Research progress on sources, ecotoxicological effect and treatment technology of microplastics in water
-
摘要:
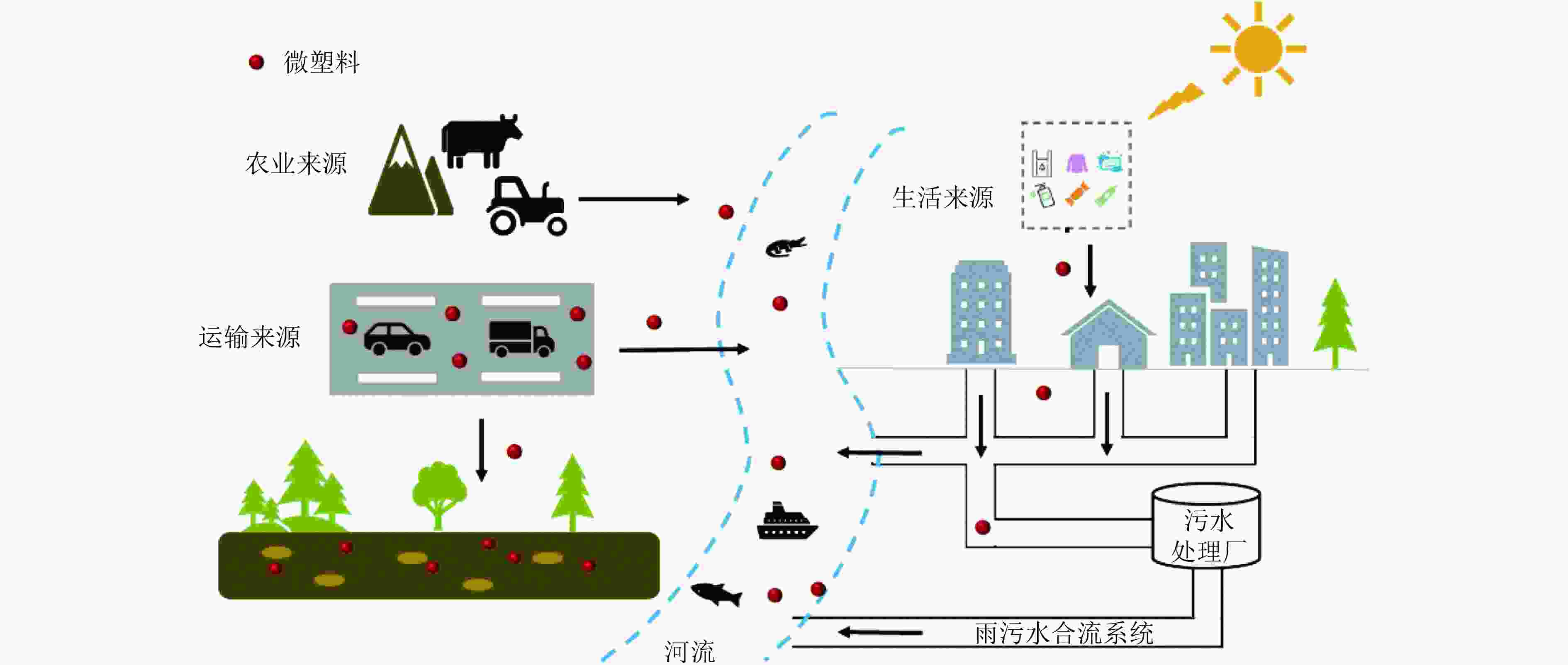
微塑料作为目前被广泛关注的新污染物之一,近年来在世界各地水环境中被频繁检出。微塑料不仅具有体积小、难降解、持久性等特点,而且可作为有毒金属、微生物、农药等污染物的载体,进一步增强它们的危害潜力。全面了解微塑料的来源和处理途径是确定微塑料污染控制关键问题以及实现对其有效管理的先决条件。回顾了国内外水环境中微塑料污染研究进展,梳理分析了水环境中微塑料的分类及来源,详细阐述了微塑料分离提取、定性定量检测方法,系统总结了微塑料对典型水生生物的单一影响以及微塑料与相关污染物对水生生物的复合影响;结合现有水污染控制技术,归纳了水中微塑料去除方法的优缺点,包括吸附、过滤、混凝沉淀、光催化、电絮凝、生物降解、膜生物反应器以及活性污泥法等技术。相关研究可为水环境中微塑料的去除与污染控制提供参考。
Abstract:Microplastics, as one of new pollutants that are widely concerned internationally, have been frequently detected in water environment around the world in recent years. Microplastics not only have the characteristics of small size, difficult degradation and durability, but also can act as carriers of toxic metals, microorganisms and pesticides and other pollutants to further enhance their hazard potentials. A comprehensive understanding of the sources and treatment approaches of microplastics is a prerequisite for identifying critical issues and their effective management. The latest progress of research on microplastic pollution in water environment at home and abroad was reviewed, the classification and sources of microplastics were analyzed, the methods of separation and extraction of microplastics, qualitative and quantitative detection were expounded, and the single effects of microplastics on typical aquatic organisms and the composite effects of microplastics and related pollutants on aquatic organisms were systematically summarized. Combined with the existing water pollution control technology, the advantages and disadvantages of microplastic removal methods, including adsorption, filtration, coagulation precipitation, photocatalysis, electric flocculation, biodegradation, membrane bioreactor and activated sludge process, were summarized. It was expected to provide reference for the removal and pollution control of microplastics in water environment.
-
表 1 微塑料鉴定方法及优缺点
Table 1. Advantages and disadvantages of identification methods of microplastics
鉴定方法 适用的粒径 优点 局限性 物理表征 显微镜计数[32] 可分析大于1 mm的较大颗粒 可快速鉴定,单位样品耗时短、成本低 无法确定样品的性质,需要与其他鉴定方法结合使用 标记方法[28] 可分析大于1 μm的颗粒,使用体视显微镜 方法简单,可快速筛选微塑料 颜料会污染其他颗粒,如有机碎片可能会被染料染色,导致微塑料丰度偏高 化学表征 傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)[33-34] 可分析大于500 μm的颗粒,通过显微镜耦合可分析低至20 μm的较小颗粒 操作简单,无损检测;可快速、准确识别微塑料的聚合物类型 实际样品制备过程复杂、耗时;易受添加剂或污染物的干扰;样品必须是红外活性的 拉曼光谱
(Raman)[35-36]可分析大于1 μm的颗粒,通过显微镜耦合 无损鉴定;可获得表面官能团的信息;具有较高空间分辨率;可分析不透明的颗粒 设备昂贵;易受样品中的生物残留物等污染物干扰 扫描电镜能谱仪(SEM-EDS)[37] 可分析μm级颗粒 具有较高的分辨率;可识别无机杂质 存在电荷效应,需要特殊涂层处理;成本较高;对样品具有破坏性 热解气相色谱-质谱联用(Pyr-GC-MS)[38] 适用于大于500 μm的颗粒 样品无需预处理;样品用量小;无需加入其他溶剂,可避免背景污染样品 对样品具有破坏性;不适用于杂质浓度较高的混合物;热解数据库仅包含特定的聚合物〔如聚乙烯 (PE)、聚丙烯 (PP)〕信息 液相色谱法[39] 需要足够的样品量
(大于1 mg)所选聚合物的回收率很高 无法确定物理特性(例如粒径信息)以及聚合物类型;每次运行只能评估少量样品;只能鉴定特定的聚合物(如PS、聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯) 表 2 微塑料去除技术优缺点
Table 2. Advantages and disadvantages of removal technologies of microplastics
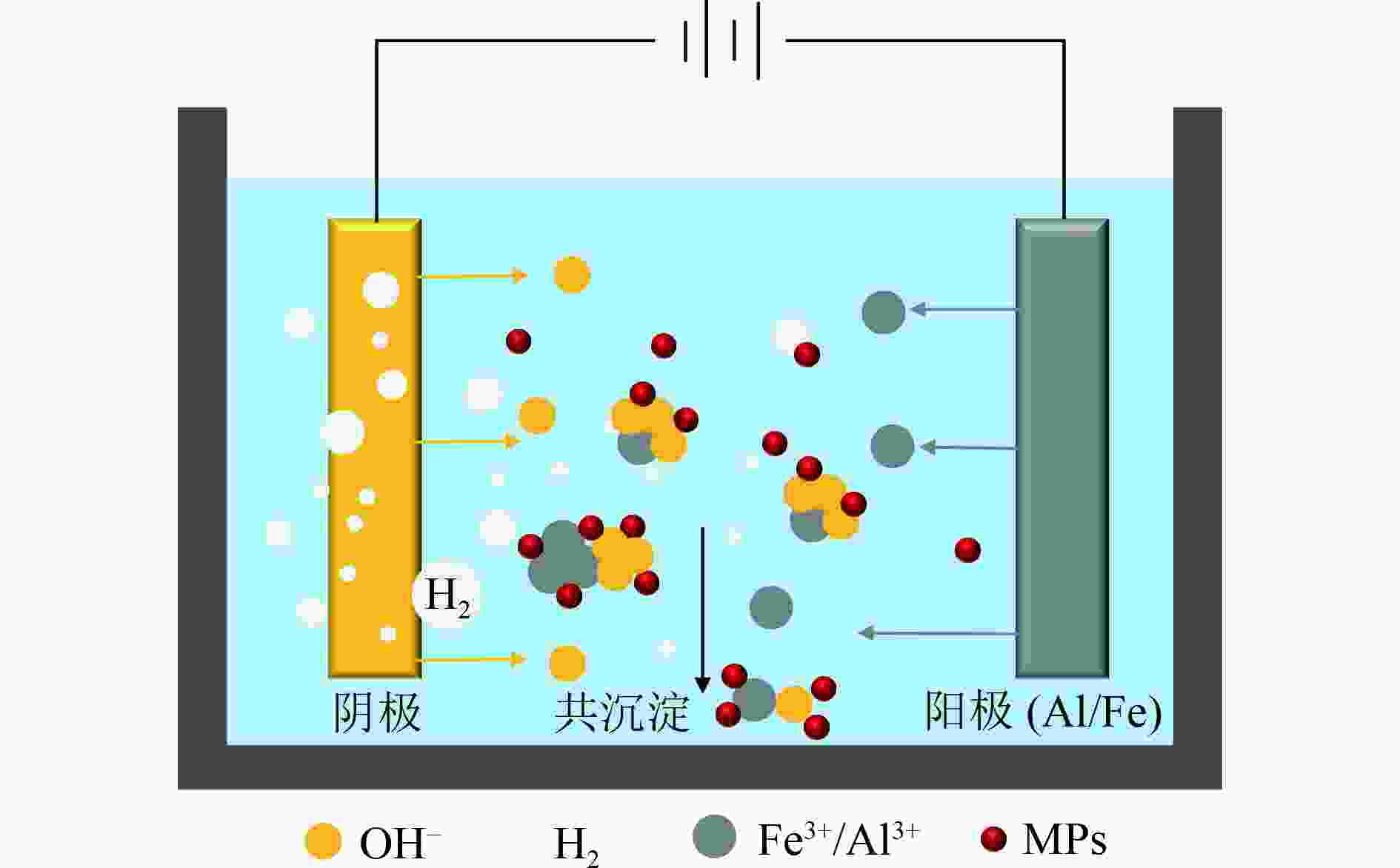
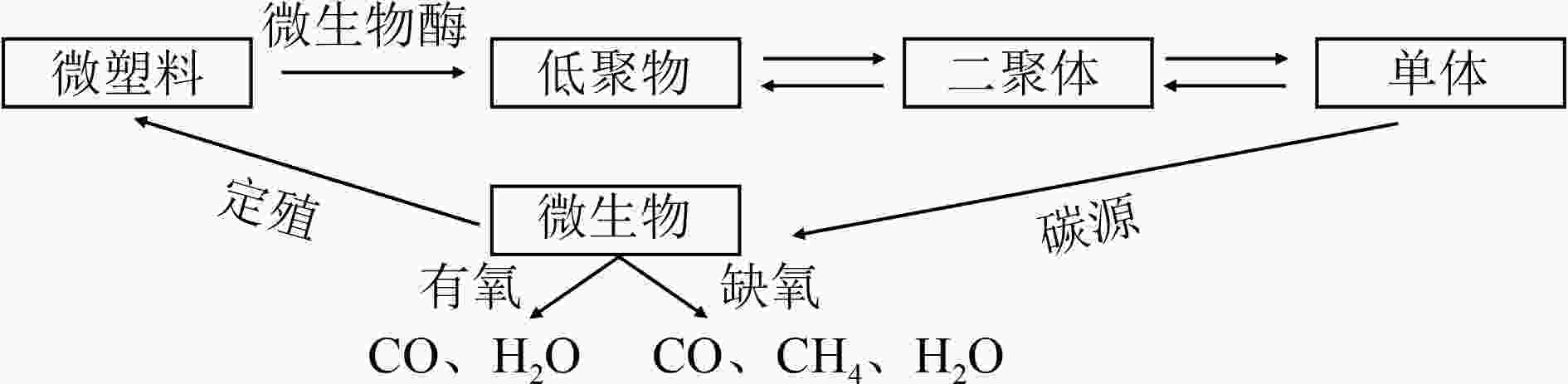
微塑料去除技术 优点 缺点 物理技术 吸附[59-60] 可重复使用性高,成本低,操作简单,无有毒化学品,可处理粒径1~5 μm的微塑料 选择性低,吸附剂制备复杂 过滤[61] 操作简单,可快速处理粒径范围广的微塑料 容易造成设备堵塞和膜污染,效率低 化学技术 混凝沉淀[62-63] 快速、低能耗、操作简单,适合处理粒径10 μm以上的微塑料 对密度小、粒径小的微塑料去除率不高;混凝剂需求量大,产泥量多 光催化[64-66] 反应速度快, 处理效率高,适合处理nm级的微塑料 成本高,需要较长时间才能达到较高的去除率;尚在工业层面进行探索 电絮凝[67-68] 无二次污染,污泥量小;节能高效,性价比高;可自动化操作 需要定期更换阳极,且阴极容易钝化 生物技术 膜生物反应
器[69-70]操作简单,处理效率高,容积大 膜易损坏和堵塞;需要定期清洗,减少膜污染 微生物降解[71-72] 处理效率高,运行成本低,无二次污染 需要通过光、热和化学氧化剂对微塑料进行预处理;处理程序复杂,耗时较长 活性污泥[73-74] 绿色环保,去除率可达60%以上 易受到温度等外界条件干扰;污泥处理复杂,需要较长的处理时间 -
[1] DING J F, JIANG F H, LI J X, et al. Microplastics in the coral reef systems from Xisha Islands of South China Sea[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2019,53(14):8036-8046. [2] COLE M, LINDEQUE P, HALSBAND C, et al. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: a review[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2011,62(12):2588-2597. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.09.025 [3] KANG J, ZHOU L, DUAN X G, et al. Degradation of cosmetic microplastics via functionalized carbon nanosprings[J]. Matter,2019,1(3):745-758. doi: 10.1016/j.matt.2019.06.004 [4] 赵艳民, 马迎群, 温泉, 等.基于不确定性的天津市北塘排污河表层沉积物微塑料污染评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(3):554-561.ZHAO Y M, MA Y Q, WEN Q, et al. Evaluation of microplastics pollution in surface sediments of Beitang Drainage River in Tianjin City based on uncertainty[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(3):554-561. [5] 岳龙飞, 李洪波, 梁淑轩, 等. 白洋淀入淀河流溶解有机物沿程变化特征及来源解析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(3):1050-1060.YUE L F, LI H B, LIANG S X, et al. Variation characteristics and source analysis of dissolved organic matter along the river into Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(3):1050-1060. [6] 吴磊石, 洪鸣, 彭梦微, 等.北部湾海域表层水体中微塑料分布特征[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(11):2556-2562.WU L S, HONG M, PENG M W, et al. Distribution characteristics of microplastics in surface water of Beibu Gulf[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(11):2556-2562. [7] 陈馨, 张仲伟, 刘运钊, 等.巢湖水体中微塑料组成及分布特征[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(12):2716-2721.CHEN X, ZHANG Z W, LIU Y Z, et al. Composition and distribution characteristics of microplastics in Chaohu Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(12):2716-2721. [8] 钱亚茹, 石磊磊, 沈茜, 等.淡水环境中微塑料污染及毒性效应研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(4):1096-1104.QIAN Y R, SHI L L, SHEN Q, et al. Research progress on pollution and toxic effects of microplastics in freshwater environment[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(4):1096-1104. [9] QIANG L Y, CHENG J P. Exposure to microplastics decreases swimming competence in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio)[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2019,176:226-233. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.088 [10] KURNIAWAN S B, SAID N S M, IMRON M F, et al. Microplastic pollution in the environment: insights into emerging sources and potential threats[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation,2021,23:101790. [11] NAPPER I E, BAKIR A, ROWLAND S J, et al. Characterisation, quantity and sorptive properties of microplastics extracted from cosmetics[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2015,99(1/2):178-185. [12] DI M X, WANG J. Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,616/617:1620-1627. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.150 [13] MAHBUB M S, SHAMS M. Acrylic fabrics as a source of microplastics from portable washer and dryer: impact of washing and drying parameters[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2022,834:155429. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155429 [14] DANNIS M L. Rubber dust from the normal wear of tires[J]. Rubber Chemistry and Technology,1974,47(4):1011-1037. doi: 10.5254/1.3540458 [15] DRIS R, GASPERI J, TASSIN B. Sources and fate of microplastics in urban areas: a focus on Paris Megacity[M]//Freshwater Microplastics. Cham: Springer, 2018: 69-83. [16] GEYER R. Production, use, and fate of synthetic polymers[M]//Plastic Waste and Recycling. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2020: 13-32. [17] ZHANG K, SHI H H, PENG J P, et al. Microplastic pollution in China’s inland water systems: a review of findings, methods, characteristics, effects, and management[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,630:1641-1653. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.300 [18] LI W C, TSE H F, FOK L. Plastic waste in the marine environment: a review of sources, occurrence and effects[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2016,566/567:333-349. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.084 [19] 宋小卫, 吴晓凤, 宋小平, 等.微塑料的提取分离方法研究进展[J]. 环境化学,2022,41(3):793-800.SONG X W, WU X F, SONG X P, et al. Research progress on the extraction and separation methods of microplastics[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2022,41(3):793-800. [20] RENNER G, NELLESSEN A, SCHWIERS A, et al. Hydrophobicity-water/air-based enrichment cell for microplastics analysis within environmental samples: a proof of concept[J]. MethodsX,2019,7:100732. [21] YARANAL N A, SUBBIAH S, MOHANTY K. Distribution and characterization of microplastics in beach sediments from Karnataka (India) coastal environments[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2021,169:112550. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112550 [22] AL-AZZAWI M S M, KEFER S, WEISSER J, et al. Validation of sample preparation methods for microplastic analysis in wastewater matrices: reproducibility and standardization[J]. Water,2020,12(9):2445. doi: 10.3390/w12092445 [23] HURLEY R R, LUSHER A L, OLSEN M, et al. Validation of a method for extracting microplastics from complex, organic-rich, environmental matrices[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2018,52(13):7409-7417. [24] COLE M, WEBB H, LINDEQUE P K, et al. Isolation of microplastics in biota-rich seawater samples and marine organisms[J]. Scientific Reports,2014,4(1):1-8. [25] TANG Y, ZHANG S H, SU Y L, et al. Removal of microplastics from aqueous solutions by magnetic carbon nanotubes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,406:126804. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126804 [26] 蔡慧文, 杜方旎, 张微微, 等.环境微纳塑料的分析方法进展[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(11):2547-2555.CAI H W, DU F N, ZHANG W W, et al. Research progress of microplastics and nanoplastics in environment[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(11):2547-2555. [27] BLAIR R M, WALDRON S, PHOENIX V R, et al. Microscopy and elemental analysis characterisation of microplastics in sediment of a freshwater urban river in Scotland, UK[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2019,26(12):12491-12504. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04678-1 [28] SHIM W J, HONG S H, EO S E. Identification methods in microplastic analysis: a review[J]. Analytical Methods,2017,9(9):1384-1391. doi: 10.1039/C6AY02558G [29] AIDENE S, SEMENOV V, KIRSANOV D, et al. Assessment of the physical properties, and the hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen content in plastics using energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy,2020,165:105771. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2020.105771 [30] LEISTENSCHNEIDER C, BURKHARDT-HOLM P, MANI T, et al. Microplastics in the Weddell Sea (Antarctica): a forensic approach for discrimination between environmental and vessel-induced microplastics[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2021,55(23):15900-15911. [31] JIANG Y J, QIN Z M, FEI J, et al. Surfactant-induced adsorption of Pb(Ⅱ) on the cracked structure of microplastics[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2022,621:91-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.04.068 [32] 李君薇.水体中微塑料的采集、分离及检测技术研究进展[J]. 塑料科技,2021,49(8):113-116. doi: 10.15925/j.cnki.issn1005-3360.2021.08.026LI J W. Research progress on collection, separation and detection technology of microplastics in water[J]. Plastics Science and Technology,2021,49(8):113-116. doi: 10.15925/j.cnki.issn1005-3360.2021.08.026 [33] LEVIN I W, BHARGAVA R. Fourier transform infrared vibrational spectroscopic imaging: integrating microscopy and molecular recognition[J]. Annual Review of Physical Chemistry,2005,56:429-474. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physchem.56.092503.141205 [34] LI J Y, LIU H H, PAUL CHEN J. Microplastics in freshwater systems: a review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection[J]. Water Research,2018,137:362-374. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.056 [35] JIN N F, SONG Y Z, MA R, et al. Characterization and identification of microplastics using Raman spectroscopy coupled with multivariate analysis[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta,2022,1197:339519. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.339519 [36] CABERNARD L, ROSCHER L, LORENZ C, et al. Comparison of Raman and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for the quantification of microplastics in the aquatic environment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2018,52(22):13279-13288. [37] WANG W F, WANG J. Investigation of microplastics in aquatic environments: an overview of the methods used, from field sampling to laboratory analysis[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2018,108:195-202. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2018.08.026 [38] HENDRICKSON E, MINOR E C, SCHREINER K. Microplastic abundance and composition in western lake superior As determined via microscopy, pyr-GC/MS, and FTIR[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2018,52(4):1787-1796. [39] WANG L, ZHANG J J, HOU S G, et al. A simple method for quantifying polycarbonate and polyethylene terephthalate microplastics in environmental samples by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters,2017,4(12):530-534. [40] MUKHERJEE A G, WANJARI U R, BRADU P, et al. Elimination of microplastics from the aquatic milieu: a dream to achieve[J]. Chemosphere,2022,303:135232. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135232 [41] 王国涛. 浙南大罗山天河水库浮游生物群落的季节变化及其水质评价[D]. 温州: 温州大学, 2021. [42] ZHANG C, CHEN X H, WANG J T, et al. Toxic effects of microplastic on marine microalgae Skeletonema costatum: interactions between microplastic and algae[J]. Environmental Pollution,2017,220:1282-1288. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.005 [43] 单宁, 祖木热提·艾比布, 米丽班·霍加艾合买提, 等.微塑料对黑麦草吸收和累积水体中环丙沙星的影响[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(12):2906-2912.SHAN N, HABIBUL Z, HOJAHMAT M, et al. Effects of microplastics on ryegrass (Lolium perenne L. ) uptake and accumulation of ciprofloxacin[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(12):2906-2912. [44] 丁平, 张丽娟, 黄道建, 等.微塑料对海洋生物的毒性效应及机理研究进展[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2021,43(2):144-153.DING P, ZHANG L J, HUANG D J, et al. Toxic effect and mechanism of microplastics on marine organisms[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology,2021,43(2):144-153. [45] MIAO L Z, WANG P F, HOU J, et al. Distinct community structure and microbial functions of biofilms colonizing microplastics[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,650:2395-2402. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.378 [46] SEELEY M E, SONG B, PASSIE R, et al. Microplastics affect sedimentary microbial communities and nitrogen cycling[J]. Nature Communications,2020,11(1):1-10. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13993-7 [47] SANGKHAM S, FAIKHAW O, MUNKONG N, et al. A review on microplastics and nanoplastics in the environment: their occurrence, exposure routes, toxic studies, and potential effects on human health[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2022,181:113832. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113832 [48] FACKELMANN G, SOMMER S. Microplastics and the gut microbiome: how chronically exposed species may suffer from gut dysbiosis[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2019,143:193-203. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.04.030 [49] WANG J, LI Y J, LU L, et al. Polystyrene microplastics cause tissue damages, sex-specific reproductive disruption and transgenerational effects in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma)[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,254:113024. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113024 [50] RAINIERI S, CONLLEDO N, LARSEN B K, et al. Combined effects of microplastics and chemical contaminants on the organ toxicity of zebrafish (Danio rerio)[J]. Environmental Research,2018,162:135-143. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2017.12.019 [51] 刘进. 典型微塑料对磺胺类抗生素在微藻和小鼠体中行为及毒性的影响研究[D]. 烟台: 烟台大学, 2022. [52] SANTOS D, FÉLIX L, LUZIO A, et al. Toxicological effects induced on early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio) after an acute exposure to microplastics alone or co-exposed with copper[J]. Chemosphere,2020,261:127748. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127748 [53] CHEN Q Q, YIN D Q, JIA Y L, et al. Enhanced uptake of BPA in the presence of nanoplastics can lead to neurotoxic effects in adult zebrafish[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2017,609:1312-1321. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.144 [54] 王燕. 微塑料与重金属(Cd、Pb、Zn)对海水青鳉复合毒性研究[D]. 重庆: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院重庆绿色智能技术研究院), 2020. [55] YIN W, WANG Y T, LIU L, et al. Biofilms: the microbial "protective clothing" in extreme environments[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(14):3423. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143423 [56] GONG M T, YANG G Q, ZHUANG L, et al. Microbial biofilm formation and community structure on low-density polyethylene microparticles in lake water microcosms[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,252:94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.090 [57] ZETTLER E R, MINCER T J, AMARAL-ZETTLER L A. Life in the "plastisphere": microbial communities on plastic marine debris[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2013,47(13):7137-7146. [58] KIRSTEIN I V, KIRMIZI S, WICHELS A, et al. Dangerous hitchhikers: evidence for potentially pathogenic Vibrio spp. on microplastic particles[J]. Marine Environmental Research,2016,120:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2016.07.004 [59] WANG Z G, SUN C Z, LI F M, et al. Fatigue resistance, re-usable and biodegradable sponge materials from plant protein with rapid water adsorption capacity for microplastics removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,415:129006. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129006 [60] SHI C L, ZHANG S L, ZHAO J F, et al. Experimental study on removal of microplastics from aqueous solution by magnetic force effect on the magnetic sepiolite[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2022,288:120564. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120564 [61] LECOANET H F, WIESNER M R. Velocity effects on fullerene and oxide nanoparticle deposition in porous media[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2004,38(16):4377-4382. [62] MA B W, XUE W J, DING Y Y, et al. Removal characteristics of microplastics by Fe-based coagulants during drinking water treatment[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2019,78:267-275. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.10.006 [63] WANG Z F, LIN T, CHEN W. Occurrence and removal of microplastics in an advanced drinking water treatment plant (ADWTP)[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,700:134520. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134520 [64] ARIZA-TARAZONA M C, VILLARREAL-CHIU J F, BARBIERI V, et al. New strategy for microplastic degradation: green photocatalysis using a protein-based porous N-TiO2 semiconductor[J]. Ceramics International,2019,45(7):9618-9624. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.10.208 [65] UHEIDA A, MEJÍA H G, ABDEL-REHIM M, et al. Visible light photocatalytic degradation of polypropylene microplastics in a continuous water flow system[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,406:124299. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124299 [66] EBRAHIMBABAIE P, YOUSEFI K, PICHTEL J. Photocatalytic and biological technologies for elimination of microplastics in water: current status[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2022,806:150603. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150603 [67] ELKHATIB D, OYANEDEL-CRAVER V, CARISSIMI E. Electrocoagulation applied for the removal of microplastics from wastewater treatment facilities[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2021,276:118877. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118877 [68] PERREN W, WOJTASIK A, CAI Q. Removal of microbeads from wastewater using electrocoagulation[J]. ACS Omega,2018,3(3):3357-3364. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b02037 [69] LI L, LIU D, SONG K, et al. Performance evaluation of MBR in treating microplastics polyvinylchloride contaminated polluted surface water[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2020,150:110724. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110724 [70] POERIO T, PIACENTINI E, MAZZEI R. Membrane processes for microplastic removal[J]. Molecules,2019,24(22):4148. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224148 [71] GANESH K A, ANJANA K, HINDUJA M, et al. Review on plastic wastes in marine environment:biodegradation and biotechnological solutions[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2020,150:110733. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110733 [72] URBANEK A K, RYMOWICZ W, MIROŃCZUK A M. Degradation of plastics and plastic-degrading bacteria in cold marine habitats[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2018,102(18):7669-7678. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9195-y [73] LARES M, NCIBI M C, SILLANPÄÄ M, et al. Occurrence, identification and removal of microplastic particles and fibers in conventional activated sludge process and advanced MBR technology[J]. Water Research,2018,133:236-246. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.049 [74] 刘俊勇, 谢沅汕, 张清科, 等.城市污水处理厂中微塑料的去除与归趋[J]. 应用化工,2021,50(4):919-923. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.04.014LIU J Y, XIE Y S, ZHANG Q K, et al. Removal and trend of microplastics in municipal wastewater treatment plants[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2021,50(4):919-923. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.04.014 [75] YUAN F, YUE L Z, ZHAO H, et al. Study on the adsorption of polystyrene microplastics by three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide[J]. Water Science and Technology:a Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research,2020,81(10):2163-2175. doi: 10.2166/wst.2020.269 [76] MA B W, XUE W J, HU C Z, et al. Characteristics of microplastic removal via coagulation and ultrafiltration during drinking water treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,359:159-167. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.155 [77] LAPOINTE M, FARNER J M, HERNANDEZ L M, et al. Understanding and improving microplastic removal during water treatment: impact of coagulation and flocculation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2020,54(14):8719-8727. [78] NAKATA K, FUJISHIMA A. TiO2 photocatalysis: design and applications[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology C:Photochemistry Reviews,2012,13(3):169-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2012.06.001 [79] LLORENTE-GARCÍA B E, HERNÁNDEZ-LÓPEZ J M, ZALDÍVAR-CADENA A A, et al. First insights into photocatalytic degradation of HDPE and LDPE microplastics by a mesoporous N-TiO2 coating: effect of size and shape of microplastics[J]. Coatings,2020,10(7):658. doi: 10.3390/coatings10070658 [80] TOFA T S, KUNJALI K L, PAUL S, et al. Visible light photocatalytic degradation of microplastic residues with zinc oxide nanorods[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters,2019,17(3):1341-1346. doi: 10.1007/s10311-019-00859-z [81] WANG L L, KAEPPLER A, FISCHER D, et al. Photocatalytic TiO2 micromotors for removal of microplastics and suspended matter[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(36):32937-32944. [82] SHEN M C, ZHANG Y X, ALMATRAFI E, et al. Efficient removal of microplastics from wastewater by an electrocoagulation process[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,428:131161. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131161 [83] LOBELLE D, CUNLIFFE M. Early microbial biofilm formation on marine plastic debris[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2011,62(1):197-200. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.10.013 [84] SOL D, LACA A, LACA A, et al. Approaching the environmental problem of microplastics: importance of WWTP treatments[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,740:140016. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140016 [85] BALASUBRAMANIAN V, NATARAJAN K, HEMAMBIKA B, et al. High-density polyethylene (HDPE)-degrading potential bacteria from marine ecosystem of Gulf of Mannar, India[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology,2010,51(2):205-211. [86] YANG Y, YANG J, WU W M, et al. Biodegradation and mineralization of polystyrene by plastic-eating mealworms: part 2. role of gut microorganisms[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2015,49(20):12087-12093. ◇ -




 下载:
下载: