Research advances of bioprocesses for NOx removal from flue gas: a critical review
-
摘要:
氮氧化物(NOx)作为PM2.5和O3的前驱物,是重要的大气污染控制指标。选择性催化还原(SCR)、选择性非催化还原(SNCR)等是目前燃煤工业锅炉烟气脱硝的主流技术,但存在投资成本高、运行条件苛刻等问题,在中小型烟气脱硝工程应用中受到限制。生物法烟气脱硝技术因其高效、低耗、可持续特征在中小规模烟气脱硝中得到青睐,近年来许多学者对其开展了较广泛的研究。综述了生物法烟气脱硝技术的研究进展,概述相关工艺的脱硝原理及技术特征。论述了化学吸收-生物降解法(BioDeNOx)的最新研究方向,重点阐述了络合吸收-生物还原(CABR)反应器的运行原理、还原机制、反应器开发、运行参数和影响因素等,讨论了CABR体系存在的问题及解决措施,并对生物法烟气脱硝技术今后的研究方向进行了展望。
Abstract:Nitrogen oxides (NOx), the precursors of PM2.5 and O3, are important air pollution control indices. Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR) are mature technologies for NOx removal from coal-fired industrial boiler flue gas. However, the application of the two technologies in small-and-medium denitrification engineering is limited because of their high investment costs, harsh operating conditions and other factors. In recent years, biological denitrification technologies have been used increasingly in small-and-medium flue-gas denitration projects. Many scholars have carried out extensive research on them. The advances of bioprocesses for NOx removal from flue gas were critically reviewed, and the denitrification principles and technical characteristics of related processes were summarized. The latest research directions of chemical absorption-biological denitrification (BioDeNOx) were reviewed, and the operational principles, reduction mechanism, reactor developments, operational parameters and influencing factors of complexation absorption-biological reduction (CABR) were emphatically elucidated. The obstacles of the CABR system and its solutions were systematically discussed, and the future trends of bioprocesses for NOx removal were prospected.
-
Key words:
- nitrogen oxides /
- BioDeNOx /
- chemical absorption /
- bioprocess /
- Fe(Ⅱ)EDTA /
- flue gas denitrification
-
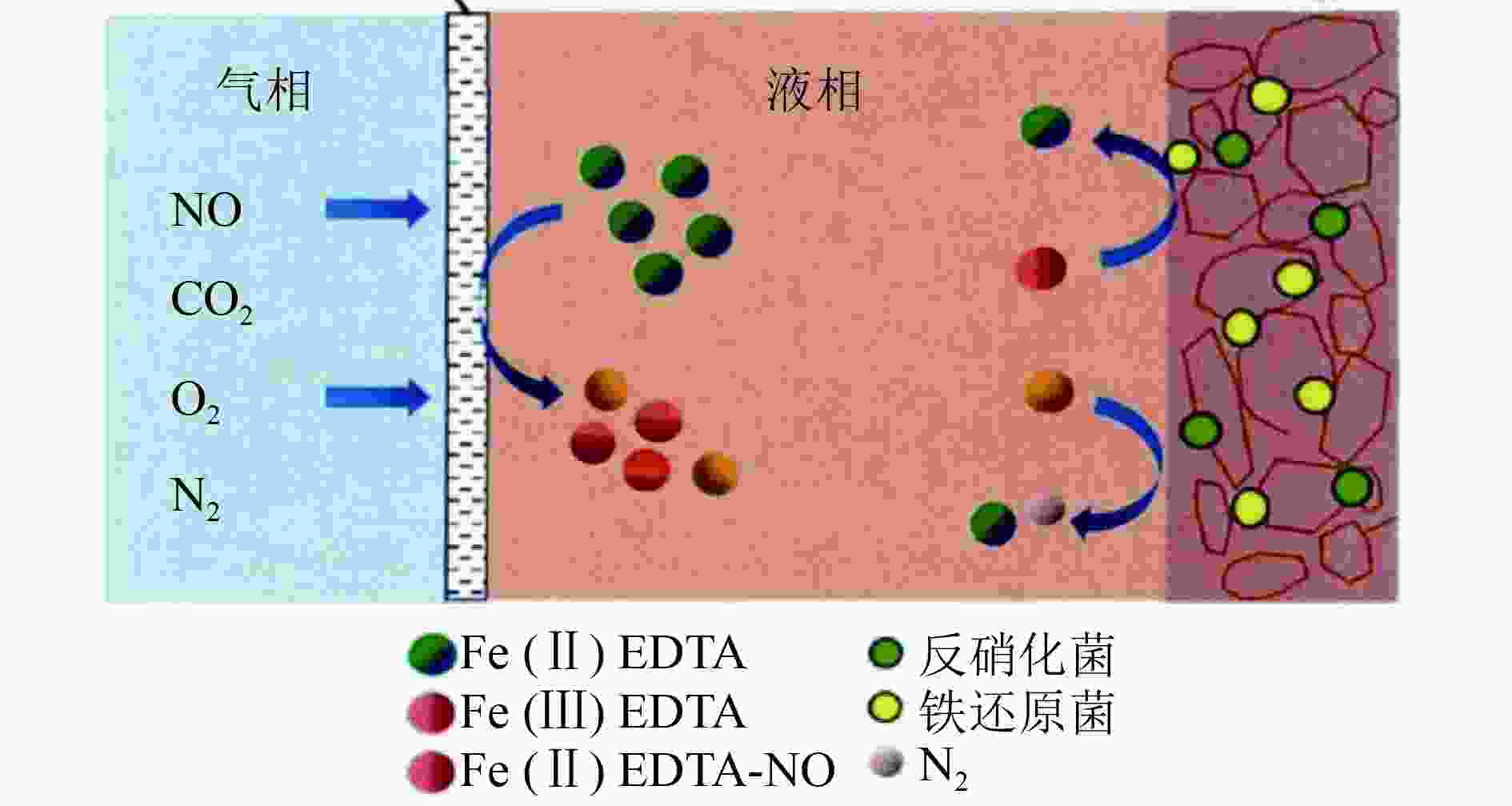
图 1 CABR 法原理[29]
Figure 1. Principle of complexation absorption-biological reduction method
图 2 微生物电化学还原过程[48]
Figure 2. Electrochemical reduction process of microorganisms
表 1 不同脱硝技术优缺点及适用性对比
Table 1. Comparison of advantages, disadvantages and applicability of different denitrification technologies
工艺类别 优点 缺点 适用性 硝化 不受氧气干扰 NO气液传质效率低,无法彻底脱氮 适用于后续有废水
反硝化的体系中反硝化 清洁环保,NO去除率较高 易受氧气干扰,受NO气液传质效率低的问题制约 适用于含氧量较
低的烟气脱硝厌氧氨
氧化同步脱硝和废水资源化 对厌氧环境要求严苛,易受氧气干扰 适用于含氨氮废水
和烟气脱硝需要同步处理的场景微藻代谢 有经济效益,绿色环保 NO去除率较低,工艺应用有待优化 适用于较高浓度NO,可用作微藻生长氮源 表 2 不同生物脱硝工艺运行参数和性能
Table 2. Operational parameters and performance of different biological denitrification processes
-
[1] YANG X, TENG F. The air quality co-benefit of coal control strategy in China[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling,2018,129:373-382. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.08.011 [2] 王凡, 田刚, 王红梅, 等.我国工业烟气SCR/SNCR脱硝技术与还原剂用量平衡[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2015,5(3):191-195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2015.03.029WANG F, TIAN G, WANG H M, et al. Analysis of industrial waste gas SCR/SNCR technology and balancing of reducing agent consumption[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2015,5(3):191-195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2015.03.029 [3] 束韫, 龙红艳, 张凡, 等.生物质基活性炭负载金属催化还原NOx[J]. 环境科学研究,2018,31(9):1588-1596.SHU Y, LONG H Y, ZHANG F, et al. Catalytic reduction of NOx by biomass-derived activated carbon supported metals[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2018,31(9):1588-1596. [4] SHARIF H M A, MAHMOOD N, WANG S Y, et al. Recent advances in hybrid wet scrubbing techniques for NOx and SO2 removal: state of the art and future research[J]. Chemosphere,2021,273:129695. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129695 [5] RAMONA Z, VIOLETA N, MARIUS M, et al. Waste gas biotreatment[J]. Journal of Biotechnology,2017,256:S62. [6] KUYPERS M M M, MARCHANT H K, KARTAL B. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology,2018,16(5):263-276. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2018.9 [7] DAVIDOVA Y B, SCHROEDER E D, CHANG D P Y U. Biofiltration of nitric oxide[R].Pittsburgh:Air and Waste Management Association, 1997. [8] CHOU M S, LIN J H. Biotrickling filtration of nitric oxide[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association,2000,50(4):502-508. [9] CHEN J M, WU C Q, WANG J D, et al. Performance evaluation of biofilters packed with carbon foam and lava for nitric oxide removal[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2006,137(1):172-177. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.01.049 [10] 陈建孟, HERSHMAN L, 陈浚, 等.自养型生物过滤器硝化氧化一氧化氮[J]. 环境科学,2003,24(2):1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2003.02.001CHEN J M, HERSHMAN L, CHEN J, et al. Autotrophic biofilters for oxidation of nitric oxide[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science,2003,24(2):1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2003.02.001 [11] WEI Z S, WANG J B, HUANG Z S, et al. Removal of nitric oxide from biomass combustion by thermophilic nitrification-aerobic denitrification combined with catalysis in membrane biofilm reactor[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy,2019,126:34-40. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2019.05.004 [12] SCHMIDT I, HERMELINK C, van de PAS-SCHOONEN K, et al. Anaerobic ammonia oxidation in the presence of nitrogen oxides (NOx) by two different lithotrophs[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2002,68(11):5351-5357. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.11.5351-5357.2002 [13] 彭锦玉. 厌氧氨氧化塔式生物滤池脱除NO研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2015. [14] 丁爽.厌氧氨氧化烟气脱硝工艺的探讨[J]. 化工进展,2017,36(11):4250-4256. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2017-0543DING S. Discussions on biological flue gas denitrification using anaerobic ammonia oxidation (Anammox) process[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2017,36(11):4250-4256. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2017-0543 [15] YEN H W, HO S H, CHEN C Y, et al. CO2, NOx and SOx removal from flue gas via microalgae cultivation: a critical review[J]. Biotechnology Journal,2015,10(6):829-839. doi: 10.1002/biot.201400707 [16] QIE F X, ZHU J Y, RONG J F, et al. Biological removal of nitrogen oxides by microalgae, a promising strategy from nitrogen oxides to protein production[J]. Bioresource Technology,2019,292:122037. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122037 [17] YOSHIHARA K I, NAGASE H, EGUCHI K, et al. Biological elimination of nitric oxide and carbon dioxide from flue gas by marine microalga NOA-113 cultivated in a long tubular photobioreactor[J]. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering,1996,82(4):351-354. doi: 10.1016/0922-338X(96)89149-5 [18] NASAGE H, YOSHIHARA K, EGUCHI K, et al. Characteristics of biological NOx removal from flue gas in a Dunaliella tertiolecta culture system[J]. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering,1997,83(5):461-465. doi: 10.1016/S0922-338X(97)83001-2 [19] 夏奡, 叶文帆, 富经纬, 等.燃煤烟气微藻固碳减排技术现状与展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(1):108-119. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2020.01.014XIA A, YE W F, FU J W, et al. Current status and prospect of carbon fixation and emission reduction technology for coal-fired flue gas by microalgae[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(1):108-119. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2020.01.014 [20] van der MAAS P, MANCONI I, KLAPWIJK B, et al. Nitric oxide reduction in BioDeNOx reactors: kinetics and mechanism[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering,2008,100(6):1099-1107. doi: 10.1002/bit.21841 [21] YANG J R, WANG Y, CHEN H, et al. A new approach for the effective removal of NOx from flue gas by using an integrated system of oxidation-absorption-biological reduction[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,404:124109. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124109 [22] SCHNEPPENSIEPER T, WANAT A, STOCHEL G, et al. Ligand effects on the kinetics of the reversible binding of NO to selected aminocarboxylato complexes of iron(Ⅱ) in aqueous solution[J]. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry,2001,2001(9):2317-2325. doi: 10.1002/1099-0682(200109)2001:9<2317::AID-EJIC2317>3.0.CO;2-F [23] 张先龙, 孟凡跃, 吴琼, 等.FeⅡEDTA络合-Na2SO3还原吸收NO性能[J]. 环境科学研究,2016,29(12):1847-1856.ZHANG X L, MENG F Y, WU Q, et al. Experimental study on complexing absorption of NO using FeⅡEDTA solution and reduction with Na2SO3 solution[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2016,29(12):1847-1856. [24] LU B H, JIANG Y, CAI L L, et al. Enhanced biological removal of NOx from flue gas in a biofilter by Fe(Ⅱ)Cit/Fe(Ⅱ)EDTA absorption[J]. Bioresource Technology,2011,102(17):7707-7712. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.05.086 [25] CHEN J, WU J L, WANG J, et al. A mass-transfer model of nitric oxide removal in a rotating drum biofilter coupled with FeⅡ(EDTA) absorption[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2018,57(24):8144-8151. [26] ZHANG D J, REN L L, YAO Z B, et al. Removal of nitrogen oxide based on anammox through Fe(Ⅱ)EDTA absorption[J]. Energy & Fuels,2017,31(7):7247-7255. [27] SANTIAGO D E O, JIN H F, LEE K. The influence of ferrous-complexed EDTA as a solubilization agent and its auto-regeneration on the removal of nitric oxide gas through the culture of green alga Scenedesmus sp[J]. Process Biochemistry,2010,45(12):1949-1953. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2010.04.003 [28] 张春燕, 赵景开, 郭天蛟, 等.络合吸收-生物还原烟气脱硝系统的研究进展[J]. 高校化学工程学报,2018,32(6):1235-1244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2018.06.001ZHANG C Y, ZHAO J K, GUO T J, et al. Chemical absorption-biological reduction processes for NOx reduction: a review[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities,2018,32(6):1235-1244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2018.06.001 [29] 赵景开. 化学吸收—生物还原耦合体系处理烟气中NOx的动力学研究及过程模拟[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. [30] van der MAAS P, van de SANDT T, KLAPWIJK B, et al. Biological reduction of nitric oxide in aqueous Fe(Ⅱ)EDTA solutions[J]. Biotechnology Progress,2003,19(4):1323-1328. [31] ZHANG S H, MI X H, CAI L L, et al. Evaluation of complexed NO reduction mechanism in a chemical absorption-biological reduction integrated NOx removal system[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2008,79(4):537-544. doi: 10.1007/s00253-008-1469-3 [32] KUMARASWAMY R, van DONGEN U, KUENEN J G, et al. Characterization of microbial communities removing nitrogen oxides from flue gas: the BioDeNOx process[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2005,71(10):6345-6352. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.10.6345-6352.2005 [33] LIU N, JIANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Evaluation of NOx removal from flue gas by a chemical absorption-biological reduction integrated system: glucose consumption and utilization pathways[J]. Energy & Fuels,2014,28(12):7591-7598. [34] van der MAAS P, PENG S, KLAPWIJK B, et al. Enzymatic versus nonenzymatic conversions during the reduction of EDTA-chelated Fe(Ⅲ) in BioDeNOx reactors[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2005,39(8):2616-2623. [35] ZHOU Z M, JING G H, ZHENG X J. Reduction of Fe(Ⅲ)EDTA by Klebsiella sp. strain FD-3 in NOx scrubber solutions[J]. Bioresource Technology,2013,132:210-216. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.022 [36] DONG X Y, ZHANG Y, ZHOU J T, et al. Reduction of Fe(Ⅲ)EDTA in a NOx scrubber liquor by a denitrifying bacterium and the effects of inorganic sulfur compounds on this process[J]. Bioresource Technology,2012,120:127-132. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.06.005 [37] LI W, WU C Z, ZHANG S H, et al. Experimental study on the inhibition of biological reduction of Fe(Ⅲ)EDTA in NOx absorption solution[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University Science B,2005,6(10):1005-1008. [38] LI W, WU C Z, ZHANG S H, et al. Evaluation of microbial reduction of Fe(Ⅲ)EDTA in a chemical absorption-biological reduction integrated NOx removal system[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2007,41(2):639-644. [39] LI N, ZHANG Y, LI Y M, et al. Reduction of Fe(Ⅱ)EDTA-NO using Paracoccus denitrificans and changes of Fe(Ⅱ)EDTA in the system[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology,2013,88(2):311-316. [40] WEN X Y, XU H, HUANG S B, et al. Simultaneous removal of sulphur dioxide and nitric oxide at different oxygen concentrations in a thermophilic biotrickling filter (BTF): evaluation of removal efficiency, intermediates interaction and characterisation of microbial communities[J]. Bioresource Technology,2019,294:122150. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122150 [41] WANG Y L, LI J J, HUANG S B, et al. Evaluation of NOx removal from flue gas and Fe(Ⅱ)EDTA regeneration using a novel BTF-ABR integrated system[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,415:125741. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125741 [42] DURMAZPINAR S, ILHAN N, DEMIR G, et al. Biological NOx removal by denitrification process in a jet-loop bioreactor: system performance and model development[J]. Environmental Technology,2014,35(11):1358-1366. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2013.868529 [43] CHEN J, YANG X A, YU J M, et al. Investigation of effect and process of nitric oxide removal in rotating drum biofilter coupled with absorption by Fe(Ⅱ) (EDTA)[J]. Environmental Science,2012,33(2):539-544. [44] LI H, HUANG S B, WEI Z D, et al. Performance of a new suspended filler biofilter for removal of nitrogen oxides under thermophilic conditions and microbial community analysis[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2016,562:533-541. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.084 [45] XIA Y F, CHEN H, ZHAO J K, et al. Shifts of biomass and microbial community structure in response to current densities in a biofilm electrode reactor for NOx removal[J]. Energy & Fuels,2019,33(6):5415-5421. [46] DAGHIO M, ESPINOZA-TOFALOS A, LEONI B, et al. Bioelectrochemical BTEX removal at different voltages: assessment of the degradation and characterization of the microbial communities[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2018,341:120-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.054 [47] ZHAO J K, ZHANG C Y, LI M F, et al. Two-stage chemical absorption-biological reduction system for NO removal: model development and footprint estimation[J]. Energy & Fuels,2017,31(8):8454-8461. [48] ZHAO J K, FENG K, LIU S H, et al. Kinetics of biocathodic electron transfer in a bioelectrochemical system coupled with chemical absorption for NO removal[J]. Chemosphere,2020,249:126095. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126095 [49] KUMARASWAMY R, KUENEN J G, KLEEREBEZEM R, et al. Structure of microbial communities performing the simultaneous reduction of Fe(Ⅱ)EDTA-NO2− and Fe(Ⅲ)EDTA−[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2006,73(4):922-931. doi: 10.1007/s00253-006-0542-z [50] DONG X Y, ZHANG Y, ZHOU J T, et al. Evaluation of simultaneous reduction of Fe(Ⅱ)EDTA-NO and Fe(Ⅲ)EDTA by a bacterial pure culture[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology,2014,89(1):111-116. [51] 李梅芳. 络合吸收—生物还原两段式烟气脱硝系统的性能研究与参数优化[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017. [52] 陈浚, 王智晔, 蒋轶锋, 等.生物转鼓过滤器反硝化去除NO过程中微生物群落结构多样性解析[J]. 环境科学,2008,29(4):1092-1098. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.04.041CHEN J, WANG Z Y, JIANG Y F, et al. Microbial diversity analysis in rotating drum biofilter for nitric oxide denitrifying removal[J]. Environmental Science,2008,29(4):1092-1098. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.04.041 [53] 林建国, 宰菲.生物还原耦合化学吸收法脱氮影响因素[J]. 生物化工,2019,5(5):65-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0387.2019.05.016LIN J G, ZAI F. Study on influencing factors of nitrogen removal by bioreduction coupled chemical absorption method[J]. Biological Chemical Engineering,2019,5(5):65-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0387.2019.05.016 [54] LI H, HUANG S B, ZHOU S F, et al. Study of extracellular polymeric substances in the biofilms of a suspended biofilter for nitric oxide removal[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2016,100(22):9733-9743. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7824-x [55] 殷祥男, 房晶瑞, 王俊杰, 等.Fe(Ⅱ)EDTA溶液脱除NO实验研究[J]. 工业安全与环保,2017,43(10):88-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2017.10.023YIN X N, FANG J R, WANG J J, et al. Removal of NO by Fe(Ⅱ)EDTA solution[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection,2017,43(10):88-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2017.10.023 [56] LI W, ZHAO J K, ZHANG L, et al. Pathway of FeEDTA transformation and its impact on performance of NOx removal in a chemical absorption-biological reduction integrated process[J]. Scientific Reports,2016,6:18876. doi: 10.1038/srep18876 [57] WANG L K, CHEN X M, WEI W, et al. Biological reduction of nitric oxide for efficient recovery of nitrous oxide as an energy source[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2021,55(3):1992-2005. [58] CHEN J, WANG J, ZHENG J, et al. Prediction and inhibition of the N2O accumulation in the BioDeNOx process for NOx removal from flue gas[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering,2016,39(12):1859-1865. doi: 10.1007/s00449-016-1660-3 [59] XIE P, LI C L, SHAO B, et al. Simultaneous removal of carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide and nitric oxide in a biofilter system: optimization operating conditions, removal efficiency and bacterial community[J]. Chemosphere,2021,276:130084. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130084 [60] RAZAVIARANI V, RUIZ-URIGÜEN M, JAFFÉ P R. Denitrification of nitric oxide using hollow fiber membrane bioreactor;effect of nitrate and nitric oxide loadings on the reactor performance and microbiology[J]. Waste and Biomass Valorization,2019,10(7):1989-2000. □ doi: 10.1007/s12649-018-0223-z -




 下载:
下载:



