Nitrogen and oxygen isotope analysis of nitrate-nitrogen pollution sources in a typical urban river
-
摘要:
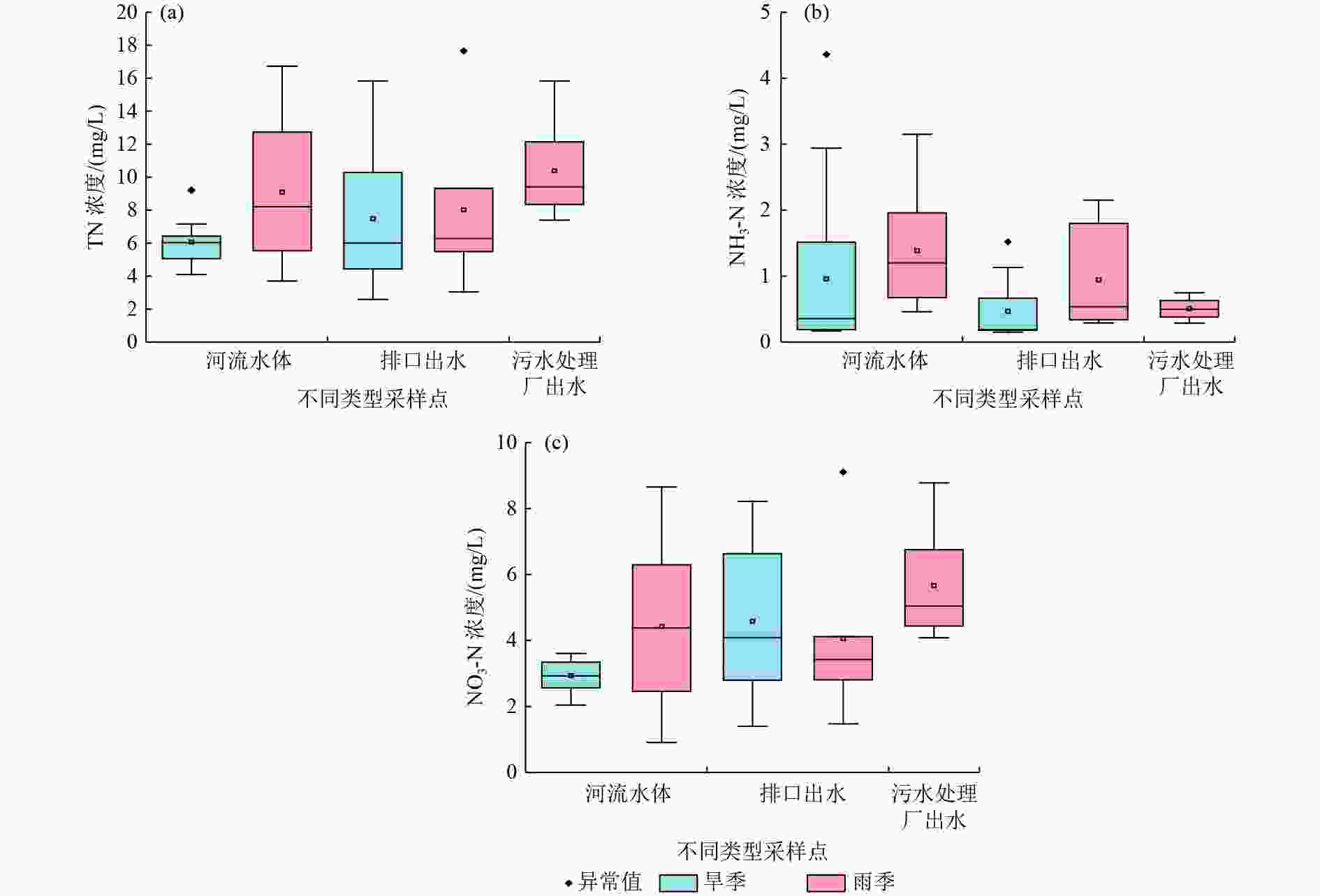
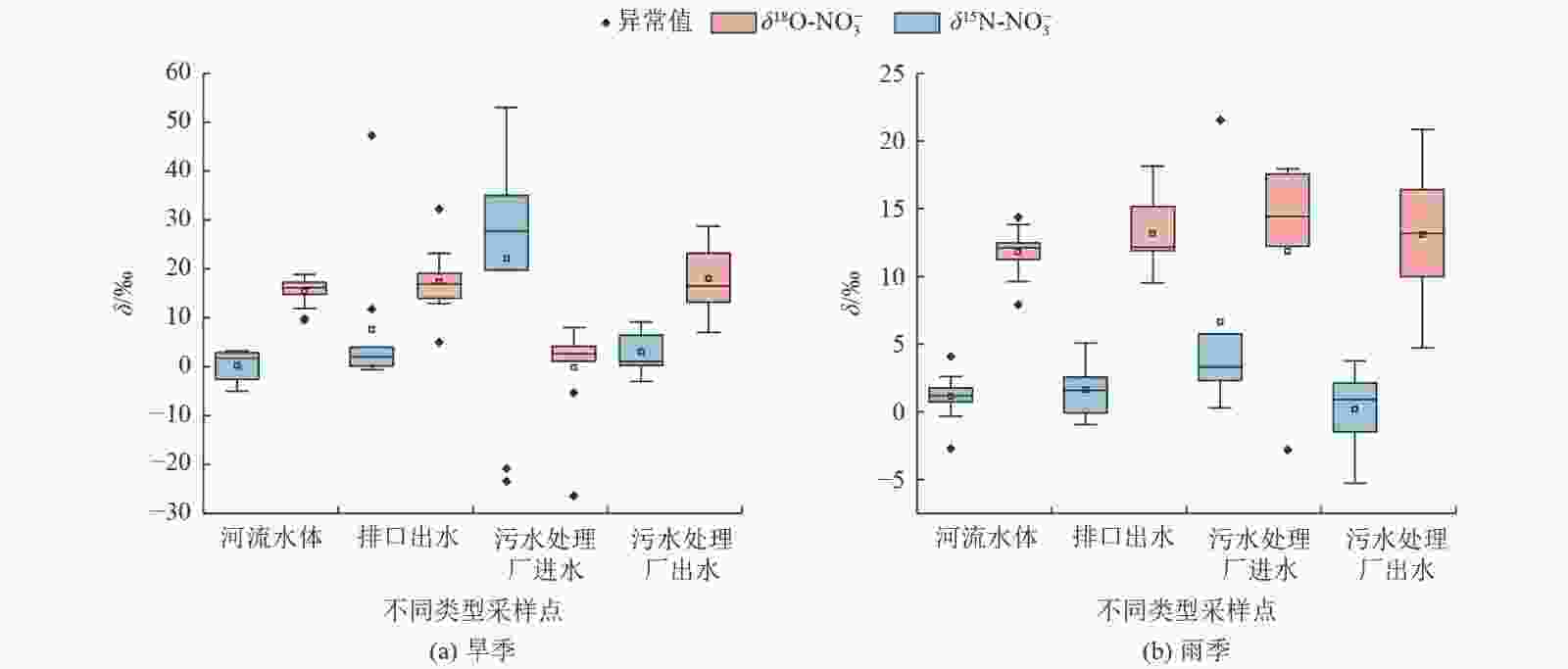
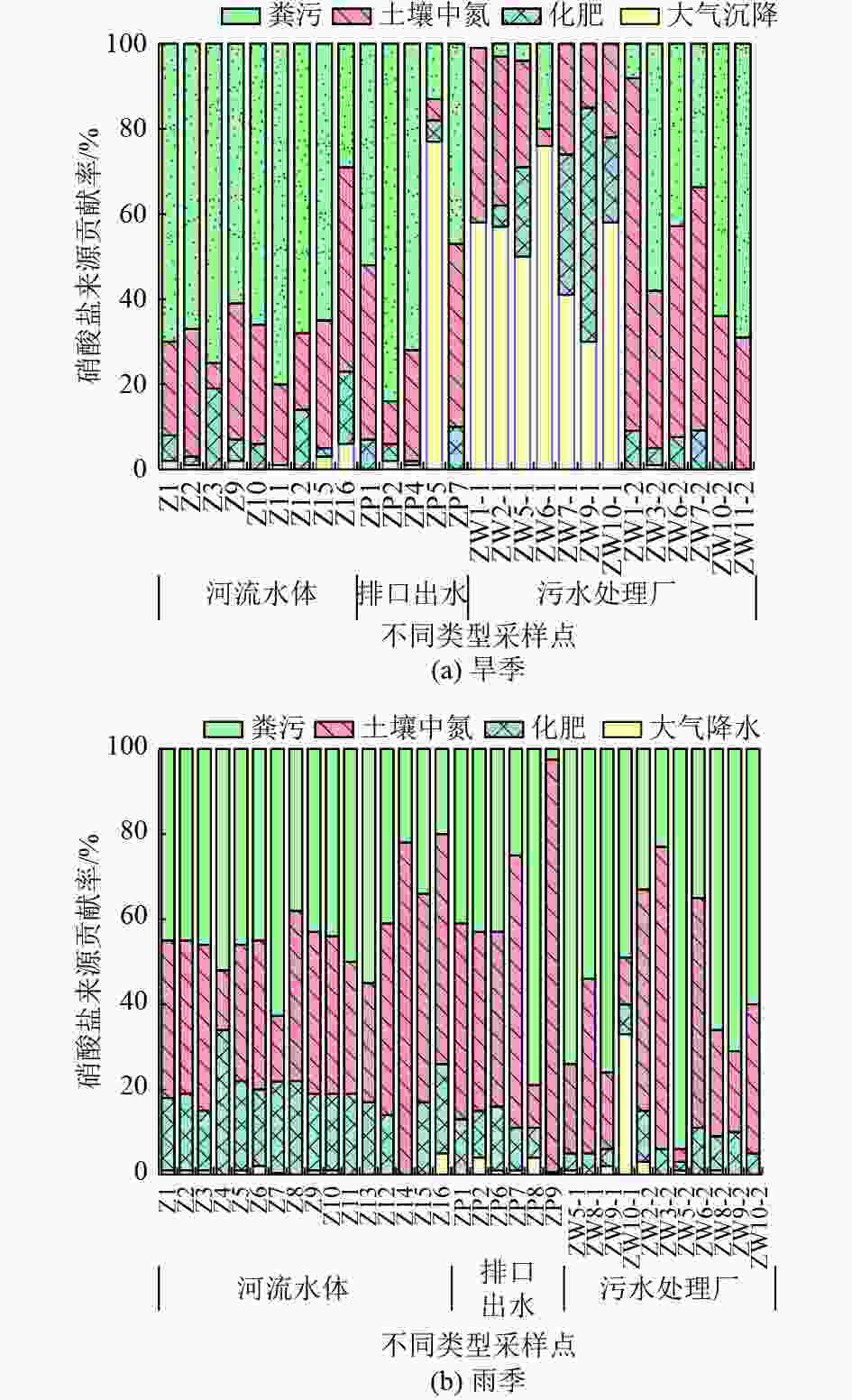
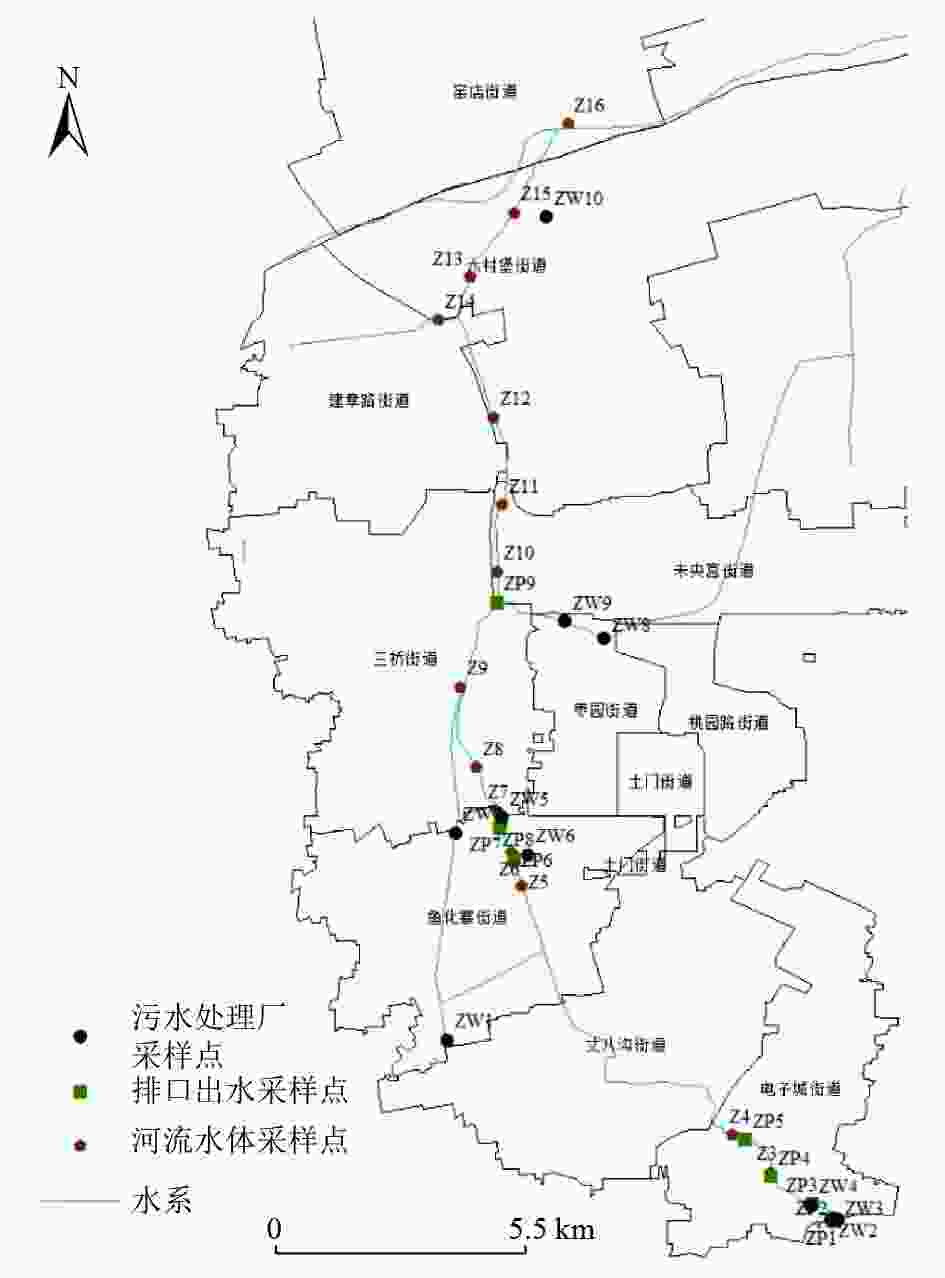
城市河流硝态氮(NO3-N)污染已经成为快速城市化发展中备受关注的水环境问题。以西安市皂河为例,于2021年的5月(旱季)和9月(雨季)采集其河流水体、排口出水和污水处理厂进出水,测定水质参数,并利用氮氧稳定同位素和Iso Source模型解析NO3-N来源。结果表明:5月和9月皂河NO3-N的δ15N分别为−26.43‰~32.29‰和−2.81‰~20.85‰,δ18O分别为−23.42‰~53.02‰和−5.26‰~21.53‰;粪污是皂河NO3-N的主要来源,皂河不同污染源NO3-N来源的平均贡献率,河流水体为粪污>土壤中氮>化肥>大气沉降,排口出水为粪污>土壤中氮>化肥>大气沉降,污水处理厂进水为大气沉降>粪污>土壤中氮>化肥,污水处理厂出水为粪污>土壤中氮>化肥>大气沉降;土壤中氮和粪污合计对皂河流域NO3-N的贡献率大于70%。控制居民生活污水排放、加强管网建设、强化畜禽粪污管理以及加强土地施肥监督等,有利于减轻城市河流NO3-N污染。
-
关键词:
- 城市河流 /
- 硝态氮(NO3-N) /
- 水化学 /
- 氮氧同位素 /
- Iso Source模型
Abstract:Nitrate-nitrogen (NO3-N) pollution in urban rivers has become a water environment problem of great concern in the context of rapid urbanization. Taking the Zaohe River in Xi'an City as an example, the river water body, discharge wastewater and inlet and outlet water of wastewater treatment plants were sampled in May (dry season) and September (rainy season) in 2021 to determine the water quality parameters and to resolve their nitrate-nitrogen sources using nitrogen and oxygen stable isotope and Iso Source models. The results showed that δ15N values of nitrate-nitrogen in the Zaohe River ranged from −26.43‰ to 32.29‰ and −2.81‰ to 20.85‰ in May and September, respectively, and δ18O values ranged from −23.42‰ to 53.02‰ and −5.26‰ to 21.53‰, respectively. Manure was the main source of nitrate pollution in the Zaohe River, and the average contribution rate of different nitrate sources in the river was in the order as follows: for river water, manure > soil organic nitrogen > fertilizer > atmospheric deposition; for discharge water, manure > soil organic nitrogen > fertilizer > atmospheric deposition; for sewage treatment plant influent water, atmospheric deposition > manure > soil organic nitrogen > fertilizer; for sewage treatment plant effluent, manure > soil organic nitrogen > fertilizer > atmospheric deposition. The combined contribution of soil organic nitrogen and manure to the Zaohe River watershed was greater than 70%. Therefore, controlling the discharge of residential sewage, strengthening the construction of pipeline networks, enhancing the management of livestock and poultry manure and strengthening the supervision of land fertilization were conducive to reducing the pollution of nitrate-nitrogen in urban rivers.
-
Key words:
- urban rivers /
- nitrate-nitrogen /
- water chemistry /
- nitrogen and oxygen isotopes /
- Iso Source model
-
表 1 NO3-N不同污染源来源的氮氧同位素特征范围
Table 1. Range of nitrogen and oxygen isotope characteristics of different sources of nitrate-nitrogen pollution
‰ 表 2 皂河不同类型采样点NO3-N来源贡献率分布
Table 2. Distribution of NO3-N source contribution at different types of sampling sites in Zaohe River
% 采样时间 氮来源 河流水体 排口出水 污水处理厂 进水 出水 旱季 大气沉降 平均值 1.67 16.00 52.86 0.67 标准差 1.83 30.51 13.51 0.75 化肥 平均值 7.89 5.40 19.14 5.00 标准差 6.59 3.01 18.57 3.92 土壤中氮 平均值 25.89 25.00 24.00 49.00 标准差 10.98 15.53 11.34 17.24 粪污 平均值 64.56 53.60 4.00 45.33 标准差 13.64 24.32 6.70 20.99 雨季 大气沉降 平均值 1.00 1.83 9.00 0.71 标准差 1.32 1.57 13.87 1.03 化肥 平均值 18.06 11.50 5.00 7.71 标准差 6.42 2.57 1.22 3.33 土壤中氮 平均值 38.00 37.83 22.75 37.00 标准差 14.44 17.05 11.14 21.71 粪污 平均值 42.94 48.83 63.25 54.57 标准差 10.33 17.23 11.90 23.39 -
[1] JIANG H, ZHANG Q Q, LIU W J, et al. Isotopic compositions reveal the driving forces of high nitrate level in an urban river: implications for pollution control[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,298:126693. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126693 [2] 张懿文, 罗建中, 陈宇阳.我国水体中硝酸盐的污染现状及危害[J]. 广东化工,2015,42(14):99-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2015.14.049ZHANG Y W, LUO J Z, CHEN Y Y. The pollution situation and harm of nitrate in water of China[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2015,42(14):99-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2015.14.049 [3] 李发东, 张妍, 李静.地下水硝酸盐去除中反硝化微生物的研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报,2013,21(1):110-118.LI F D, ZHANG Y, LI J. Research review of denitrifying microorganisms of groundwater to nitrate denitrification[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2013,21(1):110-118. [4] LI W C, LEI Q L, YEN H, et al. The overlooked role of diffuse household livestock production in nitrogen pollution at the watershed scale[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,272:122758. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122758 [5] KOHL D H, SHEARER G B, COMMONER B. Fertilizer nitrogen: contribution to nitrate in surface water in a corn belt watershed[J]. Science,1971,174(4016):1331-1334. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4016.1331 [6] 马文娟, 刘丹妮, 杨芳, 等.水环境中污染物同位素溯源的研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(2):242-250. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190081MA W J, LIU D N, YANG F, et al. Research progress in isotope methods for tracing contaminants in water environment[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(2):242-250. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190081 [7] SOLOMON D K, COOK P G, SANFORD W E. Dissolved gases in subsurface hydrology[M]//Isotope Tracers in Catchment Hydrology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1998: 291-318. [8] 张翠云, 张胜, 马琳娜, 等.污灌区地下水硝酸盐污染来源的氮同位素示踪[J]. 地球科学,2012,37(2):350-356.ZHANG C Y, ZHANG S, MA L N, et al. Nitrogen isotope tracing of sources of nitrate contamination in groundwater from wastewater irrigated area[J]. Earth Science,2012,37(2):350-356. [9] 崔坤磊, 尹希杰, 李艳利, 等.细菌反硝化法测试硝酸盐氮、氧同位素的研究与应用[J]. 应用海洋学学报,2021,40(4):629-635. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2021.04.009CUI K L, YIN X J, LI Y L, et al. Study and application of the isotopes N and O in nitrate determination by bacterial denitrification[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography,2021,40(4):629-635. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2021.04.009 [10] KANTNEROVÁ K, HATTORI S, TOYODA S, et al. Clumped isotope signatures of nitrous oxide formed by bacterial denitrification[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2022,328:120-129. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2022.05.006 [11] YUE F J, LI S L, LIU C Q, et al. Tracing nitrate sources with dual isotopes and long term monitoring of nitrogen species in the Yellow River, China[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7:8537. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08756-7 [12] LI R F, RUAN X H, BAI Y, et al. Effect of wheat-maize straw return on the fate of nitrate in groundwater in the Huaihe River Basin, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2017,592:78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.029 [13] ZHAO Y Y, ZHENG B H, JIA H F, et al. Determination sources of nitrates into the Three Gorges Reservoir using nitrogen and oxygen isotopes[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,687:128-136. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.073 [14] 张列宇, 马阳阳, 李国文, 等. 稳定同位素技术在水体硝酸盐污染源解析中的研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2023, 13(4): 1373-1383.ZHANG L Y, MA Y Y, LI G W, et al. Research progress of stable isotopes in source analysis of nitrate pollution in water[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2023, 13(4): 1373-1383. [15] 张妍, 张秋英, 李发东, 等.基于稳定同位素和贝叶斯模型的引黄灌区地下水硝酸盐污染源解析[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文),2019,27(3):484-493.ZHANG Y, ZHANG Q Y, LI F D, et al. Source identification of nitrate contamination of groundwater in Yellow River Irrigation Districts using stable isotopes and Bayesian model[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2019,27(3):484-493. [16] DANNI S O, BOUCHAOU L, ELMOUDEN A, et al. Assessment of water quality and nitrate source in the Massa Catchment (Morocco) using δ15N andδ18O tracers[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes,2019,154:108859. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2019.108859 [17] PHILLIPS D L, NEWSOME S D, GREGG J W. Combining sources in stable isotope mixing models: alternative methods[J]. Oecologia,2005,144(4):520-527. doi: 10.1007/s00442-004-1816-8 [18] 李慧, 周维博, 马聪, 等.城市化对西安市降水及河流水文过程的影响[J]. 干旱区地理,2017,40(2):322-331.LI H, ZHOU W B, MA C, et al. Effects of urbanization on regional precipitation and river hydrological process in Xi'an City[J]. Arid Land Geography,2017,40(2):322-331. [19] 李勇伟, 王思瑞, 宋康康, 等.西安城市河流生态治理方法及质量控制研究[J]. 安徽建筑,2021,28(11):18. doi: 10.16330/j.cnki.1007-7359.2021.11.006LI Y W, WANG S R, SONG K K, et al. Study on ecological management methods and quality control of urban rivers in Xi'an[J]. Anhui Architecture,2021,28(11):18. doi: 10.16330/j.cnki.1007-7359.2021.11.006 [20] 贺琳杰. 皂河黑臭水脱氨氮技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2021. [21] 毛绪美, 罗泽娇, 刘存富, 等.细菌反硝化法同时分析天然水中硝酸盐氮、氧同位素组成研究[J]. 地质科技情报,2006,25(5):97-100.MAO X M, LUO Z J, LIU C F, et al. A method of nitrogen and oxygen isotopic analysis of nitrate in water with bacterial denitrification at one time[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2006,25(5):97-100. [22] JUNG H, KIM Y S, YOO J, et al. Seasonal variations in stable nitrate isotopes combined with stable water isotopes in a wastewater treatment plant: implications for nitrogen sources and transformation[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2021,599:126488. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126488 [23] CASCIOTTI K L, McILVIN M, BUCHWALD C. Oxygen isotopic exchange and fractionation during bacterial ammonia oxidation[J]. Limnology and Oceanography,2010,55(2):753-762. doi: 10.4319/lo.2010.55.2.0753 [24] ZHANG Q Y, SHU W, LI F D, et al. Nitrate source apportionment and risk assessment: a study in the largest ion-adsorption rare earth mine in China[J]. Environmental Pollution,2022,302:119052. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119052 [25] 殷超, 杨海全, 陈敬安, 等.基于水化学和氮氧同位素的贵州草海丰水期水体硝酸盐来源辨析[J]. 湖泊科学,2020,32(4):989-998. doi: 10.18307/2020.0408YIN C, YANG H Q, CHEN J A, et al. Tracing nitrate sources with dual isotopes and hydrochemical characteristics during wet season in Lake Caohai, Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2020,32(4):989-998. doi: 10.18307/2020.0408 [26] 徐璐, 蒋勇军, 段世辉, 等.基于双同位素(δ15N-NO− 3-δ18O-NO− 3)和IsoSource模型的岩溶槽谷区地下水硝酸盐来源的定量示踪[J]. 环境科学,2020,41(8):3637-3645.XU L, JIANG Y J, DUAN S H, et al. Quantification of nitrate sources to groundwater in Karst trough-valley areas based on dual stable isotopes of δ15N-NO− 3 and δ18O-NO− 3 and the IsoSource model[J]. Environmental Science,2020,41(8):3637-3645. [27] KRUK M K, MAYER B, NIGHTINGALE M, et al. Tracing nitrate sources with a combined isotope approach (δ15NNO3, δ18ONO3 and δ11B) in a large mixed-use watershed in southern Alberta, Canada[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,703:135043. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135043 [28] YANG P H, LI Y, GROVES C, et al. Coupled hydrogeochemical evaluation of a vulnerable Karst aquifer impacted by septic effluent in a protected natural area[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,658:1475-1484. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.172 [29] XIAO J, LV G R, CHAI N P, et al. Hydrochemistry and source apportionment of boron, sulfate, and nitrate in the Fen River, a typical loess covered area in the eastern Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Environmental Research,2022,206:112570. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112570 [30] WU H Y, DONG Y, GAO L, et al. Identifying nitrate sources in surface water, regolith and groundwater in a subtropical red soil Critical Zone by using dual nitrate isotopes[J]. CATENA,2021,198:104994. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104994 [31] GUO J X, ZUO P, YANG L, et al. Determining nitrate sources in storm runoff in complex urban environments based on nitrogen and oxygen isotopes[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2022,838:155680. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155680 [32] YANG Y Y, TOOR G S. Sources and mechanisms of nitrate and orthophosphate transport in urban stormwater runoff from residential catchments[J]. Water Research,2017,112:176-184. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.039 [33] ZHANG X, ZHANG Y, SHI P, et al. The deep challenge of nitrate pollution in river water of China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,770:144674. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144674 [34] 李林霞, 李艳利, 杨梓睿, 等.沁河上游硝酸盐的定量源解析及其季节性差异[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(11):2636-2644.LI L X, LI Y L, YANG Z R, et al. Quantitative analysis and seasonal differences of nitrate sources in upper reaches of Qin River[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(11):2636-2644. [35] RIVETT M O, BUSS S R, MORGAN P, et al. Nitrate attenuation in groundwater: a review of biogeochemical controlling processes[J]. Water Research,2008,42(16):4215-4232. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.07.020 [36] XUE D M, BOTTE J, de BAETS B, et al. Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface- and groundwater[J]. Water Research,2009,43(5):1159-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.048 [37] LEHMANN M F, REICHERT P, BERNASCONI S M, et al. Modelling nitrogen and oxygen isotope fractionation during denitrification in a lacustrine redox-transition zone[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2003,67(14):2529-2542. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00085-1 [38] HILL A R, DEVITO K J, CAMPAGNOLO S, et al. Subsurface denitrification in a forest riparianzone: interactions between hydrology and supplies of nitrate and organic carbon[J]. Biogeochemistry,2000,51(2):193-223. doi: 10.1023/A:1006476514038 [39] MENGIS M, SCHIF S L, HARRIS M, et al. Multiple geochemical and isotopic approaches for assessing ground water NO3 − elimination in a riparian zone[J]. Ground Water,1999,37(3):448-457. ◇ doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.1999.tb01124.x -




 下载:
下载: