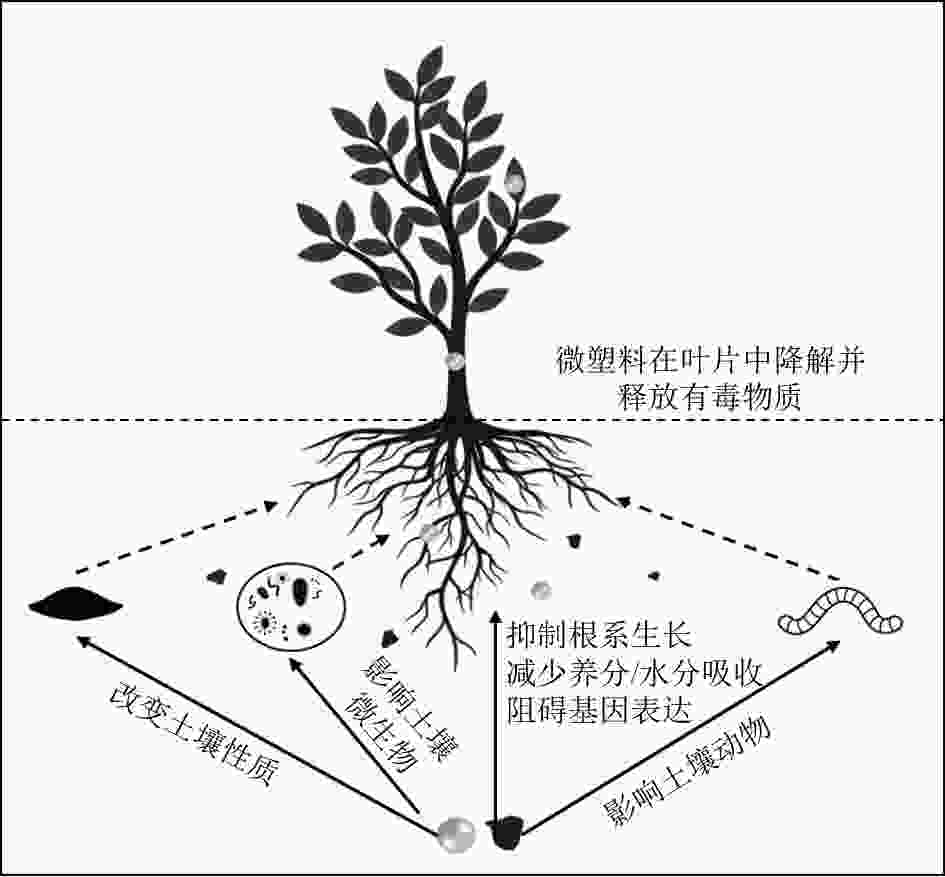
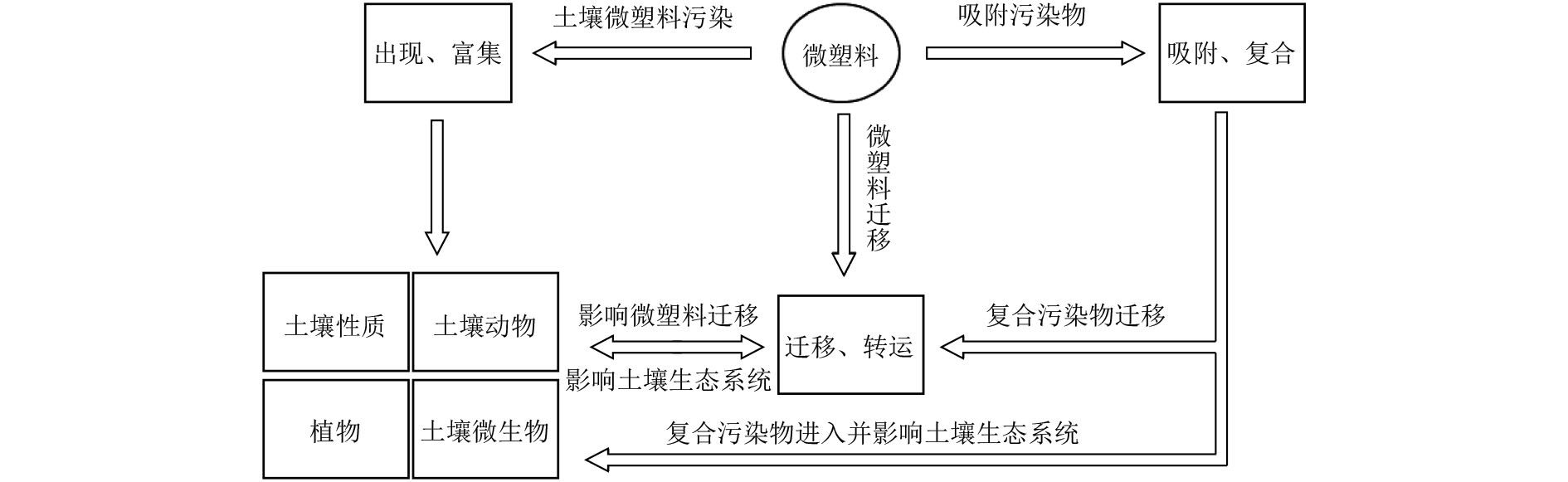
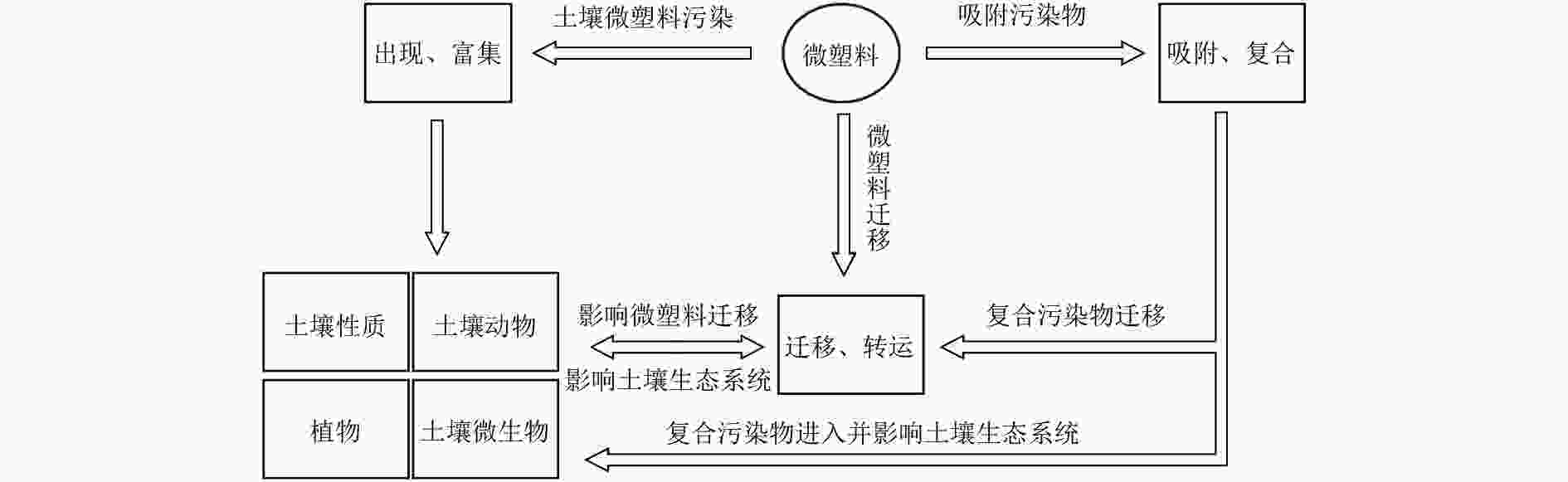
Effects of microplastics on soil ecosystems and remediation technologies
-
摘要:
由于农膜破碎、污水灌溉等活动,土壤中的微塑料含量与丰度正逐渐超越海洋,并成为土壤的主要污染源之一。土壤生物能吸收土壤微塑料,其中粮食作物中的微塑料能通过食物链进入人体,造成人体微塑料暴露风险,此外,土壤微塑料也会直接对土壤产生毒性。概述了微塑料在土壤生态系统中的来源、迁移等环境行为,重点综述了微塑料对土壤生态系统的影响。结果表明:1)微塑料能通过土壤颗粒间的空隙、植物侧根裂缝及动物运动等在土壤环境系统中迁移转运;2)微塑料能影响土壤物理化学性质、植物生长发育、动物行为和微生物多样性;3)微生物和酶能降解土壤环境中的微塑料,并直接减少土壤系统中的微塑料,而生物炭可以减轻微塑料对土壤生态系统的毒性,三者均为土壤微塑料修复技术的潜在选择。最后,提出了土壤微塑料未来可能的研究方向,以期为土壤微塑料的污染防治提供指导。
Abstract:Due to agricultural film fragmentation, sewage irrigation and other anthropogenic activities, the content and abundance of microplastics in soil are gradually surpassing those in the ocean, and becoming one of the main pollution sources of soil. Soil organisms can absorb soil microplastics, among which microplastics in food crops can enter the human body through the food chain, causing the risk of human microplastic exposure. In addition, soil microplastics can also directly cause toxicity to soil. The sources, migration and other environmental behavior of microplastics in soil ecosystem were summarized, and the impact of microplastics on soil ecosystem was emphasized. The results mainly include the following aspects: (1) Microplastics can migrate and transport in the soil environmental system through the space between soil particles, the root cracks of plants and the movement of animals. (2) Microplastics can affect soil physical and chemical properties, plant growth and development, animal behavior and microbial diversity. (3) Microorganisms and enzymes can degrade microplastics in the soil environment and directly reduce microplastics in the soil system, while biochar can reduce the toxicity of microplastics to the soil ecosystem. All three are potential options for soil microplastics remediation technologies. Finally, the possible research direction of soil microplastics in the future was proposed, in order to provide guidance for the pollution control of soil microplastics.
-
Key words:
- microplastics pollution /
- soil /
- plants /
- animals /
- microorganisms
-
表 1 微塑料对土壤物理性质的影响
Table 1. Effects of microplastics on soil physical properties
种类 浓度/% 土壤基质 处理时间 结果 数据来源 PP、HDPE、PA、PES PA、HDPE均为梯度浓度,0.05、0.10、0.20、0.40;PP、PES均为梯度浓度,0.25、0.50、1.00、2.00 壤土 35 d 所有微塑料均影响土壤容重,PES增加土壤持水能力 文献[39] 合成纤维、HDPE、PLA 合成纤维为0.001;
HDPE和PLA均为0.1砂质黏壤土 30 d 当暴露于HDPE时,土壤的pH显著低于暴露于其他处理时。对照处理的土壤平均质量直径分别比添加纤维、HDPE和PLA的土壤大24%、35%和28%。对照土壤大于2 000 µm的大团聚体数量分别比HDPE和PLA土壤大60%和53%。相反,与对照土壤相比,暴露于微塑料的土壤中63~250 µm的微团聚体数量明显更高 文献[40] PES PES为梯度浓度,0.01、0.3 黏壤土 1 a 土壤容重、土壤团聚体粒径分布和饱和导水率均无显著变化。0.3%浓度PES处理的土壤中30 μm的孔隙显著增加 文献[41] PES、HDPE、PP、PS、PET PES为0.2;HDPE、PS、PP、PET均为2 壤土 2个月 HDPE、PES、PET、PP和PS降低了土壤容重;PA、PES和PS显著减少水稳定性团聚体;所有的微塑料均改变土壤结构,其影响程度各不相同 文献[36] 注:PP(polypropylene)为聚丙烯;HDPE(high density polyethylene)为高密度聚乙烯;PA(polyamide)为聚酰胺;PES(polyester)为聚酯;PLA(polylactic acid)为聚乳酸;PS(polystyrene)为聚苯乙烯;PET(polyethylene terephthalate)为聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯。 表 2 植物对微塑料的吸收
Table 2. Absorption of microplastics in plants
微塑料 培养条件 微塑料信息 植物 吸收情况 数据来源 携带荧光与否 官能团修饰 粒径/μm 浓度/(mg/kg) 地下部 地上部 PS 水培 + COOHNH2-F 0.2 50、100 拟南芥 √ NM 文献[45] - - 0.05 10、100、1 000 洋葱 √ NM 文献[46] - - 0.1~1、5 10、20 胡萝卜 √ √(但未观察到5 μm的微塑料) 文献[28] + - 0.1 100 蚕豆 √ NM 文献[47] + - 0.1、0.3、0.5、0.7 50 黄瓜 √ √(茎/叶片/花/果实) 文献[32] + - 0.2 50 生菜 √ √ 文献[48] + - 0.2、2 50 生菜/小麦 √ √ 文献[4] + - 0.1 0.01、0.1、1、10 小麦 √ √ 文献[49] + - 0.1 1、10 生菜/萝卜 √ × 文献[50] + 羧基 0.1 0.1、1、10 水稻 √ × 文献[51] + - 0.08、1 40 水稻 √ √ 文献[52] + - 0.098 0.16、0.8、4、20、100 水蕨 √ NM 文献[53] - - 0.05 100、1 000 水稻 √ √ 文献[54] - 铕(Eu) 0.2 0.02~500 生菜/小麦 √ √ 文献[55] - - 0.2 25 白菜 √ √ 文献[56] 土培 + 羧基 281) 10、100 绿豆 NM √ 文献[57] + - 0.2 500 小麦 √ × 文献[4] + - 0.2 500 小麦 √ √ 文献[48] - 铕(Eu) 0.2 1、10 生菜 √ √ 文献[55] + - 0.02 20、40 豌豆 √ √ 文献[58] PMMA 水培 + - 0.096 75±0.058 2 000 大麦 √ × 文献[59] 注:+表示有该种处理;-表示无该种处理;√表示已观察到微塑料吸收;×表示未观察到微塑料吸收;NM表示未进行微塑料吸收情况观察。PS为聚苯乙烯;PMMA为聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯。1)单位为nm。 -
[1] GEWERT B, PLASSMANN M M, MacLEOD M. Pathways for degradation of plastic polymers floating in the marine environment[J]. Environmental Science Processes & Impacts,2015,17(9):1513-1521. [2] SUN Y R, YUAN J H, ZHOU T, et al. Laboratory simulation of microplastics weathering and its adsorption behaviors in an aqueous environment: a systematic review[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,265:114864. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114864 [3] 钱亚茹, 石磊磊, 沈茜, 等. 淡水环境中微塑料污染及毒性效应研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(4):1096-1104.QIAN Y R, SHI L L, SHEN Q, et al. Research progress on pollution and toxic effects of microplastics in freshwater environment[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(4):1096-1104. [4] LI L Z, LUO Y M, LI R J, et al. Effective uptake of submicrometre plastics by crop plants via a crack-entry mode[J]. Nature Sustainability,2020,3:929-937. doi: 10.1038/s41893-020-0567-9 [5] 刘彬, 侯立安, 王媛, 等. 我国海洋塑料垃圾和微塑料排放现状及对策[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(1):174-182.LIU B, HOU L A, WANG Y, et al. Emission estimate and countermeasures of marine plastic debris and microplastics in China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(1):174-182. [6] KUNDU A, SHETTI N P, BASU S, et al. Identification and removal of micro- and nano-plastics: efficient and cost-effective methods[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,421:129816. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129816 [7] HUANG Y, LIU Q, JIA W Q, et al. Agricultural plastic mulching as a source of microplastics in the terrestrial environment[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,260:114096. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114096 [8] 赵岩, 陈学庚, 温浩军, 等. 农田残膜污染治理技术研究现状与展望[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(6):1-14.ZHAO Y, CHEN X G, WEN H J, et al. Research status and prospect of control technology for residual plastic film pollution in farmland[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2017,48(6):1-14. [9] GALLOWAY T S, COLE M, LEWIS C. Interactions of microplastic debris throughout the marine ecosystem[J]. Nature Ecology & Evolution,2017,1:116. [10] DAWSON A L, KAWAGUCHI S, KING C K, et al. Turning microplastics into nanoplastics through digestive fragmentation by Antarctic krill[J]. Nature Communications,2018,9:1001. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03465-9 [11] WEITHMANN N, MÖLLER J N, LÖDER M G J, et al. Organic fertilizer as a vehicle for the entry of microplastic into the environment[J]. Science Advances,2018,4(4):8060. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aap8060 [12] HUERTA LWANGA E, GERTSEN H, GOOREN H, et al. Microplastics in the terrestrial ecosystem: implications for Lumbricus terrestris (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae)[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2016,50(5):2685-2691. [13] AMBROSINI R, AZZONI R S, PITTINO F, et al. First evidence of microplastic contamination in the supraglacial debris of an alpine glacier[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,253:297-301. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.005 [14] O'CONNOR D, PAN S Z, SHEN Z T, et al. Microplastics undergo accelerated vertical migration in sand soil due to small size and wet-dry cycles[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,249:527-534. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.092 [15] 朱莹, 曹淼, 罗景阳, 等. 微塑料的环境影响行为及其在我国的分布状况[J]. 环境科学研究,2019,32(9):1437-1447.ZHU Y, CAO M, LUO J Y, et al. Distribution and potential risks of microplastics in China: a review[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2019,32(9):1437-1447. [16] BHATT P, PATHAK V M, BAGHERI A R, et al. Microplastic contaminants in the aqueous environment, fate, toxicity consequences, and remediation strategies[J]. Environmental Research,2021,200:111762. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111762 [17] GATIDOU G, ARVANITI O S, STASINAKIS A S. Review on the occurrence and fate of microplastics in Sewage Treatment Plants[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2019,367:504-512. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.081 [18] CARR S A, LIU J, TESORO A G. Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants[J]. Water Research,2016,91:174-182. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.01.002 [19] BLÄSING M, AMELUNG W. Plastics in soil: analytical methods and possible sources[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,612:422-435. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.086 [20] LIU M T, LU S B, SONG Y, et al. Microplastic and mesoplastic pollution in farmland soils in suburbs of Shanghai, China[J]. Environmental Pollution,2018,242:855-862. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.051 [21] WU X L, LYU X Y, LI Z Y, et al. Transport of polystyrene nanoplastics in natural soils: effect of soil properties, ionic strength and cation type[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,707:136065. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136065 [22] TYMPA L E, KATSARA K, MOSCHOU P N, et al. Do microplastics enter our food chain via root vegetables: a Raman based spectroscopic study on Raphanus sativus[J]. Materials,2021,14(9):2329. doi: 10.3390/ma14092329 [23] HE P J, CHEN L Y, SHAO L M, et al. Municipal solid waste (MSW) landfill: a source of microplastics: evidence of microplastics in landfill leachate[J]. Water Research,2019,159:38-45. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.04.060 [24] WONG J K H, LEE K K, TANG K H D, et al. Microplastics in the freshwater and terrestrial environments: prevalence, fates, impacts and sustainable solutions[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,719:137512. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137512 [25] LUO Y Y, ZHANG Y Y, XU Y B, et al. Distribution characteristics and mechanism of microplastics mediated by soil physicochemical properties[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,726:138389. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138389 [26] LIU J, ZHANG T, TIAN L L, et al. Aging significantly affects mobility and contaminant-mobilizing ability of nanoplastics in saturated loamy sand[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2019,53(10):5805-5815. [27] 张佳佳, 陈延华, 王学霞, 等. 土壤环境中微塑料的研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文),2021,29(6):937-952.ZHANG J J, CHEN Y H, WANG X X, et al. A review of microplastics in the soil environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2021,29(6):937-952. [28] DONG Y M, GAO M L, QIU W W, et al. Uptake of microplastics by carrots in presence of As(Ⅲ): combined toxic effects[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,411:125055. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125055 [29] WANG Y, XIANG L L, WANG F, et al. Positively charged microplastics induce strong lettuce stress responses from physiological, transcriptomic, and metabolomic perspectives[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2022,56:16907-16918. [30] BOSKER T, BOUWMAN L J, BRUN N R, et al. Microplastics accumulate on pores in seed capsule and delay germination and root growth of the terrestrial vascular plant Lepidium sativum[J]. Chemosphere,2019,226:774-781. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.163 [31] YU Z F, SONG S, XU X L, et al. Sources, migration, accumulation and influence of microplastics in terrestrial plant communities[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany,2021,192:104635. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2021.104635 [32] LI Z X, LI Q F, LI R J, et al. The distribution and impact of polystyrene nanoplastics on cucumber plants[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2021,28(13):16042-16053. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-11702-2 [33] GUO J J, HUANG X P, XIANG L, et al. Source, migration and toxicology of microplastics in soil[J]. Environment International,2020,137:105263. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105263 [34] YU M, van der PLOEG M, LWANGA E H, et al. Leaching of microplastics by preferential flow in earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) burrows[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2019,16(1):31. doi: 10.1071/EN18161 [35] HUANG D F, XU Y B, YU X Q, et al. Effect of cadmium on the sorption of tylosin by polystyrene microplastics[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2021,207:111255. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111255 [36] de SOUZA MACHADO A A, LAU C W, KLOAS W, et al. Microplastics can change soil properties and affect plant performance[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2019,53(10):6044-6052. [37] LI H Z, ZHU D, LINDHARDT J H, et al. Long-term fertilization history alters effects of microplastics on soil properties, microbial communities, and functions in diverse farmland ecosystem[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2021,55(8):4658-4668. [38] WANG T, WANG L, CHEN Q Q, et al. Interactions between microplastics and organic pollutants: effects on toxicity, bioaccumulation, degradation, and transport[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,748:142427. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142427 [39] de SOUZA MACHADO A A, LAU C W, TILL J, et al. Impacts of microplastics on the soil biophysical environment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2018,52(17):9656-9665. [40] BOOTS B, RUSSELL C W, GREEN D S. Effects of microplastics in soil ecosystems: above and below ground[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2019,53(19):11496-11506. [41] ZHANG G S, ZHANG F X, LI X T. Effects of polyester microfibers on soil physical properties: perception from a field and a pot experiment[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,670:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.149 [42] HUANG Y, ZHAO Y R, WANG J, et al. LDPE microplastic films alter microbial community composition and enzymatic activities in soil[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,254:112983. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.112983 [43] ZHOU C Q, LU C H, MAI L, et al. Response of rice (Oryza sativa L. ) roots to nanoplastic treatment at seedling stage[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,401:123412. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123412 [44] ZHANG Q G, ZHAO M S, MENG F S, et al. Effect of polystyrene microplastics on rice seed germination and antioxidant enzyme activity[J]. Toxics,2021,9(8):179. doi: 10.3390/toxics9080179 [45] SUN X D, YUAN X Z, JIA Y B, et al. Differentially charged nanoplastics demonstrate distinct accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Nature Nanotechnology,2020,15:755-760. doi: 10.1038/s41565-020-0707-4 [46] GIORGETTI L, SPANÒ C, MUCCIFORA S, et al. Exploring the interaction between polystyrene nanoplastics and Allium cepa during germination: Internalization in root cells, induction of toxicity and oxidative stress[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2020,149:170-177. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.014 [47] JIANG X, CHEN H, LIAO Y, et al. Ecotoxicity and genotoxicity of polystyrene microplastics on higher plant Vicia faba[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,250:831-838. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.04.055 [48] LI L Z, ZHOU Q, YIN N, et al. Uptake and accumulation of microplastics in an edible plant[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2019,64(9):928-934. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00845 [49] LIAN J P, WU J N, XIONG H X, et al. Impact of polystyrene nanoplastics (PSNPs) on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L. )[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020,385:121620. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121620 [50] GONG W W, ZHANG W, JIANG M Y, et al. Species-dependent response of food crops to polystyrene nanoplastics and microplastics[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,796:148750. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148750 [51] WU J N, LIU W T, ZEB A, et al. Polystyrene microplastic interaction with Oryza sativa: toxicity and metabolic mechanism[J]. Environmental Science:Nano,2021,8(12):3699-3710. doi: 10.1039/D1EN00636C [52] LIU Y Y, GUO R, ZHANG S W, et al. Uptake and translocation of nano/microplastics by rice seedlings: evidence from a hydroponic experiment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2022,421:126700. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126700 [53] YUAN W K, ZHOU Y F, LIU X N, et al. New perspective on the nanoplastics disrupting the reproduction of an endangered fern in artificial freshwater[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2019,53(21):12715-12724. [54] SPANÒ C, MUCCIFORA S, RUFFINI CASTIGLIONE M, et al. Polystyrene nanoplastics affect seed germination, cell biology and physiology of rice seedlings in-short term treatments: evidence of their internalization and translocation[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2022,172:158-166. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.01.012 [55] LUO Y M, LI L Z, FENG Y D, et al. Quantitative tracing of uptake and transport of submicrometre plastics in crop plants using lanthanide chelates as a dual-functional tracer[J]. Nature Nanotechnology,2022,17:424-431. doi: 10.1038/s41565-021-01063-3 [56] ZHANG P P, WANG Y Q, ZHAO X Z, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering labeled nanoplastic models for reliable bio-nano interaction investigations[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2022,425:127959. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127959 [57] CHAE Y, AN Y J. Nanoplastic ingestion induces behavioral disorders in terrestrial snails: trophic transfer effects via vascular plants[J]. Environmental Science:Nano,2020,7(3):975-983. doi: 10.1039/C9EN01335K [58] KIM D, AN S, KIM L, et al. Translocation and chronic effects of microplastics on pea plants (Pisum sativum) in copper-contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2022,436:129194. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129194 [59] LI S X, WANG T Y, GU O J H, et al. Polystyrene microplastics disturb the redox homeostasis, carbohydrate metabolism and phytohormone regulatory network in barley[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,415:125614. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125614 [60] 骆永明, 周倩, 章海波, 等. 重视土壤中微塑料污染研究 防范生态与食物链风险[J]. 中国科学院院刊,2018,33(10):1021-1030.LUO Y M, ZHOU Q, ZHANG H B, et al. Pay attention to research on microplastic pollution in soil for prevention of ecological and food chain risks[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2018,33(10):1021-1030. [61] ZHOU Q, TIAN C G, LUO Y M. Various forms and deposition fluxes of microplastics identified in the coastal urban atmosphere[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2017,62(33):3902-3909. doi: 10.1360/N972017-00956 [62] LIU R, LIANG J W, YANG Y H, et al. Effect of polylactic acid microplastics on soil properties, soil microbials and plant growth[J]. Chemosphere,2023,329:138504. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138504 [63] PIGNATTELLI S, BROCCOLI A, RENZI M. Physiological responses of garden cress (L. sativum) to different types of microplastics[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,727:138609. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138609 [64] BI M H, HE Q, CHEN Y. What roles are terrestrial plants playing in global microplastic cycling[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2020,54(9):5325-5327. [65] HOLMES L A, TURNER A, THOMPSON R C. Interactions between trace metals and plastic production pellets under estuarine conditions[J]. Marine Chemistry,2014,167:25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.06.001 [66] WANG F Y, ZHANG X Q, ZHANG S Q, et al. Interactions of microplastics and cadmium on plant growth and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in an agricultural soil[J]. Chemosphere,2020,254:126791. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126791 [67] LAHIVE E, CROSS R, SAARLOOS A I, et al. Earthworms ingest microplastic fibres and nanoplastics with effects on egestion rate and long-term retention[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2022,807:151022. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151022 [68] LI B, SONG W H, CHENG Y L, et al. Ecotoxicological effects of different size ranges of industrial-grade polyethylene and polypropylene microplastics on earthworms Eisenia fetida[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,783:147007. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147007 [69] WANG H T, DING J, XIONG C, et al. Exposure to microplastics lowers arsenic accumulation and alters gut bacterial communities of earthworm Metaphire californica[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,251:110-116. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.04.054 [70] FEI Y F, HUANG S Y, ZHANG H B, et al. Response of soil enzyme activities and bacterial communities to the accumulation of microplastics in an acid cropped soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,707:135634. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135634 [71] JUDY J D, KIRBY J K, CREAMER C, et al. Effects of silver sulfide nanomaterials on mycorrhizal colonization of tomato plants and soil microbial communities in biosolid-amended soil[J]. Environmental Pollution,2015,206:256-263. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.07.002 [72] NDAHEBWA MUHONJA C, MAGOMA G, IMBUGA M, et al. Molecular characterization of low-density polyethene (LDPE) degrading bacteria and fungi from dandora dumpsite, Nairobi, Kenya[J]. International Journal of Microbiology,2018:4167845. [73] VIMALA P P, MATHEW L. Biodegradation of polyethylene using Bacillus subtilis[J]. Procedia Technology,2016,24:232-239. doi: 10.1016/j.protcy.2016.05.031 [74] YADAV V, DHANGER S, SHARMA J. Microplastics accumulation in agricultural soil: evidence for the presence, potential effects, extraction, and current bioremediation approaches[J]. Journal of Applied Biology & Biotechnology, 2022: 38-47. [75] HAN X, LIU W D, HUANG J W, et al. Structural insight into catalytic mechanism of PET hydrolase[J]. Nature Communications,2017,8:2106. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02255-z [76] WANG J, SUN C, HUANG Q X, et al. Adsorption and thermal degradation of microplastics from aqueous solutions by Mg/Zn modified magnetic biochars[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,419:126486. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126486 [77] LI J, YU Y F, CHEN X H, et al. Effects of biochar on the phytotoxicity of polyvinyl chloride microplastics[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2023,195:228-237. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.01.022 [78] HAN L F, CHEN L Y, LI D T, et al. Influence of polyethylene terephthalate microplastic and biochar co-existence on paddy soil bacterial community structure and greenhouse gas emission[J]. Environmental Pollution,2022,292:118386. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118386 [79] 陈斐杰, 夏会娟, 刘福德, 等. 生物质炭特性及其对土壤性质的影响与作用机制[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(1):161-172. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210067CHEN F J, XIA H J, LIU F D, et al. Characteristics of biochar and its effects and mechanism on soil properties[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(1):161-172. □ doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210067 -




 下载:
下载: