Distribution characteristics and cause of fluoride in Dalinuoer Lake in Inner Mongolia
-
摘要:
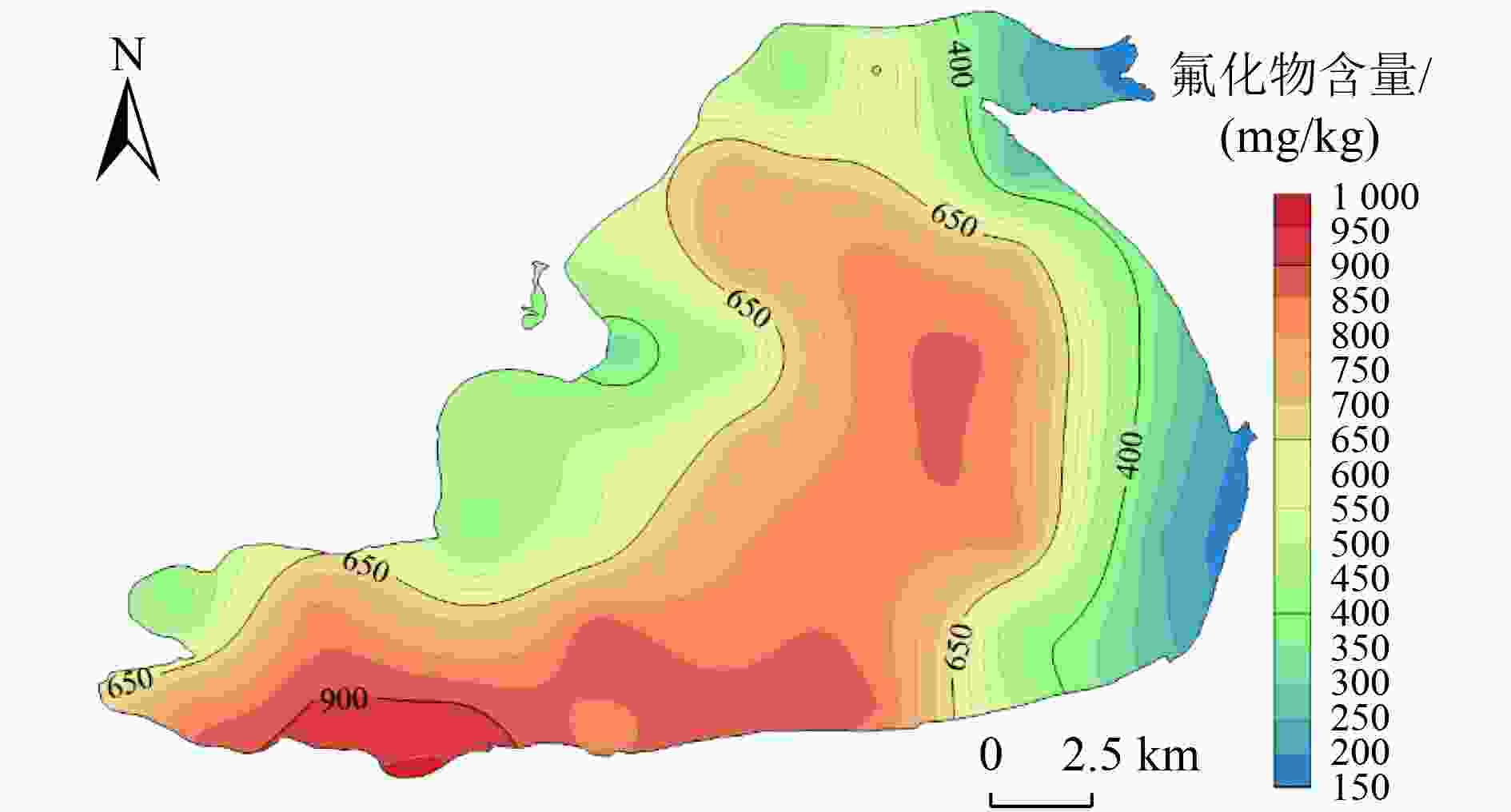
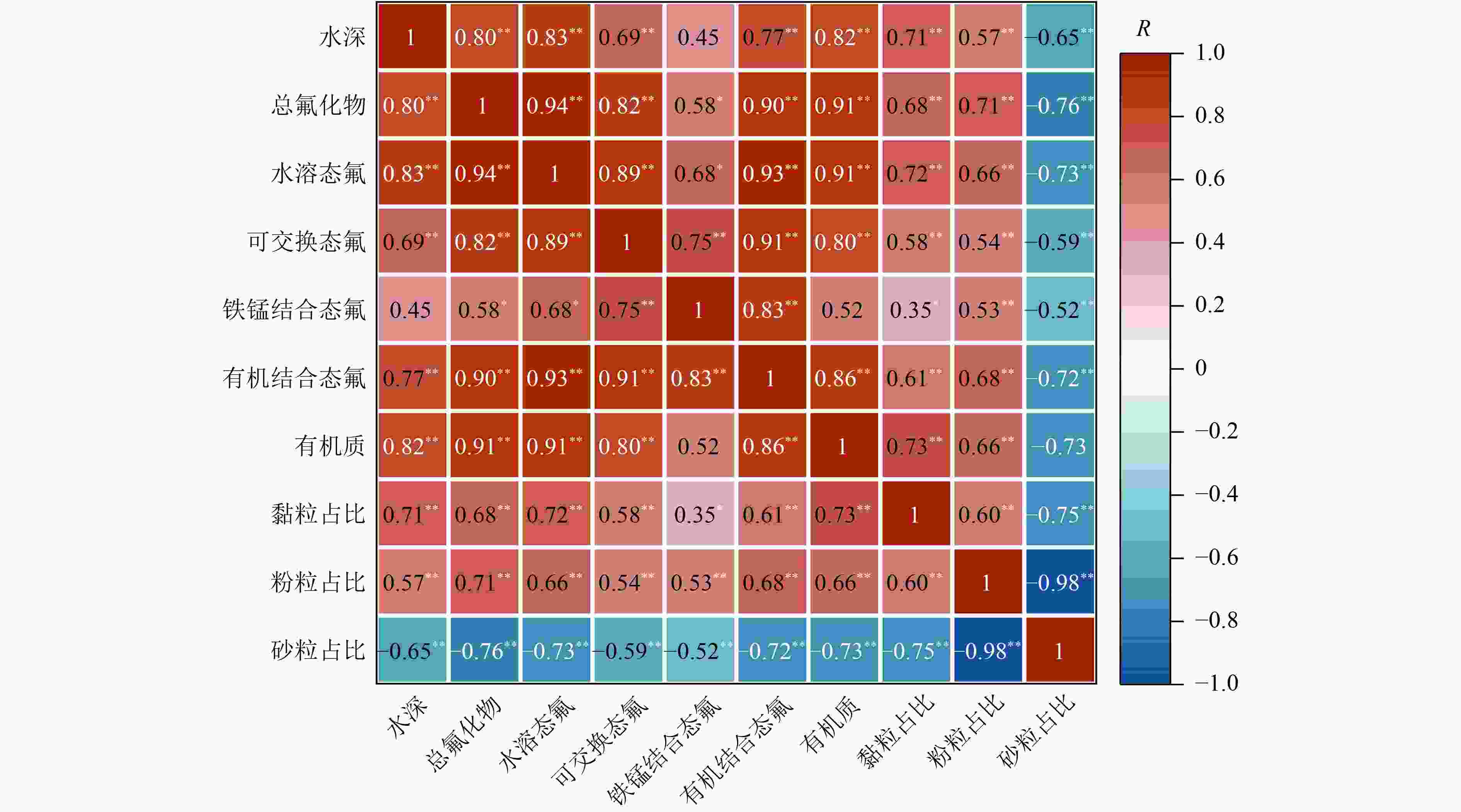
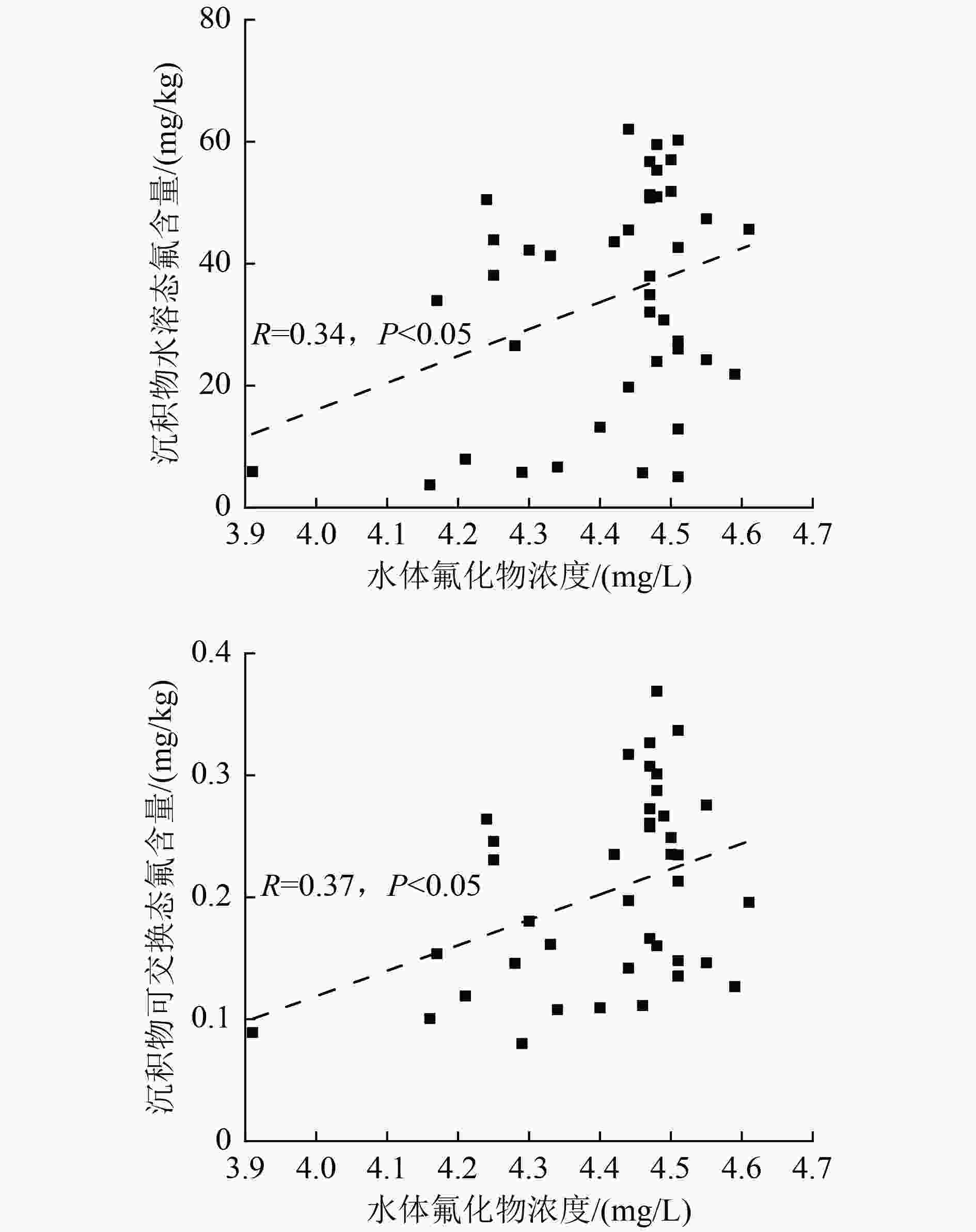
达里诺尔湖位于内蒙古高原,是典型的原生高氟区。为揭示湖泊氟化物的分布特征及成因,采集达里诺尔湖上覆水和表层沉积物,对氟化物的空间分布及其赋存形态进行了详细调查,并探讨了达里诺尔湖氟化物的来源及环境因素对水体氟化物的影响。结果表明:达里诺尔湖水体中氟化物浓度为3.91~4.61 mg/L,平均值为4.41 mg/L,显著高于GB 3838—2002《地表水环境质量标准》Ⅴ类阈值(1.5 mg/L)。表层沉积物中氟化物浓度变化范围为252.69~940.14 mg/kg,平均值为643.07 mg/kg,高值主要分布在湖泊西南部和湖心区。从形态上看,各形态氟含量整体表现为残余态>有机结合态>水溶态>铁锰结合态>可交换态,其中水溶态氟在一定环境条件下易向水体释放,成为达里诺尔湖水体中氟化物的主要内源。稳定度风险评估表明,达里诺尔湖沉积物中氟化物整体处于中等风险水平。达里诺尔湖的高氟水是在地层岩性引起的高自然本底值下,寒旱气候、特殊水化学条件、入湖河流及内流湖蒸发浓缩特征等环境因素的共同影响所致。研究结果可为达里诺尔湖及其他高氟湖泊的生态环境安全评估提供理论支持和科学依据。
Abstract:Dalinuoer Lake is located in Inner Mongolia of Plateau in Northern China, which is a typical primary high fluorine area. In order to reveal the distribution characteristics and causes of fluoride in the lake, the overlying water and surface sediments of Dalinuoer Lake were collected, and the spatial distribution and occurrence of fluoride were investigated in detail. The source of fluoride in Dalinuoer Lake and the influence of environmental factors on fluoride in water were discussed. The results indicated that the fluoride content in Dalinuoer Lake ranged from 3.91 to 4.61 mg/L, with an average value of 4.41 mg/L, significantly exceeding Grade Ⅴ threshold (1.5 mg/L) for Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB 3838-2002). The fluoride content in surface sediments varied from 252.69 to 940.14 mg/kg, with an average value of 643.07 mg/kg. Spatially, the area with high fluoride content was mainly distributed in the southwest and middle areas of Dalinuoer Lake. Regarding forms, the fluoride concentration in various forms generally showed a pattern of residual > organic bound > water soluble > iron-manganese bound > exchangeable, and the water-soluble fluoride was easy to release to the water body under certain environmental conditions, which became the main endogenous source of fluoride in Dalinuoer Lake. The stability risk assessment indicated that the fluoride in the sediment of Dalinuoer Lake was generally at a moderate risk level. The high fluorine water in Dalinuoer Lake was affected by environmental factors such as cold and dry climate, special hydrochemical conditions, the evaporation and concentration characteristics of inflow rivers and internal lakes under high natural background value caused by stratigraphic lithology. The results could provide theoretical support and scientific basis for the ecological environment security evaluation of Dalinuoer Lake and other lakes with high fluoride.
-
表 1 达里诺尔湖水体及沉积物物理化学指标
Table 1. Physical and chemical parameters in water and sediments of Dalinuoer Lake
项目 水体 沉积物 氟化物浓度/(mg/L) pH 氟化物含量/(mg/kg) 黏粒占比/% 粉粒占比/% 砂粒占比/% 有机质含量/(g/kg) 最大值 4.61 9.80 940.14 24.53 85.17 65.98 51.23 最小值 3.91 8.45 252.69 30.21 30.21 0.15 0.33 平均值 4.41 9.56 643.07 13.25 66.80 19.95 25.83 -
[1] LIU Y L, JIN M G, MA B, et al. Distribution and migration mechanism of fluoride in groundwater in the Manas River Basin, Northwest China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2018,26(5):1527-1546. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1780-8 [2] ALI S, THAKUR S K, SARKAR A, et al. Worldwide contamination of water by fluoride[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters,2016,14(3):291-315. doi: 10.1007/s10311-016-0563-5 [3] ADIMALLA N, VENKATAYOGI S. Mechanism of fluoride enrichment in groundwater of hard rock aquifers in Medak, Telangana State, South India[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2017,76(1):45. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6362-2 [4] 谢正苗, 吴卫红, 徐建民.环境中氟化物的迁移和转化及其生态效应[J]. 环境科学进展,1999(2):40-53.XIE Z M, WU W H, XU J M. Translocation and transformation of fluorides in the environmentand their biological effects[J]. Advances in Environmental Science,1999(2):40-53. [5] SINGH G, KUMARI B, SINAM G, et al. Fluoride distribution and contamination in the water, soil and plants continuum and its remedial technologies, an Indian perspective: a review[J]. Environmental Pollution,2018,239:95-108. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.002 [6] 杨金燕, 苟敏.中国土壤氟污染研究现状[J]. 生态环境学报,2017,26(3):506-513.YANG J Y, GOU M. The research status of fluorine contamination in soils of China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2017,26(3):506-513. [7] MERHABY D, OUDDANE B, NET S, et al. Assessment of trace metals contamination in surficial sediments along Lebanese Coastal Zone[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2018,133:881-890. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.06.031 [8] GONZALO C, CAMARGO J A. Fluoride bioaccumulation in the signal crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus (Dana) as suitable bioindicator of fluoride pollution in freshwater ecosystems[J]. Ecological Indicators,2012,20:244-251. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.12.019 [9] CAMARGO J A, ALONSO Á. Ecotoxicological assessment of the impact of fluoride (F−) and turbidity on the freshwater snail Physella acuta in a polluted river receiving an industrial effluent[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2017,24(18):15667-15677. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9208-x [10] WU C, WU X, QIAN C, et al. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment of high fluoride levels in the Yanchi endorheic region, northwest China[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2018,98:404-417. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.10.016 [11] SU H, WANG J D, LIU J T. Geochemical factors controlling the occurrence of high-fluoride groundwater in the western region of the Ordos Basin, northwestern China[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,252:1154-1162. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.046 [12] 易春瑶, 汪丙国, 靳孟贵.华北平原典型区土壤氟的形态及其分布特征[J]. 环境科学,2013,34(8):3195-3204.YI C Y, WANG B G, JIN M G. Fluorine speciation and its distribution characteristics in selected agricultural soils of North China plain[J]. Environmental Science,2013,34(8):3195-3204. [13] 韩伟, 叶渊, 李彦希, 等.高氟地区电解铝厂场地氟污染特征及其风险评估[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(4):727-733.HAN W, YE Y, LI Y X, et al. Fluorine pollution characteristics and risk assessment of electrolytic aluminum plant site in high fluoride area[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(4):727-733. [14] 潘自平, 刘新红, 孟伟, 等.贵阳中心区土壤氟的地球化学特征及其环境质量评价[J]. 环境科学研究,2018,31(1):87-94.PAN Z P, LIU X H, MENG W, et al. Geochemical characteristics of fluorine in soils and its environmental quality in central district of Guiyang[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2018,31(1):87-94. [15] 君珊, 张博, 王鹏飞, 等.呼伦湖水体氟化物演变特征及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(4):841-848.JUN S, ZHANG B, WANG P F, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of fluoride in lake water of Hulun Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(4):841-848. [16] 仝利红, 刘英俊, 张硕, 等.乌伦古湖水体矿化度和氟化物浓度的年际变化及模拟[J]. 湖泊科学,2022,34(1):134-141. doi: 10.18307/2022.0112TONG L H, LIU Y J, ZHANG S, et al. Modeling temporal changes in salinity and fluoride concentration of Lake Ulungur in Xinjiang, China[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2022,34(1):134-141. doi: 10.18307/2022.0112 [17] 丹旸. 内蒙古典型草原地区内陆湖面积变化研究: 以达里诺尔湖与呼日查干淖尔湖为例[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2019. [18] 李贺, 姜霞, 王书航, 等.寒旱区草原湖泊沉积物重金属地球化学基线构建: 以达里诺尔湖为例[J]. 中国环境科学,2022,42(12):5803-5813. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.12.038LI H, JIANG X, WANG S H, et al. Geochemical baseline establishment in grassland-type lake sediments in cold-arid regions: a case study in Dalinuoer Lake, China[J]. China Environmental Science,2022,42(12):5803-5813. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.12.038 [19] 甄志磊, 徐立帅, 张俊, 等.达里湖湖面演化过程及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志,2021,40(10):3314-3324.ZHEN Z L, XU L S, ZHANG J, et al. Evolution process of Dali Lake and its influencing factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2021,40(10):3314-3324. [20] 李文宝, 郭鑫, 张博尧, 等.达里湖表层水体浮游细菌群落结构的夏-冬季节差异[J]. 环境科学,2021,42(12):5814-5825.LI W B, GUO X, ZHANG B Y, et al. Characteristics of planktonic bacteria community between summer and winter surface water in Dali Lake[J]. Environmental Science,2021,42(12):5814-5825. [21] 赵万苍. 达里诺尔有机碳形态分布特征[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2010. [22] 孙园园, 何江, 吕昌伟, 等.达里诺尔湖沉积物中无机碳的形态组成[J]. 生态学报,2013,33(2):610-618. doi: 10.5846/stxb201111111714SUN Y Y, HE J, LÜ C W, et al. Forms composition of inorganic carbon in sediments from Dali Lake[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2013,33(2):610-618. doi: 10.5846/stxb201111111714 [23] 李云飞, 何江, 吕昌伟, 等.达里诺尔湖表层沉积物中Hg、As的形态分布及释放特性[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2014,33(11):2228-2233.LI Y F, HE J, LÜ C W, et al. Fractions and releases of mercury and arsenic in sediments of Dalinuoer Lake, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2014,33(11):2228-2233. [24] 李文宝, 刘志娇, 杨旭, 等.内蒙古高原达里诺尔湖夏季水体稳定同位素变化特征[J]. 湖泊科学,2019,31(2):539-550. doi: 10.18307/2019.0222LI W B, LIU Z J, YANG X, et al. Changes of stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in summer Dali-Nor Lake in Inner Mongolia of Northern China[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2019,31(2):539-550. doi: 10.18307/2019.0222 [25] 杨旭, 李畅游, 李文宝, 等.封闭型内陆湖泊夏季氮素赋存特征: 以达里诺尔湖为例[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2018,37(10):2262-2269.YANG X, LI C Y, LI W B, et al. Characteristics of nitrogen accumulation in closed inland lakes in summer: a case study of Dali-Nor Lake, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2018,37(10):2262-2269. [26] 姜霞, 王书航. 沉积物质量调查评估手册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. [27] 吴卫红, 谢正苗, 徐建明, 等.不同土壤中氟赋存形态特征及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学,2002,23(2):104-108.WU W H, XIE Z M, XU J M, et al. Characteristics of forms of fluorine in soils and influential factors[J]. Enviromental Science,2002,23(2):104-108. [28] 桂建业, 韩占涛, 张向阳, 等.土壤中氟的形态分析[J]. 岩矿测试,2008,27(4):284-286.GUI J Y, HAN Z T, ZHANG X Y, et al. Speciation analysis of fluorine in soil samples[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis,2008,27(4):284-286. [29] 李明珠, 张文超, 孙振涛, 等.不同提取剂对盐碱土壤氟形态测定结果的影响[J]. 实验技术与管理,2021,38(10):33-39.LI M Z, ZHANG W C, SUN Z T, et al. Effects of different extractants on determination results of fluorine in saline-alkali soil[J]. Experimental Technology and Management,2021,38(10):33-39. [30] 郭云艳, 周光鑫, 王雅雯, 等.南湖水系表层沉积物有机质的赋存特征、来源及生物有效性[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(6):936-943.GUO Y Y, ZHOU G X, WANG Y W, et al. Occurrence characteristics, sources and bioavailability of organic matter in surface sediments of Nanhu Lake water system[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(6):936-943. [31] SINGH K P, MOHAN D, SINGH V K, et al. Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti River sediments: a tributary of the Ganges, India[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2005,312(1/2/3/4):14-27. [32] 何志辉, 谢祚浑, 雷衍之.达里湖水化学和水生生物学研究[J]. 水生生物学集刊,1981(3):341-357. [33] 杨富亿, 文波龙, 李晓宇, 等.达里诺尔湿地水环境和鱼类多样性调查: Ⅳ. 达里湖水体中的污染物[J]. 湿地科学,2021,19(2):154-161.YANG F Y, WEN B L, LI X Y, et al. Investigation of water environment and fish diversity in Dalinor Wetlands: Ⅳ. pollutants in the water of Dali Lake[J]. Wetland Science,2021,19(2):154-161. [34] 杜昭宏, 安晓萍, 孟和平, 等.内蒙古渔业水体及其经济鱼类氟含量的分布特征[J]. 淡水渔业,2008,38(1):11-15.DU Z H, AN X P, MENG H P, et al. Fluorine distribution in fishery water body and economic fishes in Inner Mongolia[J]. Freshwater Fisheries,2008,38(1):11-15. [35] 张博, 郭云艳, 陈俊伊, 等.岱海沉积物氟化物赋存特征及其释放风险[J]. 中国环境科学,2020,40(4):1748-1756.ZHANG B, GUO Y Y, CHEN J Y, et al. Occurrence characteristics and release potential of fluoride in sediment of DaiHai Lake[J]. China Environmental Science,2020,40(4):1748-1756. [36] 王根绪, 程国栋.西北干旱区水中氟的分布规律及环境特征[J]. 地理科学,2000,20(2):153-159.WANG G X, CHENG G D. The distributing regularity of fluorine and its environmental characteristics in arid area of northwest China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2000,20(2):153-159. [37] SAHU S, GOGOI U, NAYAK N C. Groundwater solute chemistry, hydrogeochemical processes and fluoride contamination in phreatic aquifer of Odisha, India[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2021,12(3):101093. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.10.001 [38] 李静, 谢正苗, 徐建明, 等.我国氟的土壤健康质量指标及评价方法的初步探讨[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2005,31(5):593-597.LI J, XIE Z M, XU J M, et al. Preliminary study on guideline on soil health quality index of fluorine and method of its evaluation in China[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences),2005,31(5):593-597. [39] 车霏霏, 君珊, 陈俊伊, 等.呼伦湖砷的时空分布特征及成因分析[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(4):831-840.CHE F F, JUN S, CHEN J Y, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution and cause analysis of arsenic in Lake Hulun[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(4):831-840. [40] 李强, 霍守亮, 王晓伟, 等.巢湖及其入湖河流表层沉积物营养盐和粒度的分布及其关系研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2013,3(2):147-155.LI Q, HUO S L, WANG X W, et al. Distribution and correlation of nutrients and particle size in surface sediments of Lake Chaohu and its inflow rivers[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2013,3(2):147-155. [41] 刘璇, 梁秀娟, 肖霄, 等.pH对吉林西部湖泊底泥中不同形态氟迁移转化影响的实验研究[J]. 环境污染与防治,2011,33(6):19-22.LIU X, LIANG X J, XIAO X, et al. Experimental study on the impact of pH on the migration and transformation of various forms of fluorine in the lake mud of the western Jilin[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control,2011,33(6):19-22. [42] WANG Y X, SHVARTSEV S L, SU C L. Genesis of arsenic/fluoride-enriched soda water: a case study at Datong, Northern China[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2009,24(4):641-649. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.12.015 [43] 于群英, 李孝良, 汪建飞, 等.安徽省土壤氟含量及其赋存特征[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2013,22(7):915-921.YU Q Y, LI X L, WANG J F, et al. Content of fluorine and characteristics of fluorine forms in soils of Anhui Province[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin,2013,22(7):915-921. [44] 梁秀娟, 方樟, 季超, 等.高氟湖库底泥中氟的存在形态分析: 以洋沙泡水库为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2010,40(3):651-656.LIANG X J, FANG Z, JI C, et al. Analysis on the existing forms of fluorine in the bottom mud of high-fluorine lakes and reservoirs: a case study of Yangshapao reservior[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2010,40(3):651-656. [45] CHOWDHURY A, ADAK M K, MUKHERJEE A, et al. A critical review on geochemical and geological aspects of fluoride belts, fluorosis and natural materials and other sources for alternatives to fluoride exposure[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2019,574:333-359. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.04.033 [46] 王旭阳. 基于3S技术的达里诺尔湖水深反演研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2017. [47] 杨光林. 达里湖17.8~6.8 ka BP期间的水位演化及古气候环境[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017. [48] 吴磊.内蒙古萤石矿分布特征及成矿规律[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2018,30(7):10-21.WU L. Fluorite ore deposit distribution features and mineralization pattern in Inner Mongolia[J]. Coal Geology of China,2018,30(7):10-21. [49] 朱明占, 李俊霞, 秦宏飞, 等.桂南地下热水系统中氟的分布及迁移富集规律[J]. 安全与环境工程,2016,23(5):73-79.ZHU M Z, LI J X, QIN H F, et al. Distribution, migration and enrichment of fluoride in geothermal water in southern Guangxi, China[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2016,23(5):73-79. [50] 魏学.近45 a达里诺尔湖面积演变对气候的响应[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2019,33(2):110-115.WEI X. Response of Dali Lake area to climate factors in the past 45 years[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2019,33(2):110-115. [51] 赵胜男, 史小红, 崔英, 等.内蒙古达里诺尔湖湖泊水体与入湖河水水化学特征及控制因素[J]. 环境化学,2016,35(9):1865-1875.ZHAO S N, SHI X H, CUI Y, et al. Hydrochemical properties and controlling factors of the Dali Lake and its inflow river water in Inner Mongolia[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2016,35(9):1865-1875. [52] 刘琳. 基于遥感影像数据的内蒙古湖泊时空演变分析: 以2000—2018年数据为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021. [53] XIAO J, JIN Z D, ZHANG F. Geochemical controls on fluoride concentrations in natural waters from the middle Loess Plateau, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2015,159:252-261. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.09.018 [54] FENG F, JIA Y F, YANG Y, et al. Hydrogeochemical and statistical analysis of high fluoride groundwater in Northern China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2020,27(28):34840-34861. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09784-z [55] WANG W Z, LI Z, SU H, et al. Spatial and seasonal variability, control factors and health risk of fluoride in natural water in the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2022,434:128897. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128897 [56] WU J H, LI P Y, QIAN H. Hydrochemical characterization of drinking groundwater with special reference to fluoride in an arid area of China and the control of aquifer leakage on its concentrations[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2015,73(12):8575-8588. ◇ doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4018-2 -





 下载:
下载: