Study on the seasonal succession of phytoplankton functional groups in Eryuan West Lake of Dali City, Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
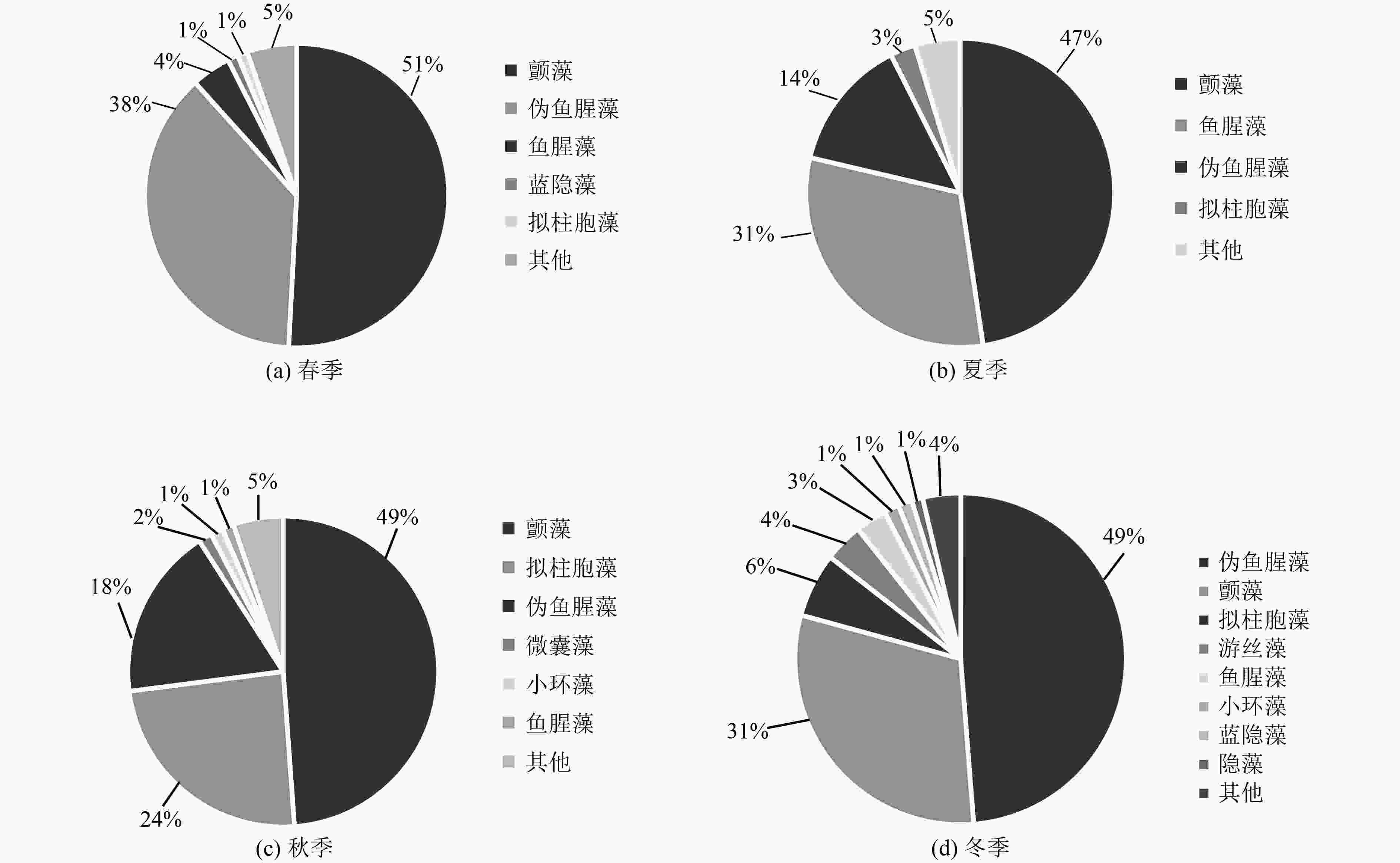
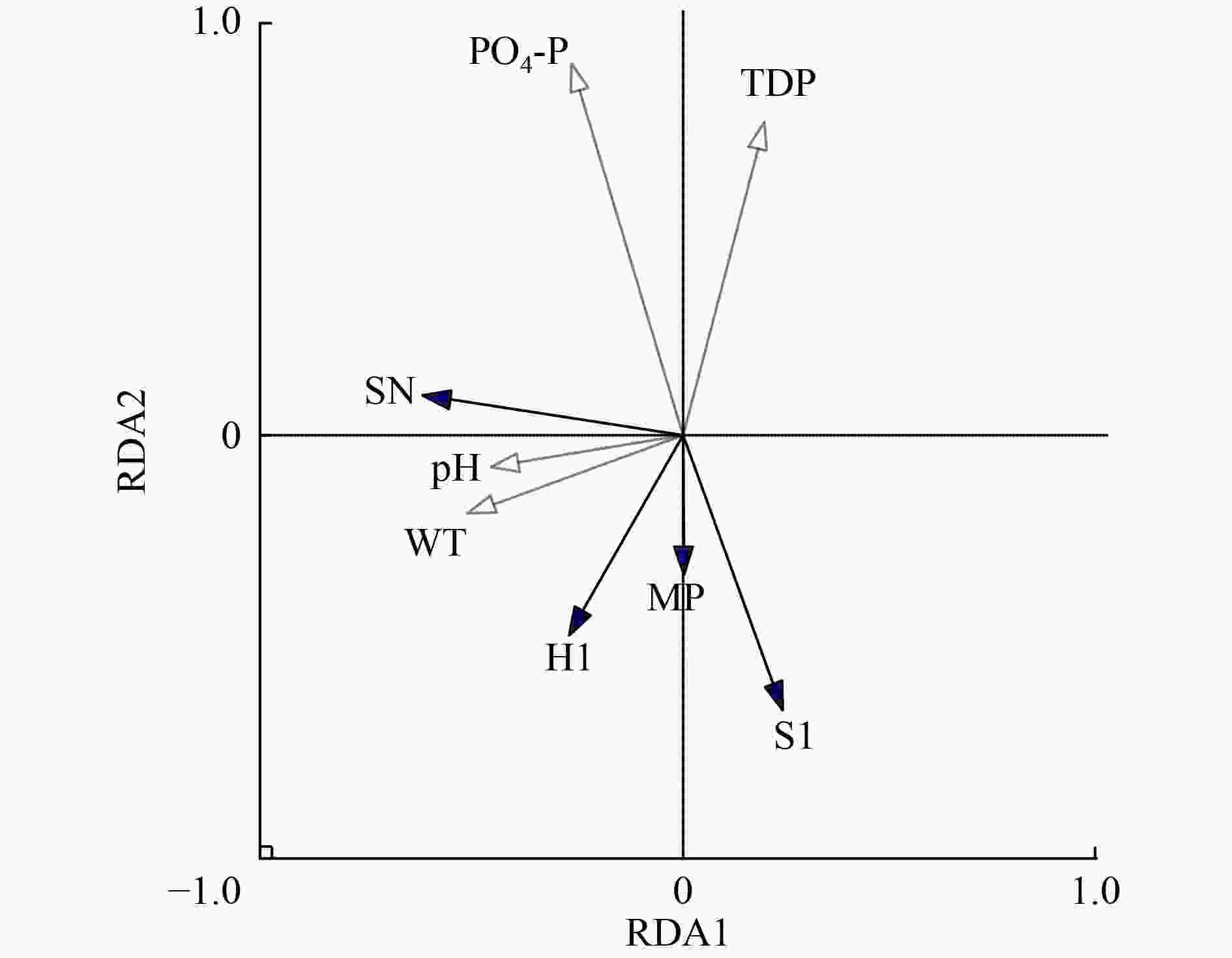
为探讨云南大理洱源西湖浮游植物功能群特征及其与环境因子的关系,于2019年9月—2020年8月每月采集浮游植物样品及水环境指标,采用修正的卡尔森营养状态指数和浮游植物功能群分类法评价洱源西湖水体富营养化程度及探讨浮游植物的季节演替特征。结果表明:洱源西湖为低透明度且浊水状态的富营养化水体;研究期间共镜检鉴定出浮游植物7门72属,划分为23个浮游植物功能群,其中MP〔颤藻(Oscillatoria sp.)〕、S1〔伪鱼腥藻(Anabaenopsis sp.)〕、H1〔鱼腥藻(Dolichospermum sp.)〕和SN〔拟柱胞藻(Cylindrospermopsis sp.)〕为优势功能群,其均为蓝藻门的丝状藻类;秋季浮游植物主要以颤藻、拟柱胞藻为主,冬季和春季主要以伪鱼腥藻和颤藻为主,而夏季主要以颤藻和鱼腥藻为主;冗余分析结果显示,洱源西湖浮游植物功能群演替的关键环境因子为水温、pH、正磷酸盐浓度与可溶性总磷浓度,尤其是可溶解性磷(主要为 PO4 3−-P)浓度变化促成了优势功能群的季节演替。洱源西湖的富营养化状态为丝状蓝藻占优势且藻类结构单一。
Abstract:To investigate the characteristics of the phytoplankton functional group and its relationship with environmental factors in the West Lake of Eryuan County, Dali City, Yunnan Province, phytoplankton samples and water environment factors were collected monthly from September 2019 to August 2020. The modified Carlson trophic state index and the phytoplankton functional group (FG) classification were used to evaluate the degree of eutrophication in the water column of the lake and to explore the seasonal succession characteristics of phytoplankton. The preliminary results showed that: 1) Eryuan West Lake was eutrophic water with low transparency and turbidity. 2) Seven phyla and 72 genera of phytoplankton were identified by microscopic examination during the study, which were divided into 23 phytoplankton functional groups. MP (Oscillatoria sp.), S1 (Anabaenopsis sp.), H1 (Dolichospermum sp.) and SN (Cylindrospermopsis sp.) were the four dominant functional groups, all of which were filamentous algae of cyanobacterial phylum. Phytoplankton in autumn was mainly dominated by Oscillatoria sp. and Cylindrospermopsis sp., while it was mainly composed of Anabaenopsis sp. and Oscillatoria sp. in winter and spring, and mainly Oscillatoria sp. and Dolichospermum sp. in summer. 3) The results of Redundancy analysis showed that the key environmental factors for phytoplankton functional group succession in Eryuan West Lake were water temperature, pH, PO4 3−-P and TDP, especially the change of soluble phosphorus concentration contributed to the seasonal succession of the dominant functional group. Therefore, filamentous cyanobacteria were dominant in the eutrophication state of Eryuan West Lake, with a homogeneous algal structure.
-
Key words:
- Eryuan West Lake /
- phytoplankton functional group /
- succession /
- environmental factors
-
表 1 洱源西湖环境因子季节变化
Table 1. Seasonal variation of environmental factors in Eryuan West Lake
季节 氮浓度//(mg/L) 磷浓度/(mg/L) Chla浓度/
(µg/L)水温/℃ DO浓度/
(mg/L)pH SD/m TN/TP TSIM TN TDN NO3 −-N NH4 +-N TP TDP PO4 3−-P 春季 1.17±
0.15a0.61±
0.16a0.089±
0.006a0.013±
0.008b0.080±
0.002ab0.017±
0.004a0.003±
0.001a32.6±
1.6b17.2±
1.6c6.3±
0.6a8.20±
0.10a0.83±
0.05a14.91±
1.45ab62.2±
0.2b夏季 1.30±
0.09a0.69±
0.09a0.094±
0.025a0.065±
0.023a0.089±
0.007ab0.019±
0.006a0.005±
0.001a41.6±
18.7ab22.6±
1.7a5.9±
0.5b8.19±
0.04a0.82±
0.20a15.36±
1.96ab63.7±
3.0ab秋季 1.20±
0.29a0.62±
0.16a0.057±
0.017b0.022±
0.001b0.118±
0.044 5a0.033±
0.028a0.013±
0.012a54.3±
9.5a19.0±
2.7b5.9±
2.4b8.33±
0.28a0.80±
0.02a11.18±
3.86b66.0±
2.5a冬季 1.22±
0.15a0.71±
0.07a0.107±
0.015a0.037±
0.011a0.070±
0.003b0.032±
0.016a0.004±
0.000a41.7±
7.8ab11.4±
0.8d7.8±
1.3a8.76±
0.66a0.79±
0.10a17.54±
1.50a62.6±
1.4ab注:数据结果为平均值±标准差;不同小写字母表示差异显著。 表 2 洱源西湖浮游植物功能群划分
Table 2. Phytoplankton functional groups division in Eryuan West Lake
FG分类 代表属(种) 所属
门类指示生境特征 B 小环藻(Cyclotella sp.) 硅藻门 中营养型的小中型水体,对硅缺乏和
分层敏感C 星杆藻(Asterionella sp.) 硅藻门 富营养型的小中型湖泊,无分层现象 D 针杆藻(Synedra sp.) 硅藻门 河流在内的浑浊水体 E 锥囊藻(Dinobryon sp.) 金藻门 小型浅水寡营养湖泊 F 蹄形藻(Kirchneriella sp.)
月牙藻(Selenastrum sp.)
卵囊藻(Oocystis sp.)绿藻门 中营养或富营养型,清澈的深水湖泊 G 实球藻(Pandorina sp.)
空球藻(Eudorina sp.)绿藻门 富营养型小型湖泊 H1 鱼腥藻(Dolichospermum sp.) 蓝藻门 小型富营养湖泊,分层的低氮水体 J 栅藻(Scendesmus sp.)
四角藻(Tetraedron)
盘星藻(Pediastrum sp.)绿藻门 混合的高营养型
浅水水体Lo 多甲藻(Peridinium sp.)
角甲藻(Ceratium sp.)甲藻门 寡营养至富
营养湖泊平裂藻(Merismopedia sp.)
色球藻(Chroococcus sp.)蓝藻门 M 微囊藻(Microcystis sp.) 蓝藻门 富或高富营养的
小中型水体MP 颤藻(Oscillatoria sp.) 蓝藻门 经常性搅动的、浑浊的淡水湖泊 舟形藻(Navicula sp.) 硅藻门 窗纹藻(Epithemia sp.) N 鼓藻(Cosmarium sp.) 绿藻门 栖息在2~3 m的连续或半连续的混合层中 NA 叉星鼓藻(Staurastrums sp.) 绿藻门 低纬度地区的静水、贫至中营养水体 P 新月藻(Closterium sp.) 绿藻门 混合程度较高的中富营养浅水水体 脆杆藻(Fragilaria sp.) 硅藻门 直链藻Melosira sp.) S1 伪鱼腥藻(Anabaenopsis sp.) 蓝藻门 对光照、冲刷敏感,适合生活于暗环境中 SN 拟柱胞藻(Cylindrospermopsis sp.) 蓝藻门 温暖的混合水体 T 转板藻(Mougeotia sp.)
并联藻(Quadrigula sp. )绿藻门 持续混合层,光限制水体 W1 裸藻(Euglena sp. )
扁裸藻(Phacus sp. )裸藻门 有机质丰富的
小型水体W2 囊裸藻(Trachelomonas sp. ) 裸藻门 中或富营养型水体 X1 小球藻(Chlorella sp. )
纤维藻(Ankistrodesmus sp. )
拟新月藻(Closteriopsis sp. )绿藻门 富至高富营养型水体 X2 衣藻(Chlamydomonas sp. ) 绿藻门 中度至高度富
营养型水体蓝隐藻Chroomonas sp. ) 隐藻门 X3 弓形藻(Schroederia sp. ) 绿藻门 混合的、寡营养
浅水水体Y 隐藻(Cryptomonas sp. ) 隐藻门 牧食强度低的
静水水体薄甲藻(Glenodinium sp. ) 甲藻门 表 3 浮游植物优势功能群与环境因子的RDA统计参数
Table 3. Statistical parameters of RDA analysis between phytoplankton dominant functional groups and environmental variables
轴 特征值 物种累计
占比/%物种与环境
相关系数物种与环境相关性的
累计占比/%轴1 0.257 4 25.74 0.692 6 66.36 轴2 0.120 1 37.75 0.616 9 97.30 轴3 0.009 7 38.71 0.282 4 99.78 轴4 0.000 8 38.80 0.177 4 100 -
[1] PADISÁK J, BORICS G, GRIGORSZKY I, et al. Use of phytoplankton assemblages for monitoring ecological status of lakes within the water framework directive: the assemblage index[J]. Hydrobiologia,2006,553(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s10750-005-1393-9 [2] 杨毓鑫, 杜春艳, 钱湛, 等.洞庭湖区南汉垸水体浮游植物群落结构特征及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(1):147-154.YANG Y X, DU C Y, QIAN Z, et al. Phytoplankton community structure and its influencing factors in Nanhan polder area of Dongting Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(1):147-154. [3] HUISMAN J, MATTHIJS H C P, VISSER P M. Harmful Cyanobacteria[M]. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2005. [4] REYNOLDS C S, HUSZAR V, KRUK C, et al. Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton[J]. Journal of Plankton Research,2002,24(5):417-428. doi: 10.1093/plankt/24.5.417 [5] 董静, 李艳晖, 李根保, 等.东江水系浮游植物功能群季节动态特征及影响因子[J]. 水生生物学报,2013,37(5):836-843.DONG J, LI Y H, LI G B, et al. Seasonal dynamics characteristics and affecting physical factors of phytoplankton functional groups in Dongjiang River[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,2013,37(5):836-843. [6] REYNOLDS C S. Phytoplankton assemblages and their periodicity in stratifying lake systems[J]. Ecography,1980,3(3):141-159. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0587.1980.tb00721.x [7] PADISÁK J, CROSSETTI L O, NASELLI-FLORES L. Use and misuse in the application of the phytoplankton functional classification: a critical review with updates[J]. Hydrobiologia,2009,621(1):1-19. doi: 10.1007/s10750-008-9645-0 [8] BECKER V, HUSZAR V L M, CROSSETTI L O. Responses of phytoplankton functional groups to the mixing regime in a deep subtropical reservoir[J]. Hydrobiologia,2009,628(1):137-151. doi: 10.1007/s10750-009-9751-7 [9] 安睿, 王凤友, 于洪贤, 等.小兴凯湖浮游植物功能群特征及其影响因子[J]. 环境科学研究,2016,29(7):985-994.AN R, WANG F Y, YU H X, et al. Characteristics and physical factors of phytoplankton functional groups in small Xingkai Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2016,29(7):985-994. [10] 陈倩. 贵州高原水库浮游植物对金属的富集与水体富营养化关系研究[D]. 贵阳:贵州师范大学, 2019. [11] 张俊芳, 胡晓红, 马沛明, 等.汤浦水库浮游植物功能群季节演替及关键驱动因子[J]. 水生态学杂志,2021,42(3):55-62.ZHANG J F, HU X H, MA P M, et al. Seasonal succession of phytoplankton functional groups and key driving factors in Tangpu Reservoir[J]. Journal of Hydroecology,2021,42(3):55-62. [12] 田永强, 俞超超, 王磊, 等.福建九龙江北溪浮游植物群落分布特征及其影响因子[J]. 应用生态学报,2012,23(9):2559-2565.TIAN Y Q, YU C C, WANG L, et al. Dynamic changes of phytoplankton’s community structure in Beixi of Jiulongjiang River, Fujian Province of East China and related affecting factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2012,23(9):2559-2565. [13] CAO J, HOU Z Y, LI Z K, et al. Succession of phytoplankton functional groups and their driving factors in a subtropical plateau lake[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,631/632:1127-1137. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.026 [14] 马巍, 苏建广, 杨洋, 等.洱海水质演变特征及主要影响因子分析[J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报,2022,20(2):112-119.MA W, SU J G, YANG Y, et al. Study on the evolution characteristics of water quality and its key impact factors of Erhai Lake[J]. Journal of China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research,2022,20(2):112-119. [15] 刘毅. 洱海浮游植物群落演替驱动因子分析及其微囊藻水华的生态风险评估[D]. 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2019. [16] 杨朝辉, 杨彪.洱源西湖湿地保护恢复措施的探讨[J]. 绿色科技,2020(16):162-165.YANG Z H, YANG B. Discussion on conservation and restoration measures of Xihu wetland in Eryuan County[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology,2020(16):162-165. [17] 孔德平, 杨发昌, 范亦农, 等.大理洱源西湖村水污染负荷分析及对策措施[J]. 环境科学与技术,2012,35(增刊 2):86-90.KONG D P, YANG F C, FAN Y N, et al. Water pollution load in the Xihu Village, Eryuan County, Dali, Yunnan with countermeasures of eutrophication control[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2012,35(Suppl 2):86-90. [18] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M].4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002: 88-284. [19] 章宗涉,黄祥飞. 淡水浮游生物研究方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1991. [20] 胡鸿钧, 魏印心. 中国淡水藻类: 系统、分类及生态[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006. [21] 黄国佳, 李秋华, 陈椽, 等.贵州高原红枫湖水库浮游植物功能分组及其时空分布特征[J]. 生态学报,2015,35(17):5573-5584.HUANG G J, LI Q H, CHEN C, et al. Phytoplankton functional groups and their spatial and temporal distribution characteristics in Hongfeng Reservoir, Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2015,35(17):5573-5584. [22] LAMPITT R S, WISHNER K F, TURLEY C M, et al. Marine snow studies in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean: distribution, composition and role as a food source for migrating plankton[J]. Marine Biology,1993,116(4):689-702. doi: 10.1007/BF00355486 [23] REDFIELD A C. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment[J]. Science Progress,1960,11:150-170. [24] 刘翔卿, 王雷, 刘阳, 等.1951—2010年云贵高原大理和丽江气温、降水的气候特征分析[J]. 气候与环境研究,2018,23(5):513-523. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9585.2017.17040LIU X Q, WANG L, LIU Y, et al. Climatological characteristics of air temperature and precipitation at Dali and Lijiang in the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau from 1951 to 2010[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research,2018,23(5):513-523. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9585.2017.17040 [25] 唐汇娟, 刘培钦, 伍洁丽, 等.广西洪潮江水库浮游植物功能类群及其对环境因子响应[J]. 水生态学杂志,2022,43(6):85-91.TANG H J, LIU P Q, WU J L, et al. Phytoplankton functional groups and their response to water physiochemical factors in Hongchaojiang Reservoir in Guangxi Province[J]. Journal of Hydroecology,2022,43(6):85-91. [26] 张辉, 彭宇琼, 邹贤妮, 等.新丰江水库浮游植物功能分组特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 中国环境科学,2022,42(1):380-392.ZHANG H, PENG Y Q, ZOU X N, et al. Characteristics of phytoplankton functional groups and their relationships with environmental factors in Xinfengjiang Reservoir[J]. China Environmental Science,2022,42(1):380-392. [27] 陶敏, 岳兴建, 罗家林, 等.四川丘陵区水库浮游植物功能群季节演替特征及驱动因子[J]. 水生生物学报,2021,45(4):826-837. doi: 10.7541/2021.2020.236TAO M, YUE X J, LUO J L, et al. Seasonal succession of phytoplankton functional groups and its driving factors in reservoirs in hilly regions of Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,2021,45(4):826-837. doi: 10.7541/2021.2020.236 [28] 苏玉萍. 筑坝河流营养特征研究: 以福建省敖江山仔大坝河段为例[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学, 2006. [29] 吴殷琪. 亚热带暴雨事件九龙江营养盐输出过程与河口响应[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2015. [30] 李磊, 李秋华, 焦树林, 等.阿哈水库浮游植物功能群时空分布特征及其影响因子分析[J]. 环境科学学报,2015,35(11):3604-3611.LI L, LI Q H, JIAO S L, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of phytoplankton functional groups in Aha Reservoir and their influencing factors[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2015,35(11):3604-3611. [31] 张欢, 张佳磊, 刘德富, 等.三峡水库水温对浮游植物群落演替和多样性的影响[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2017,7(2):134-139. doi: doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.02.020ZHANG H, ZHANG J L, LIU D F, et al. The influence of water temperature on phytoplankton community succession and diversity in Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2017,7(2):134-139. ◇ doi: doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.02.020 -





 下载:
下载: