Water ecological health assessment based on the biological integrity of macroinvertebrate: a case from Liaohe River Basin
-
摘要:
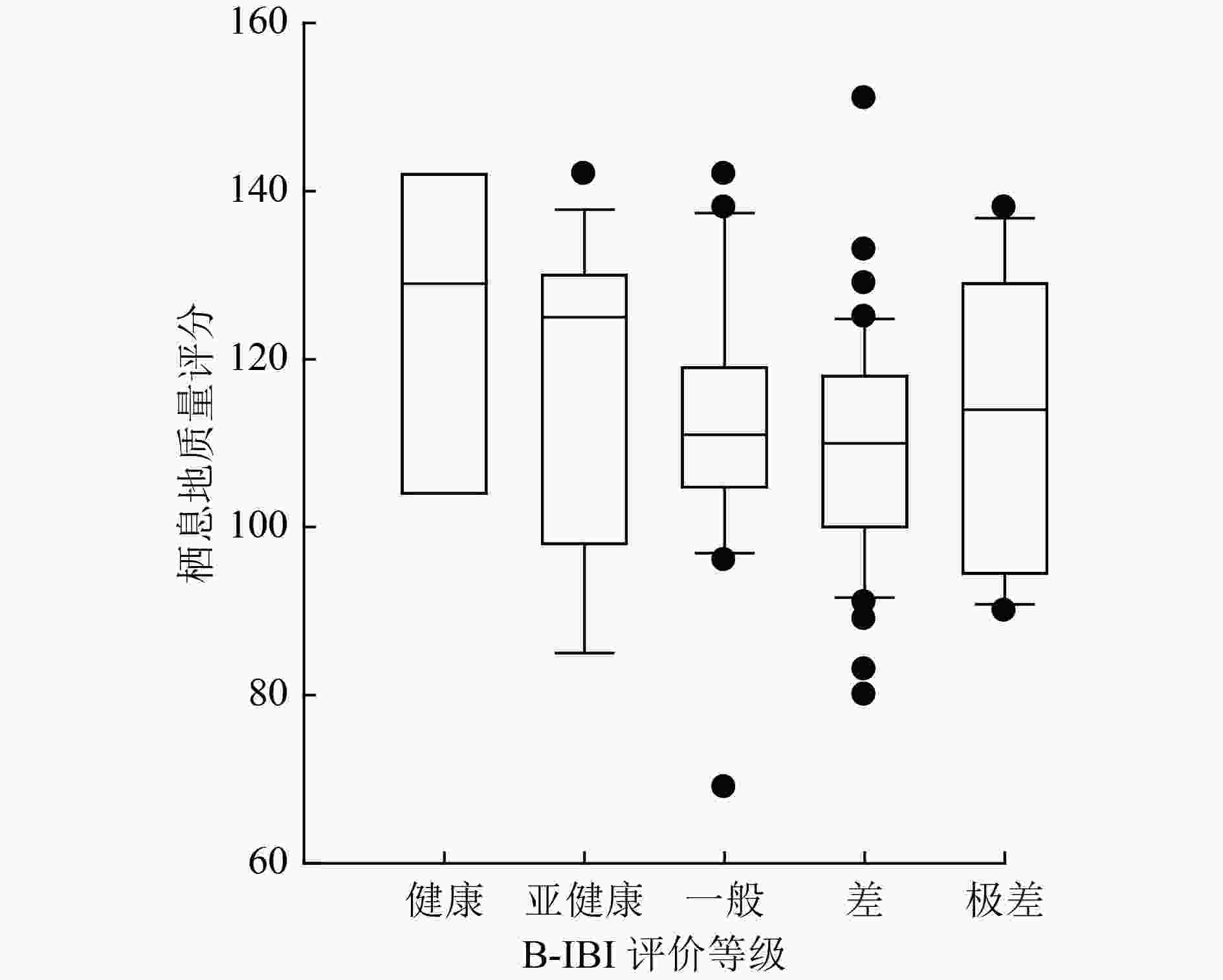
大型底栖动物完整性指数(B-IBI)在国际水生态健康评价中应用广泛,但需要结合各流域生态环境特征分别构建。以辽河流域为例,以流域99个点位水生态调查数据为基础,综合运用水质和生境质量作为参照点与受损点筛选标准,通过分布范围检验、判别能力检验和冗余性检验获得B-IBI核心参数,利用比值法进行核心参数标准化,等权求和计算B-IBI得分,最终构建适用于辽河流域的B-IBI评价体系。结果表明:辽河流域大型底栖动物包含74个分类单元,以昆虫纲为主(占总分类单元数的81.1%),个体数量最优势物种为缺尾高原纹石蛾(Hydropsyche kozhantschikovi);经筛选获得5个参照点和6个受损点,从28个备选参数中筛选出总分类单元数、毛翅目分类单元数、端足目+软体动物分类单元数、直接收集者相对丰度、黏附者分类单元数、Pielou均匀度指数6个核心参数用于计算B-IBI;B-IBI评价发现,调查时段的数据集中,4个点位处于健康等级,15个点位为亚健康等级,25个点位为一般等级,41个点位为差等级,14个点位为极差等级,流域水生态健康整体水平较差,超过1/2河段存在大型底栖动物群落结构退化现象。检验分析发现,B-IBI对水质变化具有较好的指示作用,且能有效区分出受损河段,表明B-IBI评价体系能准确表征辽河流域水生态健康状况,建议今后管理中作为辽河流域生物评价工具。
-
关键词:
- 辽河流域 /
- 大型底栖动物 /
- 水生态健康 /
- 生物完整性 /
- 底栖动物完整性指数(B-IBI)
Abstract:The benthic index of biological integrity (B-IBI) is widely used for river ecological health assessment all over the world. However, this index should be constructed separately according to the ecological environmental characteristics of each river basin. In this study, the Liaohe River Basin was taken as an example, the data of macroinvertebrates of 99 sites in Liaohe River Basin was used to calculate to B-IBI. Water quality and habitat quality were comprehensively used as the selection criteria for reference sites and impacted sites. The distribution range test, discriminant ability test and redundancy test were used to screen the core metrics of B-IBI. The ratio method was used to standardize the core metrics and add up to calculate B-IBI. The results showed that a total of 74 taxa of macroinvertebrates were found, and the dominant taxon was Insecta (accounting for 81.1% of the total taxa). The most dominant species was Hydropsyche kozhantschikovi. Five reference sites and six impacted sites were obtained after screening. Six core metrics including the number of total taxa, the taxa number of Trichoptera, the taxa number of Amphipoda and Mollusca, the relative abundance of direct collectors, the number of adherent taxa, and the Pielou evenness index, were selected from 28 candidate metrics. The evaluation results of B-IBI showed that 4 sites were in health grade, 15 sites in sub-health grade, 25 sites in normal grade, 41 sites in poor grade, 14 sites in bad grade, and the whole health level of Liaohe River Basin was poor in the survey period. The macroinvertebrate community was impacted in more than half of the sampling sites. B-IBI showed a good indicating ability for the change of water quality in Liaohe River Basin, and effectively distinguish damaged sections of the river. It was suggested that B-IBI could be used as a bioassessment tool for the river basin management in future.
-
表 1 辽河流域B-IBI 候选参数体系及其对干扰的响应
Table 1. Candidate metrics system of B-IBI in Liaohe River Basin and their response to disturbance
所属类别 参数名称 参数单位 对干扰的响应 种类组成 总分类单元数(A1) 个 下降 EPT1)分类单元数(A2) 个 下降 襀翅目分类单元数(A3) 个 下降 蜉蝣目分类单元数(A4) 个 下降 毛翅目分类单元数(A5) 个 下降 端足目+软体动物分类
单元数(A6)个 下降 个体丰度 襀翅目相对丰度(A7) % 下降 蜉蝣目相对丰度(A8) % 下降 毛翅目相对丰度(A9) % 下降 EPT相对丰度(A10) % 下降 摇蚊科相对丰度(A11) % 上升 双翅目相对丰度(A12) % 上升 (端足目+软体动物)相对
丰度(A13)% 上升 寡毛类相对丰度(A14) % 上升 优势类群 最优势类群相对丰度(A15) % 上升 敏感/耐污
类群敏感类群分类单元数(A16) 个 下降 耐污类群分类单元数(A17) 个 上升 功能摄食类群 滤食者相对丰度(A18) % 上升 刮食者相对丰度(A19) % 下降 直接收集者相对丰度(A20) % 上升 捕食者相对丰度(A21) % 下降 撕食者相对丰度(A22) % 下降 生态型 黏附者相对丰度(A23) % 下降 黏附者分类单元数(A24) 个 下降 多样性水平 Shannon-Wiener多样性
指数(A25)下降 Margalef丰富度指数(A26) 下降 Pielou均匀度指数(A27) 下降 Simpson多样性指数(A28) 下降 1) E表示蜉蝣目(Ephemeroptera);P表示襀翅目(Plecoptera);T表示毛翅目(Trichoptera)。 表 2 候选参数的相关性分析
Table 2. Correlation analysis of candidate metrics
参数 A1 A2 A4 A5 A6 A15 A20 A24 A25 A26 A27 A28 A1 1.000 A2 0.801** 1.000 A4 0.753** 0.944** 1.000 A5 0.525** 0.645** 0.357** 1.000 A6 0.499** 0.161 0.152 0.104 1.000 A15 −0.543** −0.533** −0.546** −0.244* −0.151 1.000 A20 −0.154 −0.092 0.041 −0.356** 0.045 0.126 1.000 A24 0.283** 0.382** 0.198* 0.623** 0.033 −0.004 −0.337** 1.000 A25 0.751** 0.688** 0.689** 0.353** 0.273** −0.925** −0.123 0.049 1.000 A26 0.924** 0.775** 0.756** 0.444** 0.434** −0.692** −0.122 0.109 0.883** 1.000 A27 0.290** 0.341** 0.363** 0.125 0.017 −0.881** −0.076 −0.093 0.801** 0.518** 1.000 A28 0.584** 0.546** 0.547** 0.279** 0.186 −0.970** −0.15 0.028 0.944** 0.740** 0.917** 1.000 注:**表示在0.01水平(双侧)显著相关;*表示在0.05水平(双侧)显著相关。 表 3 核心参数的标准化公式
Table 3. Standardized formula of core metrics
核心参数 标准化公式 A1 A1/21 A5 A5/3 A6 A6/4 A20 (1-A20)/(1-0.08) A24 A24/279 A27 A27/0.91 表 4 辽河流域B-IBI评价标准
Table 4. Criteria for B-IBI in Liaohe River Basin
健康 亚健康 一般 差 极差 ≥4.71 3.61~4.71 2.50~3.61 1.40~2.50 <1.40 表 5 Mann-Whitney U检验的秩和值(Z值)
Table 5. Rank sum (Z value ) of Mann-Whitney U test
水质类别 Ⅱ类 Ⅲ类 Ⅳ类 Ⅴ类 劣Ⅴ类 Ⅱ类 −1.805 −3.157 −2.772 −2.286 Ⅲ类 0.071* −2.628 −2.028 −1.260 Ⅳ类 0.002* 0.009* −0.111 −0.819 Ⅴ类 0.006* 0.043* 0.912 −0.703 劣Ⅴ类 0.022* 0.208 0.413 0.482 注:*表示P<0.05。 -
[1] KOLKWITZ R, MARSSON M. Ökologie der tierischen saprobien. beiträge zur lehre von der biologischen gewässerbeurteilung[J]. Internationale Revue der Gesamten Hydrobiologie und Hydrographie,1909,2(1/2):126-152. [2] BIRK S, BONNE W, BORJA A, et al. Three hundred ways to assess Europe’s surface waters: an almost complete overview of biological methods to implement the Water Framework Directive[J]. Ecological Indicators,2012,18:31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.10.009 [3] KARR J R. Assessment of biotic integrity using fish communities[J]. Fisheries,1981,6(6):21-27. doi: 10.1577/1548-8446(1981)006<0021:AOBIUF>2.0.CO;2 [4] RUARO R, GUBIANI É A. A scientometric assessment of 30 years of the Index of Biotic Integrity in aquatic ecosystems: applications and main flaws[J]. Ecological Indicators,2013,29:105-110. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.12.016 [5] 董婧, 卢少奇, 伍娟丽, 等.基于微生物生物完整性指数的北京市城市河道生态系统健康评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(5):1411-1419. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210368DONG J, LU S Q, WU J L, et al. Evaluation of urban river ecosystem health in Beijing based on the microbial index of biotic integrity[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(5):1411-1419. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210368 [6] HERING D, FELD C K, MOOG O, et al. Cook book for the development of a Multimetric Index for biological condition of aquatic ecosystems: experiences from the European AQEM and STAR projects and related initiatives[J]. Hydrobiologia,2006,566(1):311-324. doi: 10.1007/s10750-006-0087-2 [7] MOYA N, HUGHES R M, DOMÍNGUEZ E, et al. Macroinvertebrate-based multimetric predictive models for evaluating the human impact on biotic condition of Bolivian streams[J]. Ecological Indicators,2011,11(3):840-847. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2010.10.012 [8] 袁哲, 许秋瑾, 宋永会, 等.辽宁省辽河流域水生态完整性恢复的实践与启示[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(1):48-55. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200113YUAN Z, XU Q J, SONG Y H, et al. Practice and enlightenment of water ecological integrity restoration in Liaohe River Basin of Liaoning Province[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(1):48-55. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200113 [9] 王备新, 杨莲芳, 刘正文.生物完整性指数与水生态系统健康评价[J]. 生态学杂志,2006,25(6):707-710. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2006.06.023WANG B X, YANG L F, LIU Z W. Index of biological integrity and its application in health assessment of aquatic ecosystem[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2006,25(6):707-710. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2006.06.023 [10] LU K L, WU H T, XUE Z S, et al. Development of a multi-metric index based on aquatic invertebrates to assess floodplain wetland condition[J]. Hydrobiologia,2019,827(1):141-153. doi: 10.1007/s10750-018-3761-2 [11] MORSE J C, BAE Y J, MUNKHJARGAL G, et al. Freshwater biomonitoring with macroinvertebrates in East Asia[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment,2007,5(1):33-42. doi: 10.1890/1540-9295(2007)5[33:FBWMIE]2.0.CO;2 [12] 王硕, 张建云, 林育青, 等.基于大型底栖动物多度量指数的河流多尺度评价[J]. 环境科学研究,2019,32(2):284-292.WANG S, ZHANG J Y, LIN Y Q, et al. Multi-scale evaluation of river based on the macroinvertebrates multi-metric index[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2019,32(2):284-292. [13] 欧阳莉莉, 韩迁, 何鑫, 等.岷江成都段水生态健康评价研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(7):1654-1662.OUYANG L L, HAN Q, HE X, et al. Health assessment of Min River in Chengdu section[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(7):1654-1662. [14] 吴家乐, 甘磊, 刘素霞, 等.修复对湖北洋澜湖富营养化与生态状况的影响: 基于大型无脊椎底栖动物的评价[J]. 湖泊科学,2019,31(6):1547-1558. doi: 10.18307/2019.0616WU J L, GAN L, LIU S X, et al. Effect of restoration on the eutrophication and ecological status of Lake Yanglan (Hubei Province): assessment based on macroinvertebrates[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2019,31(6):1547-1558. doi: 10.18307/2019.0616 [15] MPCA. Development of a macroinvertebrate-based index of biological integrity for assessment of Minnesota’s rivers and streams[R]. St. Paul: Minnesota Pollution Control Agency, Environmental Analysis and Outcomes Division, 2014. [16] 张宇航, 渠晓东, 王少明, 等.浑河流域底栖动物生物完整性指数构建与健康评价[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2020,29(6):1374-1386.ZHANG Y H, QU X D, WANG S M, et al. River health assessment of Hun River Basin based on benthic index of biological integrity[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin,2020,29(6):1374-1386. [17] 周莹, 渠晓东, 赵瑞, 等.河流健康评价中不同标准化方法的应用与比较[J]. 环境科学研究,2013,26(4):410-417.ZHOU Y, QU X D, ZHAO R, et al. Standardized methods for selecting reference and impaired sites to evaluate river health[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2013,26(4):410-417. [18] 渠晓东, 刘志刚, 张远.标准化方法筛选参照点构建大型底栖动物生物完整性指数[J]. 生态学报,2012,32(15):4661-4672. doi: 10.5846/stxb201107181065QU X D, LIU Z G, ZHANG Y. Discussion on the standardized method of reference sites selection for establishing the Benthic-Index of Biotic Integrity[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2012,32(15):4661-4672. doi: 10.5846/stxb201107181065 [19] 孔维静, 张远, 侯利萍, 等. 辽河流域水生态功能区[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018. [20] 刘志刚, 渠晓东, 张远, 等.浑河主要污染物对大型底栖动物空间分布的影响[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2012,2(2):116-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2012.02.018LIU Z G, QU X D, ZHANG Y, et al. Effects of main contaminations on the spatial distribution of macroinvertebrates in the Hun River[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2012,2(2):116-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2012.02.018 [21] 郑丙辉, 张远, 李英博.辽河流域河流栖息地评价指标与评价方法研究[J]. 环境科学学报,2007,27(6):928-936.ZHENG B H, ZHANG Y, LI Y B. Study of indicators and methods for river habitat assessment of Liao River Basin[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2007,27(6):928-936. [22] 慕林青, 张海萍, 赵树旗, 等.永定河底栖动物生物完整性指数构建与健康评价[J]. 环境科学研究,2018,31(4):697-707.MU L Q, ZHANG H P, ZHAO S Q, et al. River health assessment of Yongding River based on benthic integrated biotic index[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2018,31(4):697-707. [23] RUARO R, GUBIANI É A, HUGHES R M, et al. Global trends and challenges in multimetric indices of biological condition[J]. Ecological Indicators,2020,110:105862. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105862 [24] 曹家乐, 张亚辉, 张瑾, 等.国内外水生态健康评价研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(5):1402-1410.CAO J L, ZHANG Y H, ZHANG J, et al. Research progress of water ecological health assessment at home and abroad[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(5):1402-1410. [25] 熊梅君, 李秋华, 陈倩, 等.基于GIS应用P-IBI评价贵州高原百花水库水生态系统健康[J]. 生态学杂志,2019,38(10):3093-3101.XIONG M J, LI Q H, CHEN Q, et al. Evaluation of water ecosystem health of Baihua Reservoir in Guizhou based on GIS and P-IBI[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2019,38(10):3093-3101. [26] 陈凯, 于海燕, 张汲伟, 等.基于底栖动物预测模型构建生物完整性指数评价河流健康[J]. 应用生态学报,2017,28(6):1993-2002. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201706.015CHEN K, YU H Y, ZHANG J W, et al. Predictive model based multimetric index of macroinvertebrates for river health assessment[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2017,28(6):1993-2002. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201706.015 [27] 刘帅磊, 王赛, 崔永德, 等.亚热带城市河流底栖动物完整性评价: 以流溪河为例[J]. 生态学报,2018,38(1):342-357.LIU S L, WANG S, CUI Y D, et al. Ecological assessment of a subtropical urban river based on the Benthic-Index of Biotic Integrity: Liuxi River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018,38(1):342-357. [28] 姜永伟, 卢雁, 问青春, 等.基于大型底栖动物完整性指数的辽河流域水生态健康评价[J]. 环境保护科学,2020,46(6):103-109.JIANG Y W, LU Y, WEN Q C, et al. Water ecological health assessment of Liaohe River Basin based on the integrity index of benthic macroinvertebrates[J]. Environmental Protection Science,2020,46(6):103-109. [29] 陈影. 辽河保护区河岸带自然生境恢复现状评价[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳大学, 2021. -





 下载:
下载: