Spatial correlation of PM2.5 pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and surrounding cities based on complex networks and their motif
-
摘要:
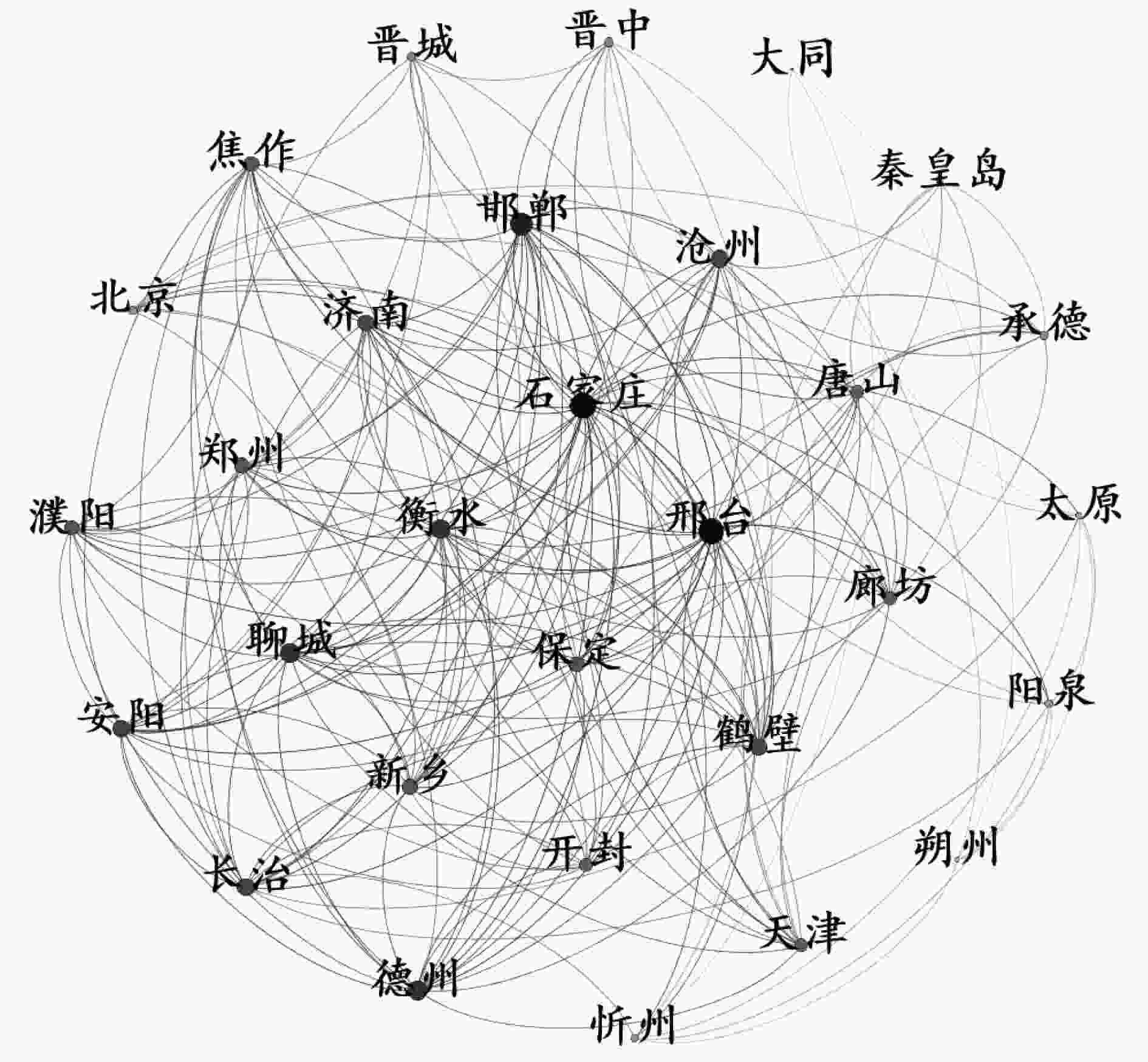
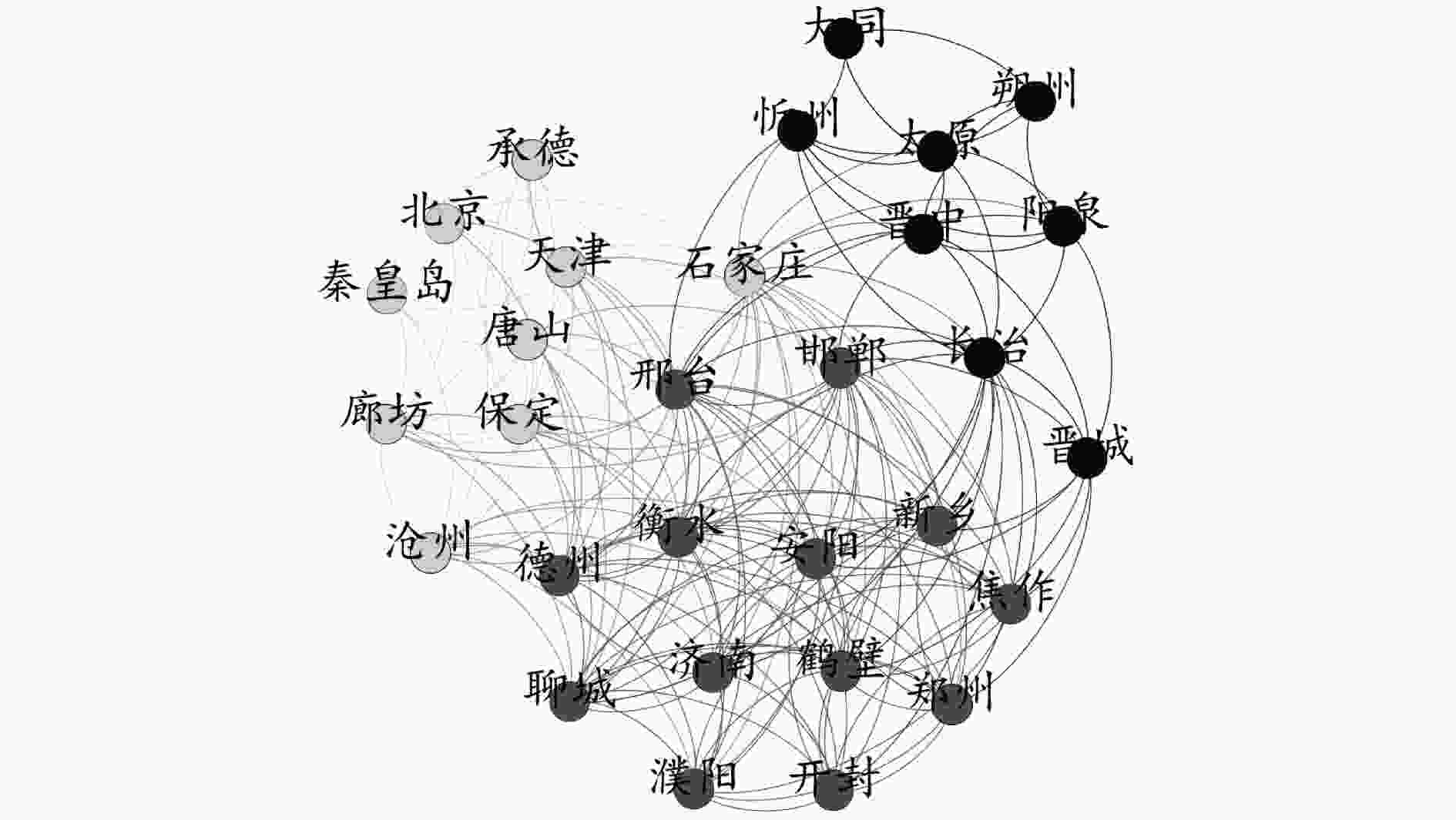
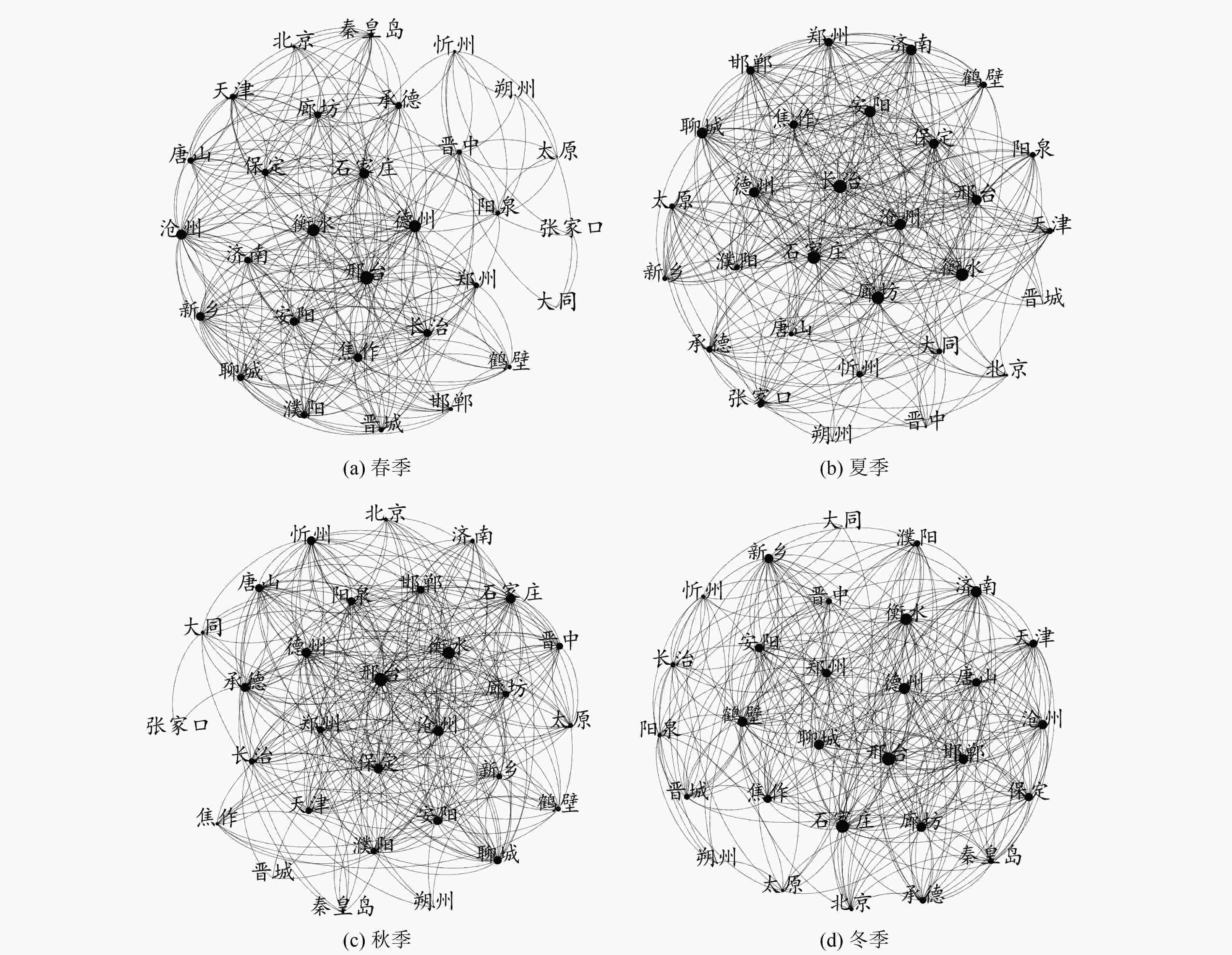
近年来,随着污染治理和生态环境保护力度的加大,京津冀区域生态环境质量持续改善,但是以PM2.5为特征污染物的大气污染问题仍然不容小觑。选取了2015年1月1日—2022年11月30日京津冀及周边31个城市的PM2.5浓度数据,结合引力模型与皮尔逊相关指数,构建了京津冀及周边城市PM2.5污染的空间关联网络,并对该网络的整体特征与模体季节变化进行了统计分析。结果表明:邢台、石家庄、邯郸3个城市的度值、中介中心性、接近中心性均排名前3,它们在该网络中处于核心位置,与多个城市存在较强的PM2.5污染空间关联,对于控制PM2.5污染的空间溢出具有较为重要的作用;模体的四季关联网络密度和平均度相差不大,但均较高,各城市间的PM2.5存在较强的空间关联,其中在冬季网络密度最高,石家庄、邢台、衡水在模体四季关联网络中起着重要作用。对于在京津冀及周边城市PM2.5污染空间关联网络中处于核心位置的城市,在加强自身PM2.5治理的同时,应制定政策减弱其对相邻城市PM2.5污染的空间溢出效应;根据不同季节模体的关联情况,制定相应的协同治理政策,加强对这些模体城市PM2.5污染的协同治理,同时减弱它们之间的PM2.5污染空间关联与溢出效应。
Abstract:In recent years, with the increase of pollution control and ecological environmental protection, the quality of the ecological environment in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region has continued to improve, but the problem of air pollution with PM2.5 characteristics should not be underestimated. PM2.5 data of 31 cities in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and surrounding areas from January 1, 2015 to November 30, 2022 were selected, combined with the gravity model and Pearson correlation index, to construct a spatial correlation network of PM2.5 pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and surrounding cities, and the overall characteristics of the network and the seasonal changes of the motif were analyzed statistically. The results showed that Xingtai, Shijiazhuang and Handan ranked top 3 in degree value, betweenness centrality and closeness centrality. They were at the core of the network and had strong spatial correlation with PM2.5 pollution in multiple cities, which played an important role in controlling the spatial spillover of PM2.5 pollution. The density and average degree of the four seasons correlation network of the motif were not different, but both were high. There was a strong spatial correlation between PM2.5 among cities, and the network density was the highest in winter. Shijiazhuang, Xingtai and Hengshui played an important role in the four seasons correlation network of the motif. For the cities in the core position of the spatial correlation network of PM2.5 pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and surrounding cities, while strengthening their own PM2.5 control, policies should be formulated to reduce the spatial spillover effect of PM2.5 pollution on neighboring cities. According to the correlation of the motif in different seasons, corresponding collaborative governance policies should be formulated to strengthen the collaborative governance of urban PM2.5 pollution of the motif, while weakening the spatial correlation and spillover effect of PM2.5 pollution between them.
-
Key words:
- Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei /
- PM2.5 /
- motif /
- collaborative governance
-
表 1 季节关联网络的平均度和图密度
Table 1. Average degree and graph density of seasonal correlation network
季节 春季 夏季 秋季 冬季 平均度 12.120 13.533 12.774 13.484 图密度 0.416 0.407 0.426 0.449 -
[1] 范凤岩, 王洪飞, 樊礼军.京津冀地区空气污染的健康经济损失评估[J]. 生态经济,2019,35(9):157-163.FAN F Y, WANG H F, FAN L J. Health damage and economic loss assessment of air pollution in Jing-Jin-Ji region[J]. Ecological Economy,2019,35(9):157-163. [2] 杨新平, 徐登国.基于中小城市空气污染指标的时间序列模型构建[J]. 环境污染与防治,2014,36(11):111.YANG X P, XU D G. Construction of time series model based on air pollution index in small and medium-sized cities[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control,2014,36(11):111. [3] 刘晓红, 江可申.中国城市PM2.5的时空分异及影响因素分析: 基于161个城市的实证研究[J]. 调研世界,2018(1):25-34.LIU X H, JIANG K S. Temporal and spatial differentiation of PM2.5 in China and its influencing factors: an empirical study based on 161 cities[J]. The World of Survey and Research,2018(1):25-34. [4] 张增凯, 王念, 李晓瑜, 等. 京津冀NOx和VOCs边际减排成本曲线及协同减排研究[J/OL]. 环境科学研究. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2022.08.01.ZHANG Z K, WANG N, LI X Y, et al. Collaborative reduction of NOx and VOCs in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on the marginal abatement cost curves[J/OL]. Research of Environmental Sciences. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2022.08.01. [5] 王会芝, 杜林蔚, 吕建华.城市群雾霾污染的空间分异及动态关联研究: 基于京津冀城市群的实证分析[J]. 中国环境管理,2020,12(1):80-86.WANG H Z, DU L W, LÜ J H. Spatial differentiation and dynamic association of haze pollution in urban agglomeration: an empirical analysis based on Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Management,2020,12(1):80-86. [6] 戴宏伟, 回莹.京津冀雾霾污染与产业结构、城镇化水平的空间效应研究[J]. 经济理论与经济管理,2019(5):4-19.DAI H W, HUI Y. The spatial effects of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region's smog pollution, industrial structure and urbanization[J]. Economic Theory and Business Management,2019(5):4-19. [7] 任毅, 郭丰, 高聪聪.京津冀城市群雾霾污染的时空特征与影响因素[J]. 首都经济贸易大学学报,2019,21(6):80-91.REN Y, GUO F, GAO C C. Spatial-temporal characteristics of haze pollution and its influencing factors in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration[J]. Journal of Capital University of Economics and Business,2019,21(6):80-91. [8] 史燕平, 刘玻君, 厉玥.京津冀地区雾霾污染的溢出效应分析[J]. 经济与管理,2017,31(4):20-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3890.2017.04.006SHI Y P, LIU B J, LI Y. The spillover effects of haze pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Economy and Management,2017,31(4):20-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3890.2017.04.006 [9] 崔宏, 刘肖, 秦巧燕.汾渭平原典型污染城市PM2.5来源分布及传输分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(5):1593-1600.CUI H, LIU X, QIN Q Y. PM2.5 source distribution and transmission analysis in typical polluted cities of Fenwei Plain[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(5):1593-1600. [10] 孟丽红, 郝囝, 邱晓滨, 等.新冠肺炎疫情期间天津市重污染天气的边界层特征[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(3):701-709.MENG L H, HAO J, QIU X B, et al. Boundary layer characteristics of heavy pollution process in Tianjin during the epidemic period of COVID-19[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(3):701-709. [11] 冯春莉, 饶永才, 孟庆江, 等. 徐州市供暖期空气污染特征及来源分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2023, 13(2): 501-509.FENG C L, RAO Y C,MENG Q J, et al. Characteristics and sources apportionment of air pollution during heating period in Xuzhou[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2023, 13(2): 501-509. [12] 吕芳, 杨宇鑫, 杨俊.气溶胶光学厚度与PM2.5浓度的时空分布特征及其关系: 以京津冀大气污染传输通道城市群为例[J]. 生态学报,2023,43(1):153-165.LÜ F, YANG Y X, YANG J. Spatiotemporal distribution characteristics and relationship analysis of aerosol optical depth and PM2.5 concentration: taking the "2+26" urban agglomeration as an example[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2023,43(1):153-165. [13] WATTS D J, STROGATZ S H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks[J]. Nature,1998,393:440-442. doi: 10.1038/30918 [14] CAO Y J, WANG G Z, JIANG Q Y, et al. A neighbourhood evolving network model[J]. Physics Letters A,2006,349(6):462-466. doi: 10.1016/j.physleta.2005.09.047 [15] 秦胜君.基于复杂网络的企业创新网络级联失效可靠性模型[J]. 科技管理研究,2017,37(7):199-204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7695.2017.07.030QIN S J. Cascading failure reliability model of enterprise innovation network based on complex networks[J]. Science and Technology Management Research,2017,37(7):199-204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7695.2017.07.030 [16] 齐林, 张健, 黎晓奇.基于复杂网络的园区循环经济系统演化规律研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境,2016,26(10):61-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2016.10.008QI L, ZHANG J, LI X Q. Evolution pattern research of the industrial park system based on complex network[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment,2016,26(10):61-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2016.10.008 [17] 胡正荣.复杂网络社会认识论中的新闻真实[J]. 新闻与写作,2022(7):1.HU Z R. News truth in epistemology of complex network society[J]. News and Writing,2022(7):1. [18] 范如国, 朱超平, 林金钗.基于复杂网络的中国区域环境治理效率关联性演化分析[J]. 系统工程,2019,37(2):1-11.FAN R G, ZHU C P, LIN J C. Analysis of the relevance evolution of regional environmental governance efficiency in China based on complex network[J]. Systems Engineering,2019,37(2):1-11. [19] 崔素丽, 董东, 仇宾, 等.关于有向复杂网络软件异常交互行为检测研究[J]. 计算机仿真,2022,39(11):294-298. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2022.11.059CUI S L, DONG D, QIU B, et al. Research on abnormal interaction detection of directed complex network software[J]. Computer Simulation,2022,39(11):294-298. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2022.11.059 [20] 王皓晴, 顾长贵.基于复杂网络理论对长三角雾霾网络的城市节点重要性研究[J]. 中国水运(下半月),2019,19(1):92-94.WANG H Q, GU C G. Research on the importance of urban nodes in Yangtze River Delta smog network based on complex network theory[J]. China Water Transport,2019,19(1):92-94. [21] 肖琴, 陆钰婷.基于复杂网络的区域空气污染PM2.5分析[J]. 应用技术学报,2019,19(1):77-83.XIAO Q, LU Y T. Application of the complex network in the PM2.5 analysis of air pollution in regions[J]. Journal of Technology,2019,19(1):77-83. [22] 逯苗苗, 孙涛.我国雾霾污染空间关联性及其驱动因素分析: 基于社会网络分析方法[J]. 宏观质量研究,2017,5(4):66-75.LU M M, SUN T. An analysis of the spatial correlation and the driving factors of haze pollution in China: an SNA-based approach[J]. Journal of Macro-Quality Research,2017,5(4):66-75. [23] 马宇博, 高广阔.基于节点重要性评价的京津冀雾霾污染网络研究[J]. 环境科学学报,2018,38(6):2287-2296.MA Y B, GAO G K. Research on haze pollution network of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on node importance evaluation[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2018,38(6):2287-2296. [24] 杨传明, HORVATH G.时空交互视角下长三角城市群雾霾污染动态关联网络及协同治理研究[J]. 软科学,2019,33(12):114-120.YANG C M, HORVATH G. Study on dynamic associative network and collaborative governance of haze pollution in Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration based on spatiotemporal interaction perspective[J]. Soft Science,2019,33(12):114-120. [25] 东童童, 邓世成, 李轩枫.区域大气污染的城市网络关联分析: 基于粤港澳大湾区的研究[J]. 资源开发与市场,2021,37(1):19-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8141.2021.01.004 [26] 刘华军, 邵明吉, 石印, 等.“一带一路”沿线城市大气污染的空间交互影响网络及其结构特征[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境,2022,32(6):76-83.LIU H J, SHAO M J, SHI Y, et al. Spatial interactive influence network and its structural characteristics of air pollution in cities along the Belt and Road[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment,2022,32(6):76-83. [27] 韩华, 刘婉璐, 吴翎燕.基于模体的复杂网络测度量研究[J]. 物理学报,2013,62(16):168904. doi: 10.7498/aps.62.168904HAN H, LIU W L, WU L Y. The measurement of complex network based on motif[J]. Acta Physica Sinica,2013,62(16):168904. □ doi: 10.7498/aps.62.168904 -





 下载:
下载: