [12] 叶家慧, 胡梦甜, 韩永伟, 等.芹菜面源污染防治种植模式综合效益评估[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(2):283-290. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200114YE J H, HU M T, HAN Y W, et al. Comprehensive benefit evaluation of planting models for the prevention and control of celery non-point source pollution[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(2):283-290. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200114 [13] 郭羽鑫, 郑宏刚, 吴碧兰, 等.洱海流域上游耕地氮磷排放强度空间分析[J]. 江苏农业科学,2020,48(16):291-297.GUO Y X, ZHENG H G, WU B L, et al. Spatial analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus emission intensity of cultivated land in the upper reaches of Erhai River Basin[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2020,48(16):291-297. [14] 庞燕, 项颂, 储昭升, 等.洱海流域农业用地与入湖河流水质的关系研究[J]. 环境科学,2015,36(11):4005-4012.PANG Y, XIANG S, CHU Z S, et al. Relationship between agricultural land and water quality of inflow river in Erhai Lake Basin[J]. Environmental Science,2015,36(11):4005-4012. [15] 金春玲. 基于SWAT模型的洱海西部和北部面源污染模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国环境科学研究院, 2018. [16] 苏静君, 李叙勇, 吴震.利用实测值估算断面泥沙年负荷的方法比较[J]. 中国环境科学,2017,37(1):218-228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.01.028SU J J, LI X Y, WU Z. Comparison of different methods estimating annual sediment loads in river cross sections based on irregularly measured data[J]. China Environmental Science,2017,37(1):218-228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.01.028 [17] 金相灿, 胡小贞.湖泊流域清水产流机制修复方法及其修复策略[J]. 中国环境科学,2010,30(3):374-379.JIN X C, HU X Z. Concept and tactic of clean water runoff generation mechanism restoration in lake watershed[J]. China Environmental Science,2010,30(3):374-379. [18] 石金昊, 朱卫红, 田乐, 等.基于SWAT模型的布尔哈通河流域面源污染的变化研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2021,40(4):130-136.SHI J H, ZHU W H, TIAN L, et al. Using SWAP to study the changes in nonpoint source pollution in Burhatong River Basin[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,2021,40(4):130-136. [19] 王荔, 张腾飞, 杨苏才, 等.焦化厂PAHs污染土壤中微生物群落多样性特征[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(4):720-726. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200251WANG L, ZHANG T F, YANG S C, et al. Characteristics of microbial community diversity in PAHs contaminated soil of a coking plant[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(4):720-726. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200251 [20] 肖雨涵, 项颂, 李丹, 等.多级串联表面流库塘-湿地净化农田径流效果评价[J]. 环境科学研究,2019,32(11):1886-1894.XIAO Y H, XIANG S, LI D, et al. Evaluation of multi stage series surface flow pond-wetland for agricultural low pollution water purification[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2019,32(11):1886-1894. [21] 贾本帅. 洱源县种植业面源污染防控技术集成示范点建设方案[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2018. [22] 苏定江, 姚娟娟, 胡欣逸, 等.昆明地区3种典型降雨参数对滇池环湖截污干渠调蓄城市雨水效果的影响[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2019,30(3):53-57.SU D J, YAO J J, HU X Y, et al. Effect of three typical rainfall parameters in Kunming area on urban rainwater storage in Dianchi sewage interception trunk canal[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2019,30(3):53-57. ◇ -




 下载:
下载: