Performance and carbon emission of applying CAST embedded with MBBR to retrofit a wastewater treatment plant
-
摘要:
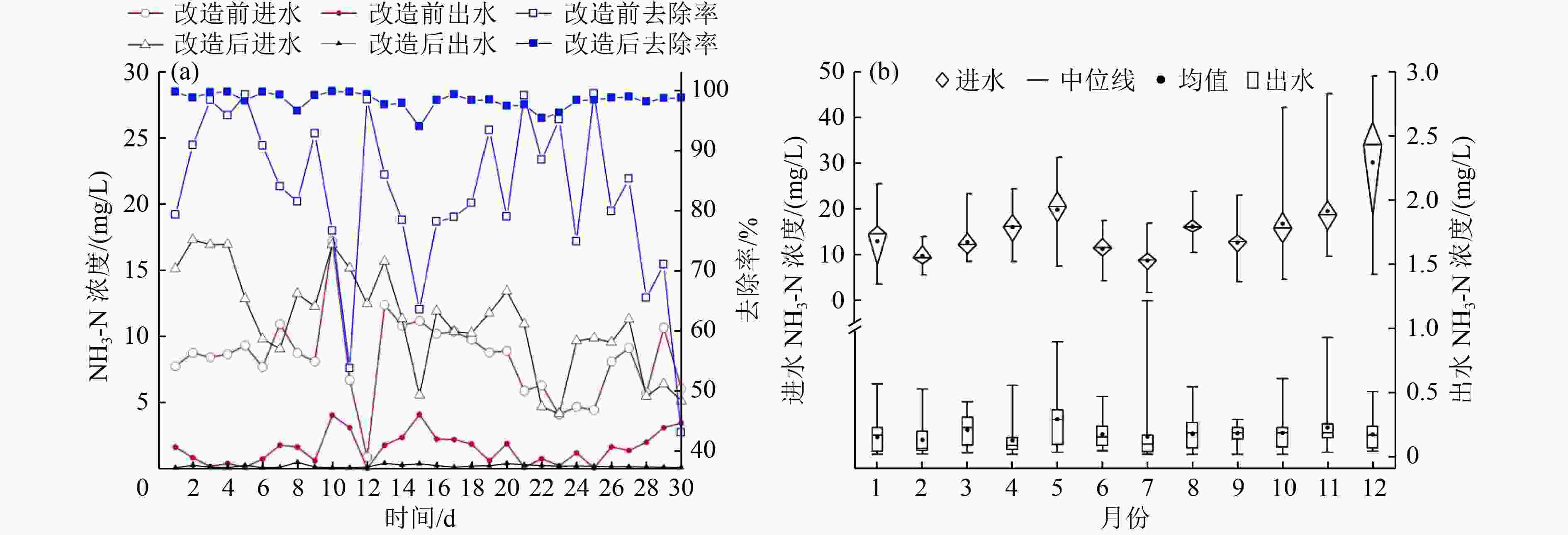
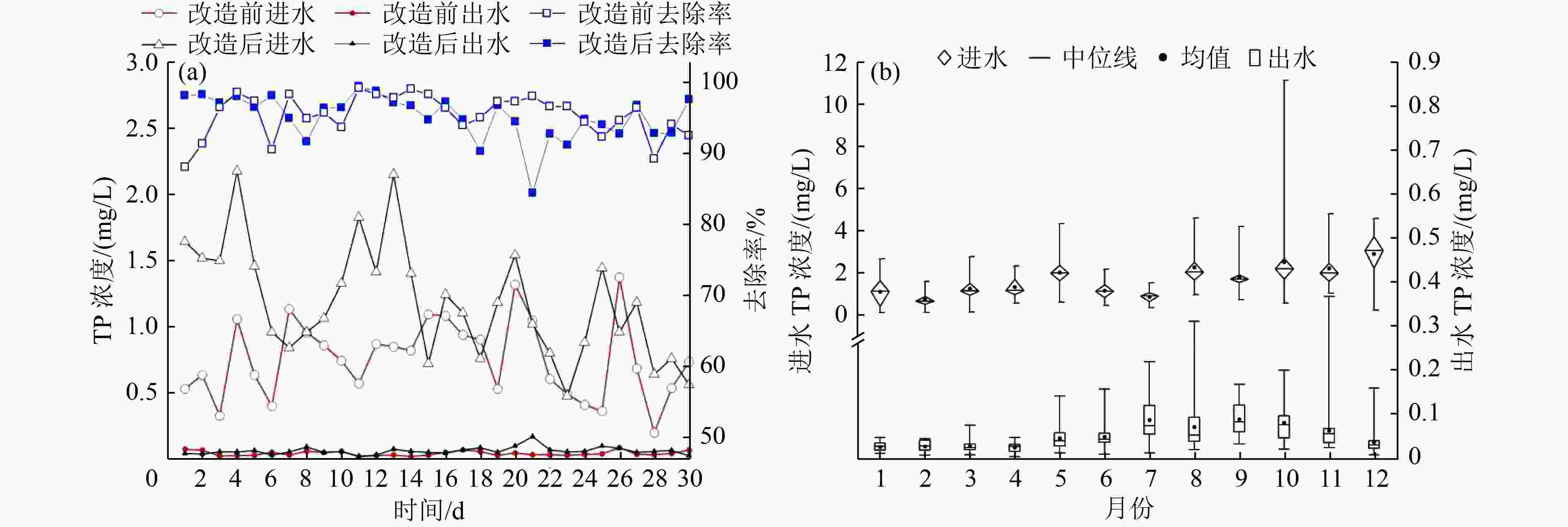
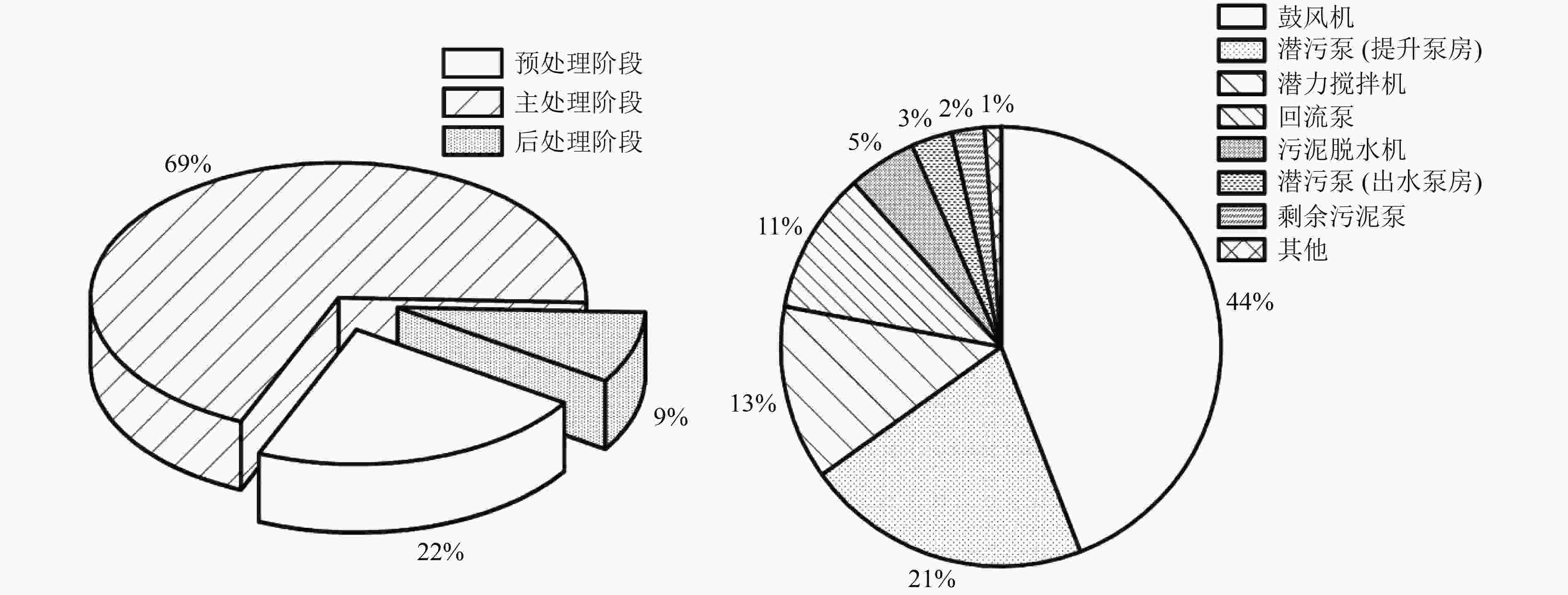
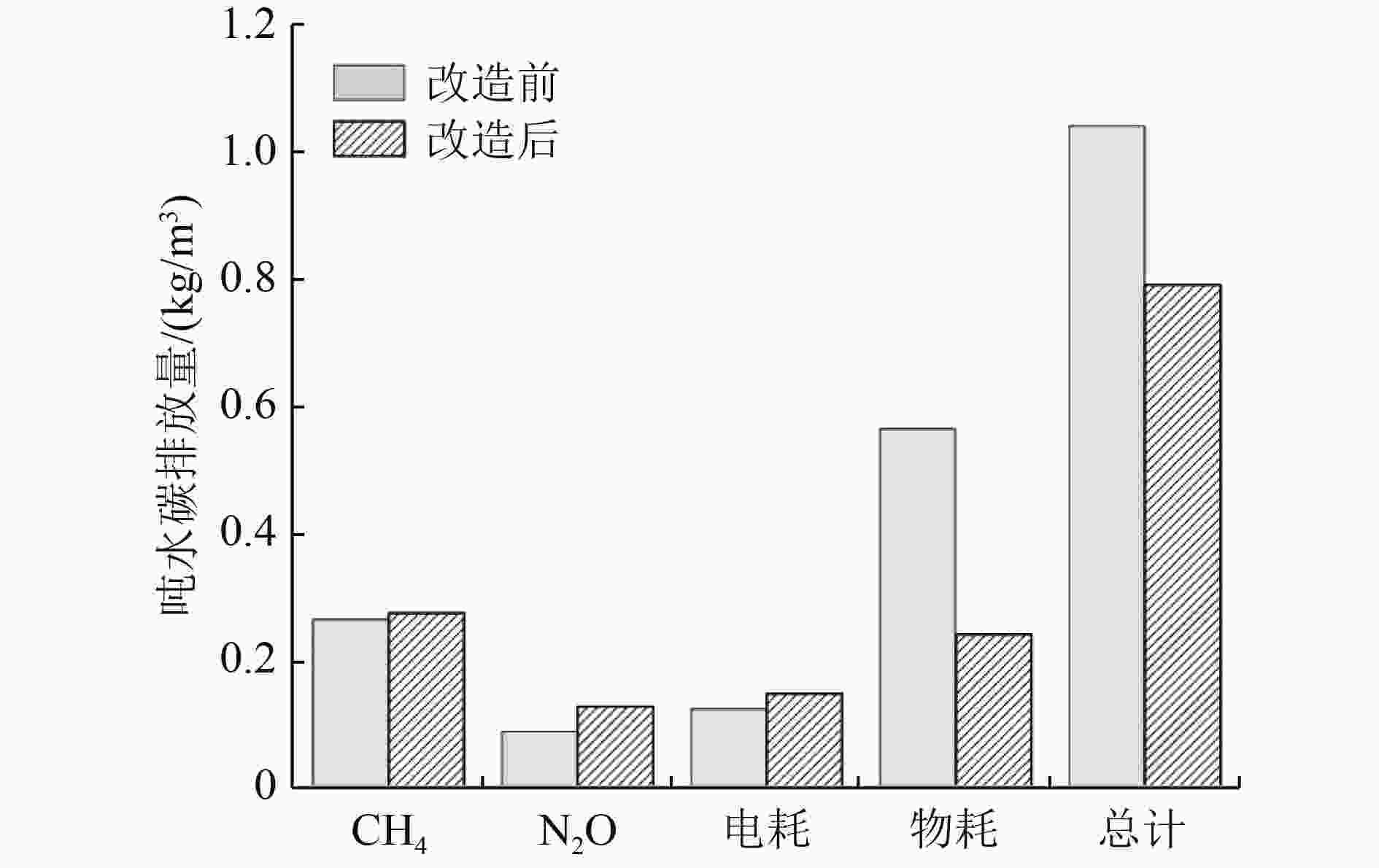
通过对比分析浙江省某污水处理厂提标改造前后的运行数据,研究移动床生物膜反应器(MBBR)工艺镶嵌循环式活性污泥工艺(CAST)对系统污染物去除效果以及电耗、药耗、物耗对碳排放量的影响。结果表明:MBBR工艺强化了系统的生物脱氮除磷效果,提高了系统的抗冲击负荷能力。改造后污水处理厂出水COD与NH3-N、TN、TP浓度的全年平均值分别为13.7、0.2、4.3、0.05 mg/L,均能稳定达到浙江省地方标准DB 33/2169—2018《城镇污水处理厂主要水污染物排放标准》要求。改造后污水处理厂内部电耗分布无明显变化,吨水电耗增加19%,而全年消耗的外加碳源、混凝剂、消毒剂均不同程度下降,吨水药剂总用量减少44%。改造后污水处理厂碳排放量由1.04 kg/m3降至0.79 kg/m3,处理过程产生的CH4和物耗对污水处理厂整体碳排放的贡献较大。
Abstract:The effects of applying the cyclic activated sludge technology (CAST) process embedded with moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) on pollutant removal, electricity consumption, chemical consumption, and carbon emission were investigated by comparing and analyzing the operational data of a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) in Zhejiang Province before and after upgrading and retrofit. The results showed that MBBR could strengthen the biological removal of nitrogen and phosphorus and improve the anti-shock loading capacity of the system. After retrofitting, the water quality of the effluent could meet the Zhejiang Provincial Standard for Discharge of Major Water Pollutants for Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant (DB 33/2169-2018) stably, with the annual average values of COD, NH3-N, TN and TP being 13.7, 0.2, 4.3 and 0.05 mg/L, respectively. There was no significant change as to the distribution of electricity consumption within the WWTP after retrofitting. The electricity consumption per ton water increased by 19%, while the annual consumption of external carbon source, coagulants and disinfectants decreased by varying degrees, and the total chemical consumption per ton water decreased by 44%. The carbon emission of the WWTP decreased from 1.04 kg/m3 to 0.79 kg/m3 after retrofitting, and the direct methane emission and material consumption in the treatment process contributed greatly to the overall carbon emission of the WWTP.
-
表 1 设计进出水水质
Table 1. Design of influent and effluent quality
mg/L 项目 进水 改造前出水 改造后出水 化学需氧量(COD) ≤450 ≤50 ≤30 五日生化需氧量(BOD5) ≤120 ≤10 ≤6 悬浮物(SS) ≤150 ≤10 ≤10 氨氮(NH3-N) ≤15 ≤5(8) ≤1.5(3) 总氮(TN) ≤25 ≤15 ≤10(12) 总磷(TP) ≤1.5 ≤0.5 ≤0.3 注:括号内数值为每年11月1日—次年3月31日执行。 -
[1] 刘向荣, 简德武, 简爽.高排放标准下城镇污水处理厂的提标改造探[J]. 中国给水排水,2019,35(20):19-25. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2019.20.004LIU X R, JIAN D W, JIAN S. Discussion on the upgrading of municipal wastewater treatment plant under high emission standard[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2019,35(20):19-25. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2019.20.004 [2] HE Y, ZHU Y S, CHEN J H, et al. Assessment of energy consumption of municipal wastewater treatment plants in China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,228:399-404. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.320 [3] YANG J W, CHEN B. Energy efficiency evaluation of wastewater treatment plants (WWPTs) based on data envelopment analysis[J]. Applied Energy,2021,289:116680-116694. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.116680 [4] 张捍民, 邹翔, 姜威.城镇污水处理厂综合效益评价:以辽河流域为例[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2017,7(5):573-579. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.05.079ZHANG H M, ZOU X, JIANG W. Evaluation of comprehensive benefits of urban sewage treatment plants: taking Liaohe River Basin as an example[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2017,7(5):573-579. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.05.079 [5] 蔡木林, 卢延娜, 刘琰, 等.城镇污水处理厂出水排放限值分级及提标成本研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,34(7):1562-1568.CAI M L, LU Y N, LIU Y, et al. Classification of effluent discharge limits of municipal sewage treatment plant and cost of upgrading standard[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,34(7):1562-1568. [6] SU H S, YI H, GU W Y, et al. Cost of raising discharge standards: a plant-by-plant assessment from wastewater sector in China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2022,308:114642-114650. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114642 [7] DI BIASE A, KOWALSKI M S, DEVLIN T R, et al. Moving bed biofilm reactor technology in municipal wastewater treatment: a review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2019,247:849-866. [8] 杨祝平.CAST-MBBR及SF-AO工艺在污水处理中的应用比较[J]. 中国给水排水,2019,35(14):41-46. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2019.14.007YANG Z P. Application and comparison of CAST-MBBR & SF-AO process in municipal wastewater treatment[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2019,35(14):41-46. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2019.14.007 [9] 周祯领, 吴迪, 韩文杰, 等.MBBR镶嵌氧化沟在某污水处理厂的提标效果分析[J]. 中国给水排水,2019,35(17):1-6. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2019.17.001ZHOU Z L, WU D, HAN W J, et al. Retrofitting effect of oxidation ditch embedded with MBBR in a wastewater treatment plant[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2019,35(17):1-6. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2019.17.001 [10] 刘强, 王泰, 沈浡, 等.MBBR工艺用于污水厂提标改造的低温运行效果[J]. 中国给水排水,2020,36(13):7-13. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2020.13.002LIU Q, WANG T, SHEN B, et al. Operation effect of MBBR applied in upgrading and reconstruction of a wastewater treatment plant in Tianjin at low temperature[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2020,36(13):7-13. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2020.13.002 [11] 张晶晶, 杨翠春, 丁鹏霖, 等.MBBR工艺用于唐山某污水厂提标改造效能分析[J]. 中国给水排水,2020,36(15):78-85. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2020.15.014ZHANG J J, YANG C C, DING P L, et al. Efficiency analysis of MBBR process applied in upgradation of a wastewater treatment plant in Tangshan[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2020,36(15):78-85. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2020.15.014 [12] 吴琼, 郭庆辉, 张宏伟, 等.A2/O-MBBR工艺用于沈水湾污水处理厂提标改造[J]. 中国给水排水,2020,36(24):99-103.WU Q, GUO Q H, ZHANG H W, et al. Application of A2/O-MBBR process in upgrading and reconstruction of Shenshuiwan wastewater treatment plant[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2020,36(24):99-103. [13] 吴桐, 凌宇, 王海燕, 等.MBBR填料研究与应用进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(6):988-995. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190144WU T, LING Y, WANG H Y, et al. Review on the research and application development of MBBR carrier[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(6):988-995. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190144 [14] MASSOOMPOUR A R, RAIE M, BORGHEI S M, et al. Role of carrier characteristics affecting microbial density and population in enhanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal from wastewater[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2022,302:113976-113985. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113976 [15] 马娟, 王谨, 俞小军, 等.不同运行模式下改良型CAST工艺处理生活污水的除磷性能[J]. 环境科学,2017,38(12):5146-5153. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201705206MA J, WANG J, YU X J, et al. Phosphorus removal capacity of domestic wastewater treated by a modified CAST process under different operating modes[J]. Environmental Science,2017,38(12):5146-5153. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201705206 [16] 谢淘, 汪诚文.污水处理厂温室气体排放评估[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版),2012,52(4):473-477. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2012.04.011XIE T, WANG C W. Greenhouse gas emissions from wastewater treatment plants[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science & Technology),2012,52(4):473-477. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2012.04.011 [17] IPCC. 2006 IPCC guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories[R]. Kanagawa: Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES), 2006. [18] 张岳, 葛铜岗, 孙永利, 等.基于城镇污水处理全流程环节的碳排放模型研究[J]. 中国给水排水,2021,37(9):65-74. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2021.09.011ZHANG Y, GE T G, SUN Y L, et al. Research on carbon emission model based on the whole process of urban sewage treatment[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2021,37(9):65-74. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2021.09.011 [19] 宋宝木, 秦华鹏, 马共强.污水处理厂运行阶段碳排放动态变化分析: 以深圳某污水处理厂为例[J]. 环境科学与技术,2015,38(10):204-209.SONG B M, QIN H P, MA G Q. Analysis for dynamic changes of wastewater treatment plant carbon emissions in operation phase: with a wastewater treatment plant in Shenzhen as an example[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2015,38(10):204-209. [20] IPCC. AR5 synthesis report: climate change 2014[EB/OL]. Geneva: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. (2014-10)[2021-12-11]. https://www.ipcc.ch/assessment-report/ar5/. [21] 杨世琪. 城镇污水处理系统碳核算方法与模型研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2013. [22] 余娇, 赵荣钦, 肖连刚, 等.基于“水-能-碳”关联的城市污水处理系统碳排放研究[J]. 资源科学,2020,42(6):1052-1062. doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.06.04YU J, ZHAO R Q, XIAO L G, et al. Carbon emissions of urban wastewater treatment system based on the “water-energy-carbon” nexus[J]. Resources Science,2020,42(6):1052-1062. doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.06.04 [23] 生态环境部. 2019年度减排项目中国区域电网基准线排放因子[R/OL]. (2020-12-29)[2021-12-25]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/ydqhbh/wsqtkz/202012/W020201229610353340851.pdf [24] 王向阳. 污水处理碳足迹核算及环境综合影响评价研究[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学, 2019. -





 下载:
下载: